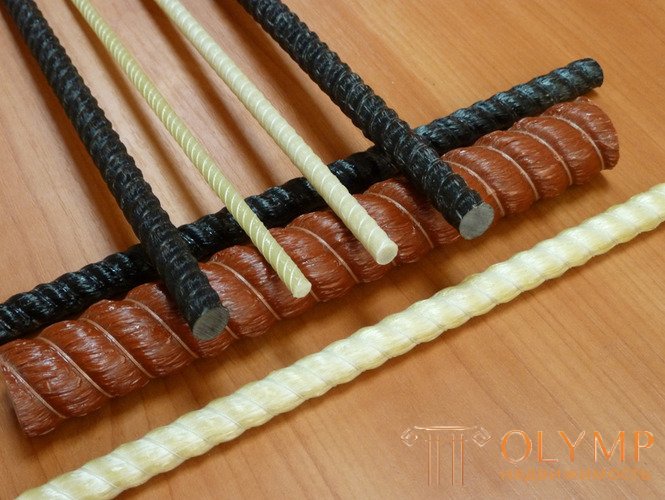

Composite reinforcement (English fiber-reinforced plastic rebar, FRP rebar ) - non-metallic rods of glass, basalt, carbon or aramid fibers impregnated with thermosetting or thermoplastic polymeric binder and hardened. The reinforcement made of glass fibers is called fiberglass (AAS), of basalt fibers - basalt-plastic (ABP), of carbon fibers - carbon-plastic. For adhesion to concrete, special edges are formed on the surface of composite reinforcement in the production process or sand coating is applied.

The specific strength of the TSA is 10 times higher than the specific strength of steel reinforcement AIII.
Composite reinforcement is not exposed to the effects of water and salts, so its use may be justified by the use in reinforcement of structures exposed to water, especially sea water, and other corrosive media.
Does not create cold bridges. Does not interfere with radio waves.
Does not create suggestive currents and magnetic fields.
Composite fittings of small diameter are transported in coils.
It does not harm the environment, is not toxic when decomposed. Does not absorb radiation.
When the ambient temperature changes, it expands and contracts with concrete structures, avoiding cracking and cracking.
The modulus of elasticity (E) of composite reinforcement is 4 times less than that of steel reinforcement (45 GPa for AAS versus 200 GPa for AIII). The low stiffness of composite reinforcement does not allow to realize its high strength potential when reinforcing concrete. According to clause 6.1.14 of the Code of Rules SP 63.13330.2012, the ultimate deformation of concrete when working in tension is about e = 0.0002. With such a deformation (ε), the stress in the TSA according to Hooke's law (σ = Eε) will be 45 GPa * 0.0002 = 9 MPa, which is about 1% of the tensile strength of the TSA.
Under comparative loading of concrete reinforced with composite reinforcement and concrete reinforced with steel reinforcement, with the same deformations of reinforced concrete according to Hooke's law, the stress in the composite reinforcement will be 4 times less than in steel reinforcement. Therefore, in order to give concrete the same strength, the reinforcement ratio (ratio of reinforcement areas and concrete) for composite reinforcement should be 4 times higher than for steel reinforcement.
The low stiffness of some types of composite reinforcement severely limits its use in construction.
Composite reinforcement does not have a yield area and tensile failure is brittle. In this regard, it is impossible to change the shape of the reinforcement without heating.
TSA loses bearing properties at 150 ° С, ABP - at 300 ° С (steel reinforcement works up to 600 ° С).
As a result of the experiments carried out at the Gvozdyov ZhBI Institute With the support of the KSM Association, it was proved that high-quality composite fittings produced with complied with GOST are able to compete in concrete structures with metal in no way inferior in performance.
When cutting TSA dust is formed, consisting of the finest glass fiber needles. It pollutes the workplace, tools and protective equipment. High risk of getting glass splinters, damage to eyes and respiratory tract.
Fiberglass reinforcement (ASP) is a composite reinforcement made of fiberglass, imparting strength, and thermosetting resins acting as a binder. One of the advantages of fiberglass reinforcement are light weight and high strength. Having high strength and corrosion resistance, is an alternative to metal reinforcement.
Basalt plastic reinforcement (ABP) is a composite reinforcement made from basalt fiber and resin. A significant difference of this building material from those listed above is a higher resistance to aggressive media. However, despite the high fire resistance of basalt fiber, the heat resistance of basalt reinforcement does not differ from fiberglass, as the polymer matrix is not able to withstand temperatures above 160 C.
Composite fittings are used in industrial and civil construction for the construction of residential, public and industrial buildings, in low-rise and cottage construction for use in concrete structures, for layered masonry walls with flexible connections, for repairing the surfaces of reinforced concrete and brick structures, as well as for work in the winter the time when curing accelerators and antifreeze additives are introduced into the masonry mortar causing corrosion of steel reinforcement.
In road construction it is used for the construction of embankments, the installation of coatings, for elements of roads that are exposed to the aggressive influence of anti-icing agents, for mixed elements of roads (such as "asphalt concrete - rails"). It is also used to strengthen the slopes of roads, in the construction of bridges (roadway, riding surface of span structures, sofa-type supports), for bank protection, in the form of nets in the asphalt base.
There are the following global brands of fiberglass reinforcement, manufactured in several countries: Schӧck, Dextra, Aslan, V-rod, DACOT, TUF-Bar, ATP-FRP Italy, FRP-Composites.
In Russia, the use of composite reinforcement increases every year. Large design and construction companies appear, massively using composite reinforcement in construction. This is facilitated by the appearance of regulatory documents: GOST 31938-2012, SNiP 52-01-2003, SP.
PKA and ANK-S are used in armored soil, gabions, in fastening of mine workings with fiberglass anchors, ground fastening along the tunneling road, in drilling anchor micro piles with a load of steel or non-metallic composite reinforcement fixed in the well by injection of cement mortar.
Fiberglass reinforcement is recommended for use as a working reinforcement in concrete structures used in areas with a seismicity of 7-9 points.
It is possible to use ANC instead of the following types of steel reinforcement for bearing elements of immersion and drill-injected nipples: - hot-rolled reinforcing steel of a periodic profile of class AIII (A 400), AIV (A 600), AV (A 800) according to GOST 5781; - thermomechanically reinforced reinforcing steel of a periodic profile of class At400s, At500s, At600, At600s, At800 according to GOST 10884; - steel reinforcing screw profile according to TU-14-2-686-86, TU-14-1-5492-2004.
ANK can be used to strengthen the soil base under various building structures, including under the culvert built in the body of embankments for various purposes.
NIIZhB has developed a new method of non-filter manufacture of composite reinforcement of a periodic profile - the method of single-extrusion.
With this method of production, the core consisting of fibrous filaments impregnated with a polymeric binder is first divided into separate parts, passed through separate channels, and then reconnected with simultaneous spiral braiding and tension of the winding bundle embedded in the bundle of fibers. The authors obtained patents for the production technology of valves.
The fittings manufactured by the nidltrusion method have high anchorage properties in a concrete environment, reliable fastening of the spiral winding on a power rod, as well as high physicomechanical properties.
Manufacturing technology of non-metallic reinforcement by way of a non-filter broach.
The technology of forming and curing rod-impregnated polymer binder fibers by drawing through a system of nozzles with a gradually decreasing cross-section.
Equipment for the production of composite reinforcement (fiberglass or basalt-plastic):
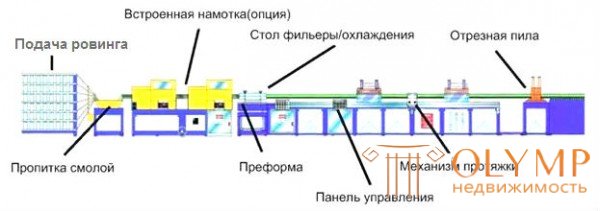
LINE DEVICE (IT CAN BE OTHER).
The principle of continuous broaching makes it possible to manufacture non-metallic reinforcement from any type of fiber, and its manufacturability and temperature conditions of curing of binders should be taken into account.
| Specifications | Metal fittings of class A-III (A400C) GOST 5781-82 | Non-metallic composite reinforcement (AAS - fiberglass, ABP - basalt-plastic) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel 35GS, 25G2S, etc. | TSA - glass fibers with a diameter of 13-16 micron-bound polymer; ABP - basalt fibers with a diameter of 10-16 microns connected by polymer |
| Specific gravity | By building code | Lighter than metal fittings |
| Temporary tensile strength, MPa | 390 | 600-1200 - АСП (with an increase in the diameter, the temporary resistance to stretching decreases, for example АСП8-1200, АСП16-900, АСП20-700) 700–1300 - UPS |
| Modulus of elasticity, MPa | 200,000 | 45 000-TSA 60 000-ABP |
| Relative extension, % | 14 | 2,2-TSA and ABP |
| Behavior under load (stress-strain relationship) | Curved line with yield point under load | Straight line with elastic linear dependence under load before failure |
| Coefficient of linear expansion αх * 10-6 / ° C | 13-15 | 9-12 |
| Density, t / m³ | 7.85 | 1.9-TSA and ABP |
| Corrosion resistance to aggressive media | Corroded with rust products | Stainless material of the first group of chemical resistance |
| Thermal conductivity | Heat conductive | Non-conductive |
| Electrical conductivity | Electrically conductive | Non-conductive - dielectric |
| Released profiles | 6-80 | Russia: 4-20. Foreign suppliers 6-40 |
| Length | Rods 6-12 m long (standardized size - due to the requirement of carriage) | Any length on request |
| Environmental friendliness | Eco-friendly | Eco-friendly - does not emit harmful and toxic substances |
| Durability | By building code | Predicted durability of at least 80 years |
| Physical and mechanical properties of reinforcement (except for the elongation under load) |
|
|
| Replacement of reinforcement according to the magnitude of elongation under load (equal elongation under the same load, within the elastic deformation of the steel reinforcement) |
|
|
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)