5.1 Goals and Objectives of Surveys
Are held:
- To ensure the design of various types of construction engineering and geological characteristics of construction sites.
- With the exploration and exploitation of deposits of building materials.
- To provide data on engineering and geological conditions for the reconstruction and other types of construction work in built-up areas.
Main tasks:
- The study of geomorphological, geological, hydrogeological conditions and modern geological processes.
- Determination of strength and deformation properties of soils for the calculation of rational types of foundations and structures.
- Determination of the distribution of conditions of occurrence, genesis, age, thickness, engineering-geological properties of rocks in the array and properties associated with them groundwater, as well as all types of modern geological and engineering-geological processes and phenomena.
Results of the research:
- Engineering and geological conclusion with an assessment of the geological conditions of construction.
- Maps, sections, tables of results of laboratory and field research of soils - graphs, charts, tables, photos.
5.2 Surveys by type of construction
Industrial and civil construction (CBC).
Researches are carried out in one or two stages. For low-rise construction and for building areas, it is usually limited to the PZ stage. In case of intra-quarter building, surveys are carried out in 2 stages. The depth and number of workings depend on the geological conditions and the class of structures, but in any case, exploration workings must go through the full depth of influence of the structures. Building codes for surveys during construction regulate the volume of field work.
Hydraulic engineering. Surveys are carried out in three stages:
TEO. The first stage - Collection and systematization of materials and field survey of the construction area in conjunction with surveyors in order to select the possible location of the dam and possible options for its position.
PZ. The second stage - General engineering and geological surveys of the river valley, selection of the hydroelectric complex area, engineering and geological surveys, drilling along a number of diameters, monitoring the river level. The general and comparative characteristics of individual variants are given.
RF - The third stage - Conduct detailed research on the areas of the selected construction options. Be sure to carry out field geophysical work, field experimental work to determine the coefficient of filtration and other types of work.
Roads and railways.
Researches are carried out in two stages, each of which has its own tasks.
The first stage - conduct surveys to select a rational direction of the road, identify geological processes and phenomena that are harmful and dangerous for construction and operation, such as landslides, deep swamps, salt marshes, avalanche-prone places, ice frost occurrences, etc.
At the second stage , surveys and exploration work are performed on the selected road and engineering sites — bridges, pipelines, dams, embankments and tie-ins into the ground, i.e., where the relief will change, etc. The depth and distance between the exploration workings depend on geological and geomorphological road conditions, road class, features of its construction and operation. Engineering and geological conclusion should contain not only the geological assessment of the route, but also to predict the changes that will occur as a result of the construction and operation of roads.
Tunnels and subways.
Surveys are conducted on a special assignment, undergo deeper workings, pump out water from wells that meet aquifers, investigate the corrosive properties of the soil and other types of work.
Piping
These include water pipelines, oil pipelines, gas pipelines, steam pipelines, brine pipelines, sludge pipelines, tailings lines, sewage pipelines. Researches are carried out on the planned routes of the main pipelines and distributing networks. Exploration and design is carried out in two stages, which include the choice of the route, its profile, work on the final version and under special engineering and geological conditions, additional special studies are carried out in separate areas.
5.3 Geotechnical and geo-ecological problems of cities
Urban planning is carried out in all natural areas in diverse and often complex engineering geological conditions. The underreporting of one of these factors leads to a reduction in the service life of the objects and a rise in the cost of their reconstruction or restoration, to increased pollution of the geological environment.
Features of engineering geology and geo-ecology of cities include:
- Diversified civil, industrial, hydrotechnical, mining, municipal, transport, land, buried, underground construction, i.e., various types of impact on the geological environment.
- A large variety of types of structures in terms of weight, size, configuration, structures, operating conditions, loads (static, dynamic, variable mode).
- Large areas of urban areas, where new construction is underway, are undergoing complete demolition of old structures or existing facilities are being reconstructed (summing up a new foundation, building floors, changing the internal layout, roofing type, etc.). At the same time, base rocks experience not only an increase in loads, but sometimes a series of load and unload cycles. As a result, the soil is compacted in the zone of influence of the structure, some physical and mechanical properties of soils change.
- In existing cities, the atmosphere, hydrosphere, relief, vegetation and soil cover (embankment, trimming, planning, etc.) have been subjected to technogenic change; and the older the city, the greater these processes. Under the influence of dynamic impacts from moving vehicles under the carriageway of roads, soil compaction occurs to a depth of 1.5-2.0 meters. When water leaks from engineering networks, man-made aquifers are formed.
- In many cities (St. Petersburg, Kiev, Omsk, etc.) construction is conducted on alluvial soils.
- With the expansion of urban areas within the city limits, there are old landfills, cemeteries, depleted and still existing quarries, agricultural land, which complicates the geo-ecological situation of the urban area.
The main urban planning document is the general plan of the city, on the basis of which detailed plans for the development and planning of individual residential complexes, industrial hubs, transport and engineering communications are being developed. The master plan should take into account the features of the geological structure of the territory, hydrogeological conditions, engineering-geological and geo-ecological zoning, taking into account the types and characteristics of man-made load on the geological environment.
5.4 Protection of the natural environment
In construction, the most important task is to forecast possible violations of the natural environment and to develop recommendations for their elimination, that is, in other words, this requires a system for managing natural processes that will accompany construction.
The most important managing tool is the regulatory legal mechanism, which regulates in this case the geo-environmental aspects of production, including construction, activity. It should be noted that engineering surveys and geological engineering, in particular, relate to the type of construction activity and are subject to mandatory licensing. The latter are included as an integral element - the mandatory fulfillment of the requirements for the protection and remediation of the environment during the performance of these works.
Russia has a unified system of state standards in the field of nature protection and improving the use of natural resources. The system of standards includes a number of documents (in the form of GOSTs): on the protection of water bodies, flora, fauna, atmosphere, and also on the protection of the soil from pollution and erosion, the rational use of the surface and the bowels of the earth's crust. The system of standards is an effective means of state-legal regulation and management of all activities in the field of environmental protection.
In addition to the state, there are standards for individual sectors of the national economy, which detail state standards for local conditions, take into account the peculiarities of the earth's crust of each region and the nature of their economic activity in this region and during this activity.
Naturally, only regulations and control over their execution cannot solve the problem. Unfortunately, at the moment the most effective of the management mechanisms is economic, in the form of achieving profit, the “profitability” of environmental activities in construction to the fullest extent in our country and abroad so far is not working enough. This is, in particular, the result of the almost complete lack of environmental education and training.
Basics of monitoring. In recent years, human activity in the protection of the natural environment has increased dramatically. In connection with this, monitoring appeared as a new branch of science. Monitoring is a system of observation, assessment and prediction of the state of the environment surrounding man. In addition to this, another term has entered into practice - litomonitring, which is applicable to the crust or, in other words, to the geological environment.
The main purpose of litomonitoring is to identify violations in the natural environment and develop a forecast for its preservation. This applies to the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and the earth's crust. Monitoring works in the interests of the person and identifies the necessary conditions for his normal life. The monitoring system organically fits into the global (world), regional (oblast) and local (district) levels. Monitoring within one state is called national.
In Russia, within the framework of monitoring, a network of stations has been established that monitor the state of the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and the earth's crust (especially soils). The results of the observations of these stations are used by the authorities to take measures to eliminate the identified environmental violations. Stations have the right to monitor the implementation of state regulations on the preservation of the natural environment. Besides public institutions, the station attracts public organizations and the public to its work. In cities, public conservation committees are being created.
Currently, the program “Litomonitoring of Russia” is being carried out, which includes issues of monitoring, evaluating, monitoring and forecasting the state of the earth's crust, which is exposed to violations under the influence of man-made (construction) human activity. In this work, the leading role belongs to engineering geology.
The protection of the earth's crust consists of three main problems:
• protection of the geological environment;
• soil protection;
• combating engineering and geological processes. The geological environment includes the terrain and rocks of the earth's crust. Construction of facilities seriously violates the geological environment. Therefore, when designing facilities, a program should be drawn up to prevent or restore the technologically disturbed geological environment. It should be remembered that nature, in turn, is constantly changing the geological environment. Due to natural causes associated with global geological processes occurring both in the deep zones of the Earth and in its surface part, it is worth mentioning such phenomena as earthquakes, volcanism, river erosion, etc.
Soil protection. The surface layer of the earth's crust - soils play one of the most important roles in the flow of life processes, in the formation of the primary natural organic matter and in the decomposition of residues of living organisms and waste products. Largely following the ideas of V.I. Vernadsky, the soil can be seen as the boundary between "living" and "inanimate" and as a source of food: The total soil cover on the planet is decreasing, over the last fifty years, the arable land area the size of the Indian subcontinent lost on Earth, many soils lose their fertility. This is largely due to the negative impact of man-made activities. The legal protection of the soil is a set of legislative measures aimed at the effective and rational use of them, the full conservation and protection from harmful influences. Before construction, the soil layer should be removed and placed in another territory, where the soil can subsequently bring a person the necessary benefits.
Construction and operation of facilities often lead to the formation of engineering-geological processes that seriously violate the integrity of the earth's crust (landslides, landslides, dips in the earth’s surface above underground workings, water flooding of objects, etc.). Protection of the earth's crust in these cases is to develop ways to protect territories. It should be remembered that the choice of protection method is dictated by the local geological conditions and the natural environment (Figure 34).
Reclamation of disturbed land. Comprehensive restoration of the surface of the earth's crust, disturbed in the process of man-made human activity, is called land reclamation. At present, a scientific classification of disturbed lands has been developed, and their characteristics have been given for their suitability for a particular economic use. This allows you to solve practical problems of reclamation.
Reclamation experience has shown that even very badly disturbed lands can be brought back to life. The main objectives of reclamation are as follows:
• exclusion or minimization of adverse effects of man-made human activities, in particular in the production of construction pits, quarries, dumping dumps, etc .;
• restoration of ecological balance in places of disturbance of the earth's surface.
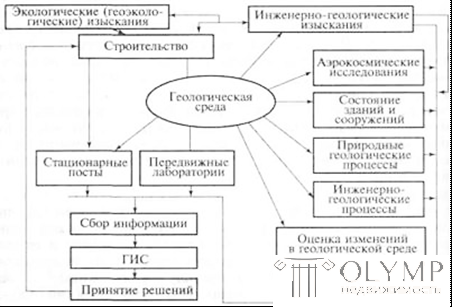
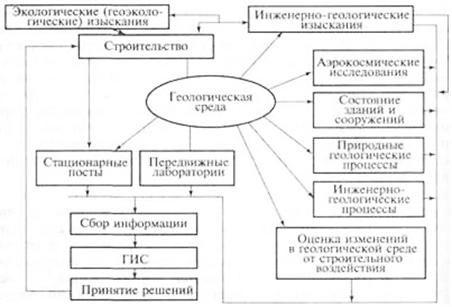
Figure 34 - Scheme of geographic information system for assessing the impact of construction on the geological environment
When developing reclamation projects for this site, the relief of the terrain, the type of rocks, the nature of the groundwater, the climate, and features of the vegetation are taken into account. Geological engineers, ecologists, biologists, geodesists, soil scientists and other specialists take part in the development. The projects envisage a complex set of mining, hydrotechnical, hydrogeological, ameliorative, construction and agricultural works. Reclamation can be mainly of two types: mining and biological.
Mining and Technical Reclamation. Its main task is to bring the damaged surface of the earth to the conditions before the applied impact. Work begins with the planning of the territory and covering with a layer of soil (up to 15 cm). On the basis of this, a turf layer is created which strengthens the surface of the earth well, especially the slopes of the relief. If necessary, groundwater is regulated by drainage. Measures are being taken to prevent the emergence of engineering geological processes, stable slopes are created, the surface of the earth is strengthened from erosion and waving with the wind.
Biological reclamation involves the development of a territory for residential development or the creation of recreation areas. After planning, the surface is covered with soil, followed by planting trees, shrubs and sowing crops. In places of worked quarries it is possible to create reservoirs.
The experience of reclamation has shown the following: 1) reclamation of the disturbed territory according to the land level should be carried out as soon as possible after completion or during the construction of the facility; 2) slopes of slopes and land dumps should be covered with forest or sown with perennial grasses. To plant a forest, the ground surface needs to be flattened to 18–20 °, for gardening, to 11 °, and crops, to 3 to 5 °.
The tasks of the builders to protect the natural environment. In the production of works, as well as in the operation of facilities, violations of the natural environment are almost inevitable. The task of the builders is to always find the means and technical capabilities to eliminate them. To do this, in projects for construction and for the period of operation of facilities, it is necessary to include natural-compatible solutions, with the help of which one can either prevent or reduce to a minimum environmental disturbances. Environmental measures should be developed on the basis of construction experience, forecast of development dynamics and changes in the earth's surface due to natural and man-made factors. On the implementation of these activities during the construction period must be stated in the act of commissioning of objects.
Builders must treat nature conservation, as their most important official duty, to be the organizers and leaders of all environmental work. When designing, the degree of future disturbance of nature should be assessed. There are cases when construction must be abandoned.It is undesirable to occupy land suitable for agriculture; it is more expedient to use unsuitable or unsuitable land for construction. During the construction period, special attention should be paid to soil conservation. The overburden soils that are formed when opening the pits should be involved in the construction industry (dumping embankments, territory planning, etc.) and should not be dumped.
An equally important measure to protect nature during the construction and operation of facilities is the fight against dusting of air, pollution of water bodies and green areas, against increased erosion, soil poisoning.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)