What is different from the difoMost consumers do not care what is in front of them: RCD (residual current device) or difatomat (differential automatic). But when developing projects for the power grid of private houses or apartments, this question has a certain value. In general, the problems that our citizens have with organizing the protection of their own homes, in terms of electrical safety, are significant. But what to say, if still in many remote areas such things as "bugs" in traffic jams are the norm? Recently, a friend of mine asked me a question about what is in my dashboard UZO or difavtomat . How to distinguish them. Since the problem, in professional opinion, is very serious, we offer you a small educational program on this topic, including electricians, especially young ones.
This knowledge will allow you to understand exactly what “lives” in your switchboard: a UZO or difavtomat, why put it there and how much will it help, or why will it save in the future? An experienced electrician, who has more than one short circuit in the background, such questions may even offend! However, among young people, little attention is paid to theory, although consumers ask these questions all the time. And now I will tell you a few options about how the RCD differs from the difavtomat . The difference between the Uzo and the differential automaton according to its functional purposeIf you look at the RCD and difavtomat, then in appearance these two devices are very similar to each other, but the functions that they perform are different. Recall what functions the RCD and differential automaton performs. The residual current device works if a differential current, a leakage current, appears in the network to which it is connected. If a leakage current occurs, a person may be the first to suffer if they touch damaged equipment. In addition, when a leakage current appears in the wiring, the insulation will heat up, which can cause a fire and fire. Therefore, the RCD is installed to protect against electrical shock, as well as from damage to electrical wiring in the form of leaks that are accompanied with a fire. For more details on how this device works, see the RCD operation principle in the article. Now look at the differential automaton. This is a unique device that combines both a circuit breaker (more understandable to the public as an "automatic") and the previously considered RCD. Those. a differential automaton is able to protect your wiring from both short circuits and overloads, as well as from the occurrence of leaks associated with the previously described situations. Now the main point where everyone starts to get confused: remember that the RCD, unlike the difavtomat, does not protect the network from overload and short circuit. And most consumers think that by installing an RCD, they are protected from everything! In simple terms, the RCD is simply an indicator that controls leakage and that current does not flow past your main consumers: electrical appliances, light bulbs, etc. If somewhere in the network the insulation is damaged and a leakage current appears, the RCD reacts to it and turns off the network. If at the same time to turn on all electrical appliances (heaters, hair dryers, irons), that is, to intentionally create an overload, the RCD will not work. And the wiring, if there are no other safety devices, be sure to burn along with the RCD. If the RCD and the connected phase and zero, and get a huge short-circuit, the RCD also does not work. Why do I mean all this, I just want to draw your attention to the fact that, as the RCD does not protect the network from overloads and short circuits, then you probably agree with me that you need to protect it yourself. That is why the RCD is always connected in series with a gun. These two devices work in a pair, so to speak: one protects from leaks, the other from overloads and short circuit. By using a difavtomat instead of an RCD, you get rid of the situations described above: it will protect against everything. Let us draw the line, the main difference between the RCD and the difactom is that the RCD does not protect the network from overloads and short circuits. The visual difference between Uzo and difavtomateIn fact, there is a mass of external features that make it easy to distinguish between UZD and diphavtomat. Look at the picture. Visually, these two devices are very similar: like a case, a switch, a “test” button, some kind of circuit on the case, and incomprehensible letters. But to be more corrosive, you will notice: the schemes are different, the tumblers are different, the letters will not be repeated. Which of these devices is RCD, and which one is difavtomat? Above, we examined the functional differences between these devices, and now we will consider how the UZO differs from a difavtomat visually - so to say, the differences are noticeable to the naked eye. 1. Marking by rated currentOne of the ways to visually distinguish an RCD from a diphavtomat is current marking. On any device its technical characteristics are indicated. For devices that we consider the main characteristics are the rated operating current and rated leakage current.
If there is only a figure on the instrument case in large letters (nominal current value), this is the RCD. . On its case the figure is 40A. This means that the device is rated for a rated current of 40 (A). If at the beginning of the inscription there are Latin letters B, C or D, and then comes a number, then you have a differential automaton. For example, in the ABDT32 difavtomat, the “C” stands for the value of the rated current, which indicates the type of characteristic of the electromagnetic and thermal release .
Once again, read carefully and remember. If spelled "16A" - this is an RCD whose rated current should be no more than 16 amperes. If it is spelled "C16", this is a diffuser, where the letter "C" is a characteristic of the releasers "embedded" in the device, designed for a rated current of 16A. 2. The electrical circuit shown on the deviceOn the case of any executive or protective devices, the manufacturer always puts his concept. They are really similar to the RCD and the differential automaton.
We will not list now everything that is depicted there (this is the topic of a separate article), but only highlight the main differences. On the circuit, the RCD is an oval, which denotes a differential transformer — the heart of the device, which reacts to leakage currents and an electromechanical relay, which closes and opens the circuit, power contacts for connecting wires, etc. In the diagram of the difavtomat, except for all similar elements, the designations of the thermal and electromagnetic releasers that react to the overload and short circuit current are distinctive.
Therefore, looking at the wiring diagram, which is shown on the case, you now know how they differ. If the diagram shows a thermal and electromagnetic release, this is a differential automatic. This is the schematic difference between the RCD and diphavtomat . 3. Name on the device caseIf you, as a simple consumer, find it difficult to remember what distinguishes an RCD from a difavtomat , we ’ll inform you: knowing the problem the article is about, many manufacturers, so that customers do not get confused, write the name of the device on the case.
It is written on the side surface of the RCD circuit breaker - a differential switch. It is written on the side surface of the case of a difactomta - a differential current circuit breaker. Although such inscriptions are not applied on all products, as a rule, on Russian manufacturers and I have not seen such markings on all foreign products. 4. Abbreviated inscription on the deviceBasically, the question of how to distinguish an RCD from a diphavtomate is set for products of foreign manufacture. If we are talking about domestic products, then there are no questions at all. On such devices, as a rule, it is written in Russian that this is an RCD or differential automatic AVDT.
Let me remind you that the protective cutout device (RCD) is now correctly called differential switches (VD). Differential automatic - he is a differential current circuit breaker (AVDT). Summing up how to distinguish ouzo from difavtomataBy price parameters, RCDs and difavtomats differ . This is especially true of imported products. Normal difavtomat costs slightly cheaper than the RCD, complete with a conventional machine. The quality of imported devices is higher. Domestic ones are also quite good, but they lose in such important characteristics as response time, inferior in reliability of mechanical parts, elementary inferior in quality of cases. As for the reliability of operation, these two devices are not inferior to each other. Since the difavtomat is a combined device, I would note from the shortcomings of operation that when it is triggered it is difficult to determine what caused the shutdown: overload, short circuit or leakage current. True, the device is evolving: some diphavomats are equipped with differential current actuation indicators. A positive aspect of AVDT is the ease of installation: it is important for an electrician to tighten a couple of smaller screws in a tight mounting box. On the other hand, this increases the reliability of the circuit: the smaller the connections, the better. But if the device breaks, it must be replaced. In the case of UZO paired with a gun, the repair process looks cheaper: either one element or another changes. This should be taken into account when designing your networks, taking into account the risk of certain negative events and their possible frequency. Options for the implementation of schemes with these devices, you can think of a lot, the main thing is that you understand and remember why you are doing this. |
To solve the problem of protecting the wiring from overloads and leakage currents, you can use a pair of devices - a circuit breaker and RCD. But the same problem is solved by a differential circuit breaker, which combines both these devices in a single package. About the correct connection difavtomata and his choice and will be discussed further.
The content of the article
A differential or differential circuit breaker combines the functions of a circuit breaker and RCD. That is, this device alone protects the wiring from overloads, short circuits and leakage currents. The leakage current is generated when a malfunction of the insulation or when touching the current-carrying elements, that is, it still protects the person from being hit by electricity.
Difavtomats are installed in electrical distribution panels, most often on din-rail. They are put instead of a bunch of automatic + UZO, physically take a little less space. How specifically - depends on the manufacturer and type of performance. And this is their main plus, which can be claimed when upgrading the network, when the space in the panel is limited, and you need to connect a certain number of new lines.
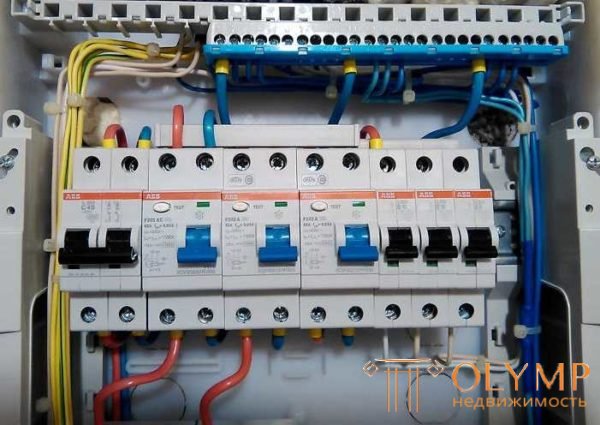

Difavtomaty are used to protect the wiring from increased loads and people from electric shock
The second positive point is cost savings. Typically, a difavtomat costs less than a pair of automatic + UZO with similar characteristics. Another positive point is that it is necessary to determine only the nominal value of the circuit breaker, and the RCD is built in by default with the required characteristics.
There are also disadvantages: when you exit and fail one of the parts of the difavtomat, you will have to change the whole device, and this is more expensive. Also, not all models are equipped with flags, which can be used to determine why the device triggered - due to overload or leakage current - which is of fundamental importance when figuring out the reasons.
Since the difavtomat combines two devices, it has the characteristics of both of them and when choosing, it is necessary to take everything into account. Let us see what these characteristics mean and how to choose a differential automaton.
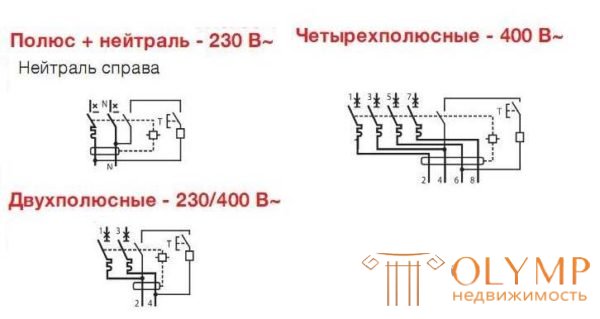
Designation of difavtomat on schemes
Rated current
This is the maximum current that the machine can withstand for a long time without loss of performance. Usually it is indicated on the front panel. Rated currents are standardized and can be 6 A, 10 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, 63A.
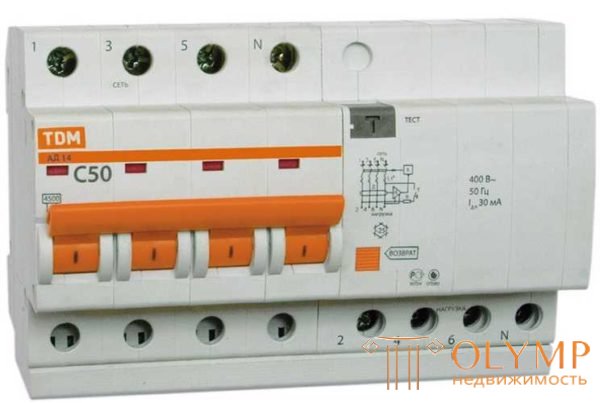

Four-pole difavtomat to connect to the network 380 V
Small denominations - 10 A and 16 A - are placed on the lighting lines, medium ones - on powerful consumers and outlet groups, and powerful - 40 A and above - are mainly used as an introductory (common) difavtomat. It is selected depending on the cable cross-section, just like when choosing the rating of the circuit breaker.
Time-current characteristic or type of electromagnetic release
It is displayed next to the nominal value, indicated by the Latin letters B, C, D. It indicates what overloads with respect to the nominal the automatic switch-off occurs (to ignore short-term starting currents).
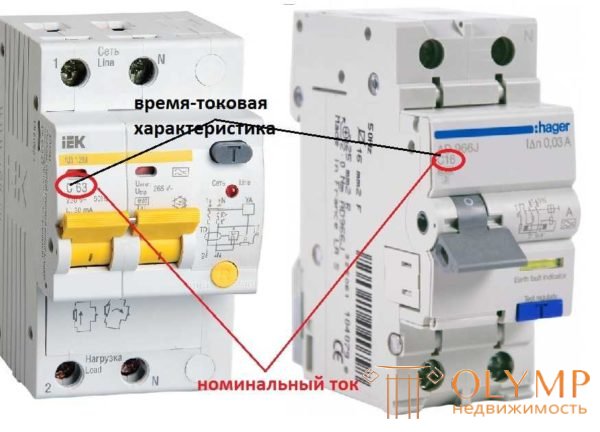

Diphiftomat nominal and its time-current characteristic
Category B - if the current is exceeded by 3-5 times, C - when the nominal is exceeded by 5-10 times, type D is disconnected at loads that exceed the nominal value by 10-20 times. Type C apartments are usually placed in apartments, B in rural areas can be placed, in enterprises with powerful equipment and large starting currents - D.
Rated voltage and network frequency
For which networks the device is intended - 220 V and 380 V, with a frequency of 50 Hz. There are no others in our trading network, but still, it’s worth checking out.
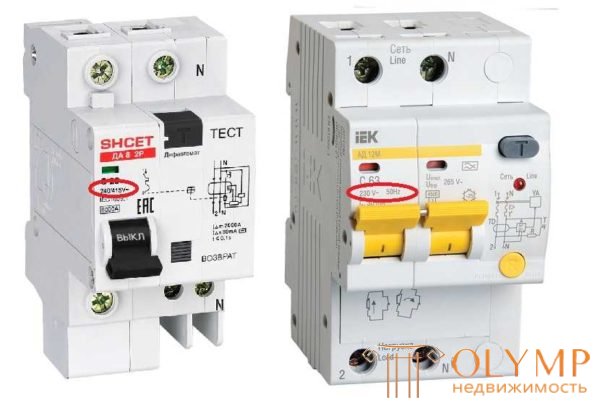

Voltage and frequency for which the differential circuit breaker is designed
Differential automata can have double labeling - 230/400 V. This suggests that this device can work in the network for 220 V and 380 V. In three-phase networks, such devices are put on outlet groups or on individual consumers, where used only one of the phases.
As water difavtomats on three-phase networks, devices with four inputs are necessary, and they differ significantly in size. It is impossible to confuse them.
Nominal tripping differential current or leakage current (setpoints)
Displays the sensitivity of the device to the resulting leakage currents and shows under what conditions the protection will work. In everyday life, only two ratings are used: 10 mA for installation on a line in which only one powerful device or consumer is installed, which combines two dangerous factors - electricity and water (a flowing or storage electric water heater, a cooking surface, an oven, a dishwasher and etc.).
For lines with a group of sockets and outdoor lighting, difavtomats are installed with a leakage current of 30 mA, they are not usually placed on the lighting lines inside the house - for economy.
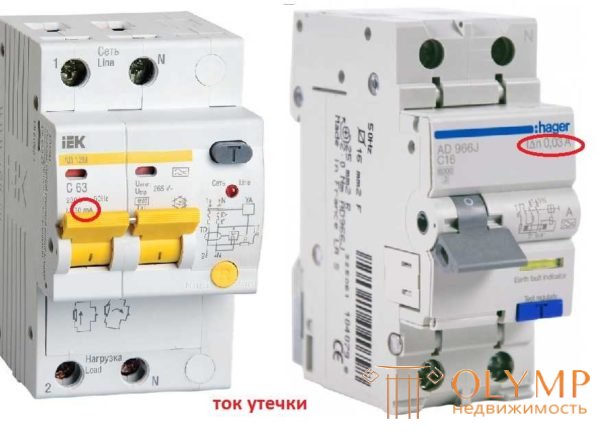

Leakage current or settings on differential machine
The device can be written simply in milliamperes (as in the photo on the left) or the letter of the current setting (in the photo on the right), followed by numerals in amperes (at 10 mA, 0.01 A, at 30 mA, 0 , 03 A).
Differential protection class
Displays from what type of leakage current protects this device. There is a letter and graphic image. Usually put an icon, but maybe a letter (see table).
| Letter designation | Graphic designation | Decryption | Application area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au |  | Responds to alternating sinusoidal current | Put on the line, which is connected to a simple technique without electronic control |
| BUT |  | Reacts to sinusoidal alternating current and pulsating DC | It is applied on lines from which the equipment with electronic control is powered |
| AT |  | Captures variable, impulse, constant and smoothed constant. | Mainly used in production with a large number of various equipment. |
| S | With shutdown time delay 200-300 ms | In complex schemes | |
| G | With shutdown time delay of 60-80 ms | In complex schemes |
The choice of differential protection class difavtomata is based on the type of load. If it is a microprocessor-based technique, class A is needed, AC class is suitable for lighting or powering simple devices. Class B in private houses and apartments are rarely placed - there is no need to “catch” all types of leakage currents. Connecting a class S and G difavtomat makes sense in multilevel protection schemes. They are set as input if there are other differential disconnect devices in the circuit. In this case, when one of the downstream leakages triggers, the input will not turn off and the healthy lines will be in operation.
Rated breaking capacity
Shows what current is able to disable the differential when a fault occurs and stay healthy. There are several standard values: 3000 A, 4500 A, 6000 A, 10 000 A.
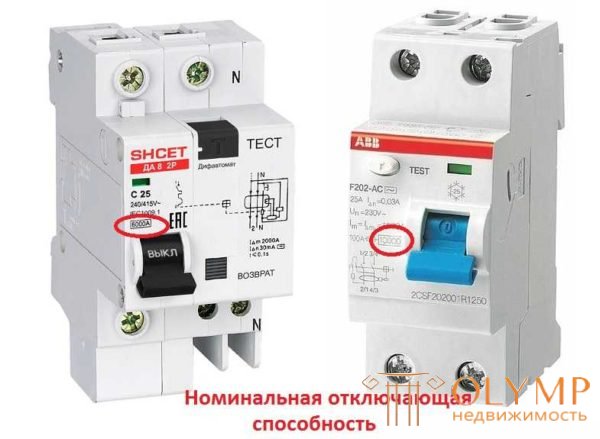

Breaking capacity diphiftomata
Выбор дифавтомата по этому параметру зависит от типа сети и от дальности расположения подстанции. В квартирах и домах на достаточном удалении от подстанции используют дифавтоматы с отключающей способностью 6 000 А, близко к подстанциям ставят на 10 000 А. В сельской местности, при подводе электропитания по воздушке и в давно не модернизированных сетях достаточно 4 500 А.
На корпусе эта цифра указана в квадратной рамке. Местоположение надписи может быть разным — зависит от производителя.
Класс токоограничения
Чтобы ток короткого замыкания принял максимальное значение, должно пройти какое-то время. Чем быстрее будет отключено электропитание от поврежденной линии, тем меньше меньше вероятность получения повреждений. Класс токоограничения отображается цифрами от 1 до 3. Третий класс — отключает линию быстрее всего. Так что выбор дифавтомата по этому признаку прост — желательно использовать устройства третьего класса, но они дороги, зато дольше остаются работоспособными. Так что при наличии финансовой возможности, ставьте дифавтоматы этого класса.

Токоограничение дифавтомата
На корпусе эта характеристика изображена в маленькой квадратной рамке рядом с номинальной отключающей способностью. Она может стоять справа (у Legranda) или снизу (у большинства других производителей). Если вы такой отметки не нашли ни на корпусе, ни в паспорте, значит этот автомат не имеет тоокограничения.
Температурный режим использования
Большинство дифференциальных защитных автоматов рассчитаны на работу в помещениях. Они могут эксплуатироваться при температурах от -5°C до + 35°C. В этом случае на корпусе ничего не ставят.
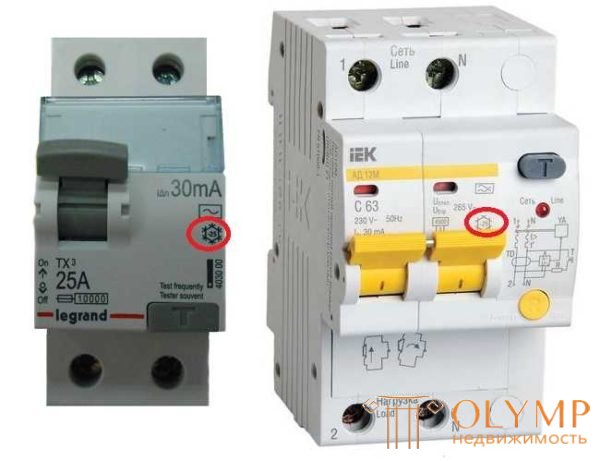

Обозначение повышенной морозостойкости дифавтомата
Иногда щитки стоят на улице и обычные защитные устройства не подойдут. Для таких случаев выпускаются дифавтоматы с более широким диапазоном температур — от -25°C до +40°C. В этом случае на корпусе ставят специальный знак, который немного похож на звездочку.
The presence of markers on the cause of the drawdown
Not all electricians like to install dihavtomatas, because they believe that a bunch of protective circuit breaker + RCD is more reliable. The second reason - if the device works, it is impossible to determine what caused that - overload, and you just need to turn off some device, or leakage current, and you need to look for where and what happened.
In order to solve at least the second problem, manufacturers began to make flags that indicate the cause of the drawdown of the difavtomat. In some models, this is a small platform, the position of which determines the cause of the shutdown.
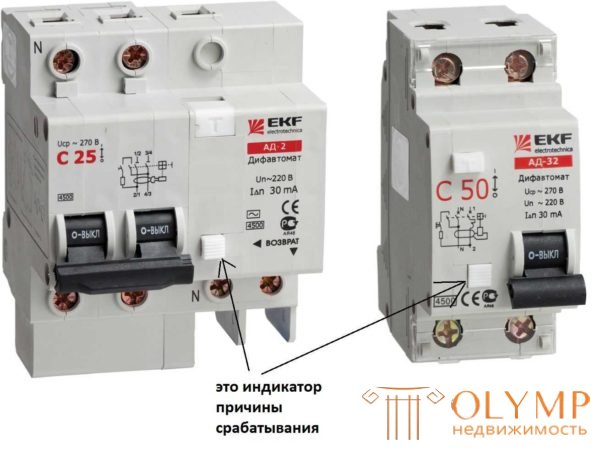

A checkbox that indicates the reason for the trip.
If the shutdown caused an overload, the indicator remains flush with the case, as well as the photo on the right. If the difavtomat worked in the presence of a leakage current, the flag appears at some distance from the case.
Type of design
There are two types of automatic machines: electromechanical or electronic. Electromechanical more reliable, as they remain operable even when power is lost. That is, if the phase disappears, they will be able to trigger and disable also zero. Electronic work requires power supply, which is taken from the phase wire and loses its working capacity when the phase is lost.
Electricity is not worth saving, especially on devices that provide protection for wiring and life. Therefore, it is recommended to always buy components from well-known manufacturers. The market leader is Legrand (Legrand) and Schneider (Schneider), Hager (Hager), but their products are expensive, and there are a lot of fakes. Not so high prices for IEK (IEK), ABB (ABB), but there are more problems with nm. In this case, it is better not to get involved with unknown manufacturers, as they are often simply unworkable.
The choice is actually not that small, even if we confine ourselves to only these five firms. Each manufacturer has several lines, which differ in price, and significantly. To understand the difference, you must carefully look at the technical characteristics. Each one influences the price, so carefully read all the data before purchasing.
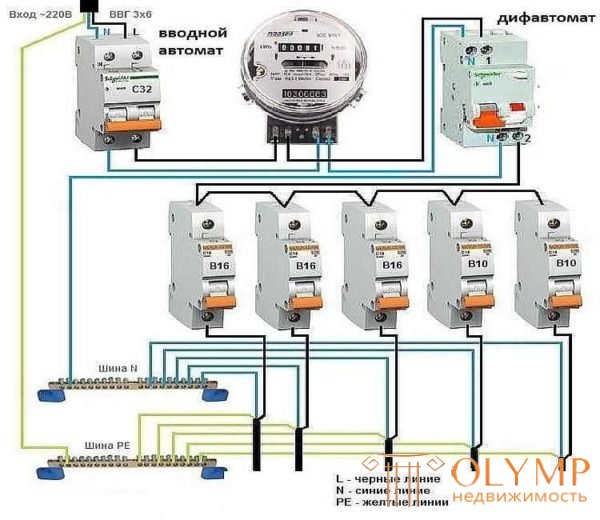
Let's start with the methods of installation and connection of conductors. Everything is very simple, there are no special difficulties. In most cases, it is mounted on a dinrake. To do this, there are special projections that hold the device in place.

Dinriku mount
Connection of the power supply unit to the power grid is made by wires in isolation. Section is selected on the basis of nominal. Usually the line (power supply) is connected to the upper sockets - they are signed with odd numbers, the load - at the lower ones - are signed with even numbers. Since both the phase and zero are connected to the differential automaton so as not to be confused, the sockets for the “zero” are signed with the Latin letter N.
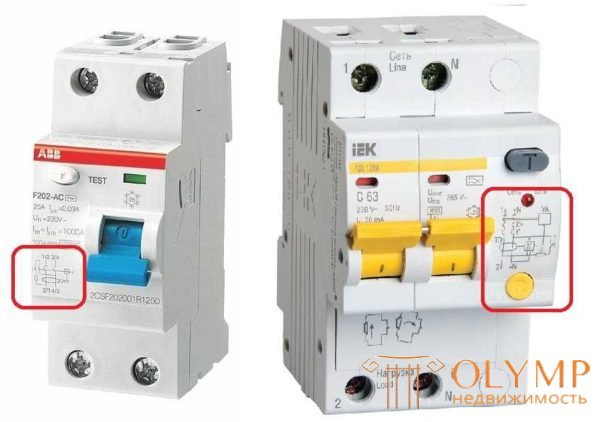

Connection diagram difavtomata usually on the body
In some lines, you can connect the line to both the upper and lower slots. An example of such a device in the photo above (left). In this case, the numbering is written in the scheme through a fraction - 1/2 at the top and 2/1 at the bottom, 3/4 at the top and 4/3 at the bottom. This means that it does not matter to connect the line from above or below.
Connecting the difavtomat on the distribution board
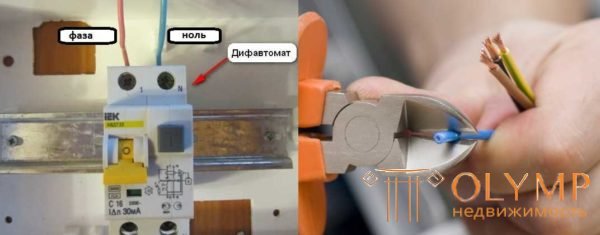
Before connecting the line, the wires are removed from the insulation at a distance of about 8-10 mm from the edge. At the desired terminal slightly loosen the mounting screw, insert the conductor, tighten the screw with a sufficiently large force. Then pull the wire several times to make sure the contact is normal.
After you have connected the unit, supplied power, you need to check the operation of the system and the installation. First we test the unit itself. To do this, there is a special button, signed by “Test” or simply by the letter T. After the switches are turned on, we press this button. In this case, the device must "knock out". This button artificially creates a leakage current, so we checked the performance of the typing machine. If there was no triggering - it is necessary to check the correctness of the connection, if everything is correct, the device is faulty
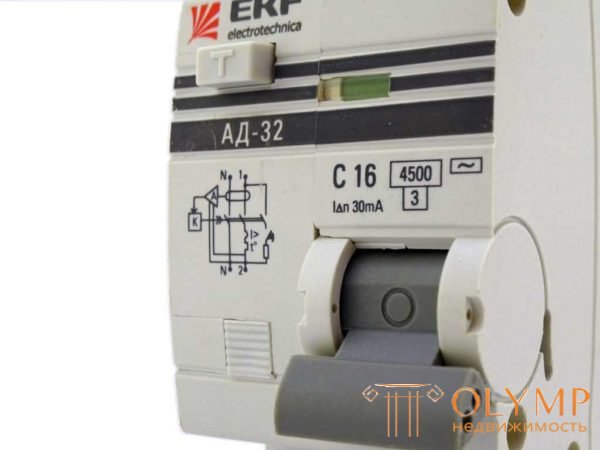

If by pressing the "T" button the dialpad works, it is operational
A further check is to connect a simple load to each outlet. This will check the correctness of the disconnection of the outlet groups. And the last thing is the alternate switching on of household appliances, to which separate power lines are installed.
When developing a wiring diagram in an apartment or house there may be many options. They can differ in convenience and reliability of operation, degree of protection. There are simple options that require a minimum of costs. They are usually implemented in small networks. For example, in country houses, in small apartments with a small amount of household appliances. In most cases, you have to install a large number of devices that ensure the safety of wiring and protect against electric shocks.

Schemes come in different levels of complexity.
It does not always make sense to install a large number of protective devices. For example, in the summer cottage where there are only a few sockets and lighting, it is enough to put only one difavtomat at the entrance, from which separate lines will go to groups of consumers — sockets and lighting.

A simple wiring diagram for a diphiftomat on a small network
This scheme does not require large expenditures, but when leakage current appears on any of the lines, the difavtomat will work, de-energizing everything. Until clarification and elimination of the causes of light will not.
As already mentioned, individual diphavomats put on “wet” groups. These include the kitchen, bathroom, outdoor lighting, as well as appliances that use water (except for the washing machine). This way of building a system gives a higher degree of security and better protects the wiring, equipment and people.
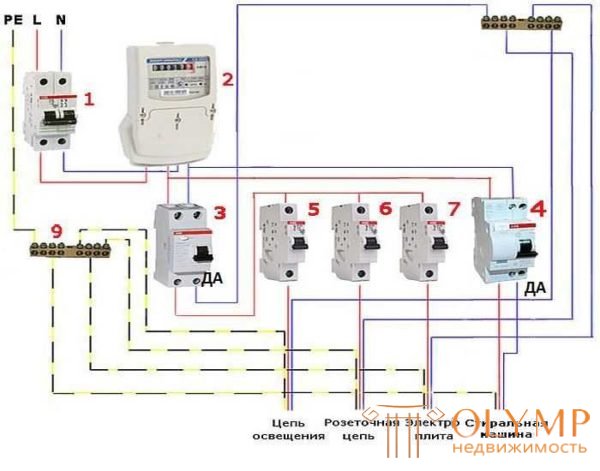
More sophisticated and reliable scheme: connecting a difavtomate to every potentially dangerous device
The implementation of this method of wiring devices will require large material costs, but the system will work more reliably and stably. Since when one of the protective devices triggers, the rest will remain operational. Such a connection difavtomata used in most apartments and small houses.
In extensive power supply networks, the need arises to make the system even more complex and expensive. In this version, after the counter, an input differential automat of class S or G is installed. Then, each group has its own automaton, and if necessary it is also placed on individual consumers. See the connection for this case in the photo below.
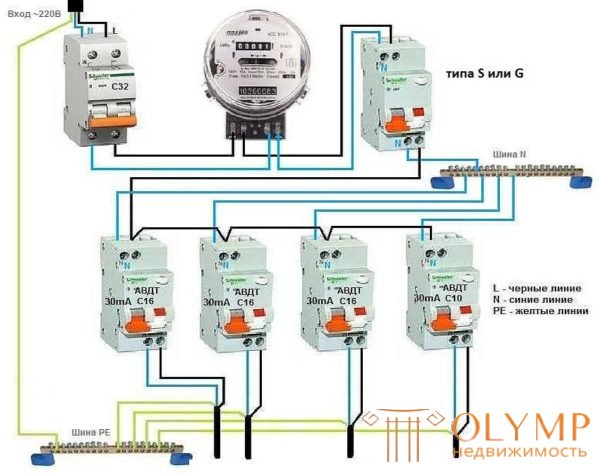
Selective installation scheme
With this construction of the system, when one of the linear devices triggers, all the rest will remain in operation, since the input automatic differential shutdown device has a delay in response.
Sometimes after connecting a difavtomat it does not turn on or is cut down when any load is connected. That means something is wrong. There are a few common mistakes that occur when assembling a dashboard yourself:
Now you can not only choose and connect a differential circuit breaker, but also understand why he knocks out exactly what went wrong and correct the situation on his own.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)