The room in which the carving is done must be dry, bright and spacious. For performing small work, an ordinary table with a cap board is suitable, and for large planes, a joiner's workbench or a laid on joinery cover. The dimensions of the cover are 1300 x 900 x 70 mm. Small carvings are performed while sitting; large carvings are standing and sitting; the height of the chair should be 650 ... 750 mm.
Light when carving should fall in front and. left. It is recommended for this to use daylight, from which the eyes are less tired and the cutting line is more clearly visible. With artificial lighting, it is advisable to use two or three lamps with adjustable height and length.
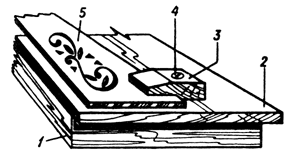
Small blanks are fixed with the help of carpentry clamps and adjustable stops, as well as clamps and derzhak. The grip clip (Fig. 1) is an ordinary softwood block in which a quarter is chosen, the height of the fold is equal to the thickness of the carved board. In a pre-drilled through hole screw the screw, which holds the workpiece.
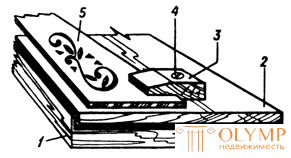 |
| Fig. 1. Clamp for woodcarving: 1 - table; 2 - draft board; 3 - holder; 4 - a screw; 5 - working plane. |
In woodcarving used flat and semicircular chisels. Flat chisels are used for stripping the background in relief threads; they are also used in the contour thread. The width of their cloth - 3 ... 30 mm.
Semicircular chisels with different radii of curvature (sloping, medium and steep) are the main tool for all types of threads, except for triangular-grooved, where they are used only for cutting out semicircular holes. The width of the canvas such chisels - 3 ... 25 mm.
Chisels-angles (Fig. 2, a) with a cutting width of 5 ... 15 mm are used to select narrow grooves. The angle of their canvas - up to 70 °. They can have a straight neck and a curved, like a cranberry.
Clumps (Fig. 2, b) have a short blade 2 ... 15 mm wide and a long curved neck. Such chisels are necessary for making relief and high-relief carving.
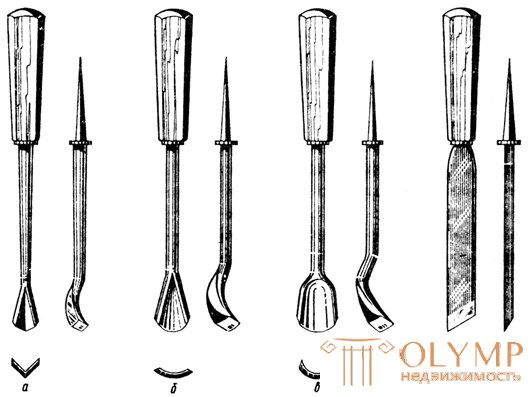 |
| Fig. 2. Cutting tool: a - chisel-corners; b - cranberry chisels; in - chisel ceraziki; g - a knife jamb. |
Chisel-ceraziki (Fig. 2, c) resemble steep semicircular chisels. The width of their cloth - 2 ... 3 mm.
A chisel-cutter, or a knife-jamb (Fig. 2, d) is a slanting knife with one-sided sharpening. Knife-jamb - the main tool for flatfloor thread. Knives are long and short. Long knives are obtained by cutting the usual straight chisel at an angle of 60 ... 70 °, and short ones (the length of the blade is up to 50 mm) by cutting off a part of the blade of the straight chisel at the same angle.
The handles most convenient in operation are shown in fig. 2. Such a handle is slightly zaovalena in the head, which creates convenience when pressing on it. Expedient handle length — up to 130, diameter — up to 28 mm.
The chisel should cut the wood without much effort. The quality of work chisel depends on its proper sharpening.
Consider how to sharpen a straight chisel (Fig. 3, a, b). First you need to get a sharpening angle of 20 ° and a flat, flat chamfer. The grinding angle is checked for the width of the chamfer, which should be 2.5 times the thickness of the blade. So, with a blade thickness of 5 mm, the width of the chamfer should be about 13 mm. Having obtained the necessary width of the chamfer, the sharpening is continued not on the grindstone, but on the fine-grained bar. Sharpen smooth movements back and forth, trying to keep your hand at the same height, so as not to tampe the chamfer. The burr formed during turning is removed with several movements of the blade along the bar. Rule the chisel on the wheel, producing the same movement as when sharpening. They only rule it much longer than sharpen it (until a smooth shiny surface of the cutting part is obtained).
It is recommended to sharpen chisels and grind their surfaces on a microcorundum bar, and to rule on a smooth leather belt using GOI paste. To do this, and use a felt circle.
Narrow straight chisels move in the process of grinding in different directions, otherwise they form a groove in the bar. Rule them on weight. The jamb is sharpened and ruled by the same methods as the straight chisel (Fig. 3, c).
A semicircular chisel is sharpened on a sharpener or a bar, slowly turning it from side to side and moving from right to left. The resulting profile fossa in the bar will give the chamfer the correct shape. The internal surface of the chisel is sharpened with a rounded bar on the table or on the weight. A semicircular chisel is ruled only by weight (Fig. 3, d).
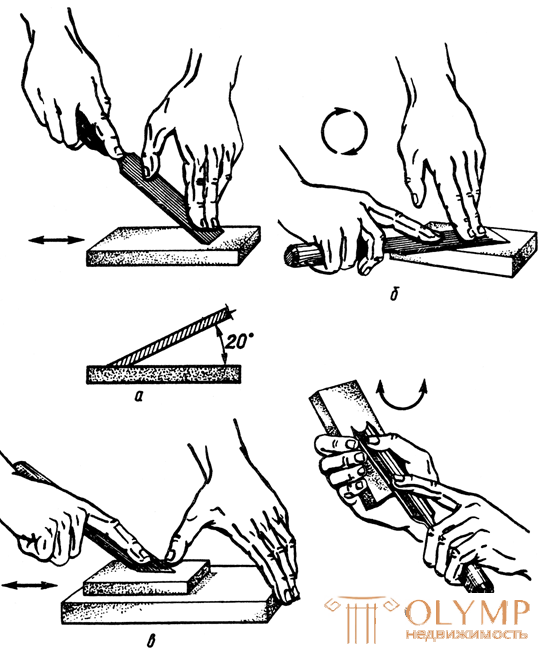 |
| Fig. 3. Preparation of the tool for work: a, b - sharpening the straight chisel from the chamfer side and from the front side; in - the position of the knife jamb when grinding on a fine-grained bar; d - editing a semicircular chisel on weight. |
Small chisels honed on fine-grained bars and circles. For each profile, it is desirable to have separate donkey and bars.
The sharpening tools are checked by cutting samples on a soft, smooth board. With a smooth and shiny trace, the honing is considered complete.
When sharpening a tool for threading, you must adhere to some rules: do not make sharp passes of the hand, do not press hard on the tool.
Store chisels should be suspended, for which it is recommended to nail the rail with the profile holes for the tool to the wooden shield. The storage room for the instrument must be dry. For better preservation, the blades and blades of the chisel are smeared with a thin layer of engine oil.
The woodcarver in the process of working and uses another tool - carpentry and metalwork. To the auxiliary tool, which should have a cutter, include a joiner's square, ernok, gauge, Malka, compasses with a ruler, compasses carpentry and measuring, metal tape measure.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)