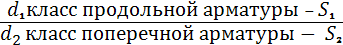
Non-tensioned reinforcement of reinforced concrete elements is carried out mainly in the form of welded meshes and frames produced on special welding machines. Apply flat and rolled welded mesh.
Welded grids (GOST 8478-81) are made of steels classes BI, Bp-I, AI-A, II-II, A-III. Grids are flat and rolled with longitudinal and transverse reinforcement. Rolled nets with longitudinal working reinforcement are manufactured with a diameter of longitudinal bars not exceeding 5 mm. With a diameter of more than 5 mm apply mesh with transverse working reinforcement or flat. The maximum diameter of the transverse rods of flat and rolled nets is 8 mm. Grid length in a roll - 50 - 10m. Therefore, for use in the construction of the grid is cut in place.
The grids are marked with a trace like this:
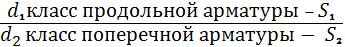
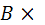 L
L 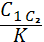
where d1 is the diameter of the longitudinal rods;
d2 - the same transverse; S1 is the pitch of the longitudinal rods; S2 - the same transverse; B - pitch, rods. L is the length of the grid, C1 and C2 is the length of the free ends of the longitudinal rods;
K - the length of the free ends of the transverse rods; if C1 = C2, then only C1 and K is left in the designation.
for example
. 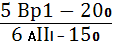 3260 × 1600
3260 × 1600 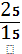
welded meshes are formed by resistance spot welding at the intersections of longitudinal and transverse rods using the table “Relationship between diameters of welded rods”.
Welded. the frames consist of longitudinal and transverse rods, with the longitudinal rods being arranged in one or two rows relative to the transverse ones and may have a one-sided or two-sided arrangement. Unilateral arrangement is preferable, since this simplifies the welding of the frame and provides better adhesion of the reinforcement to the concrete
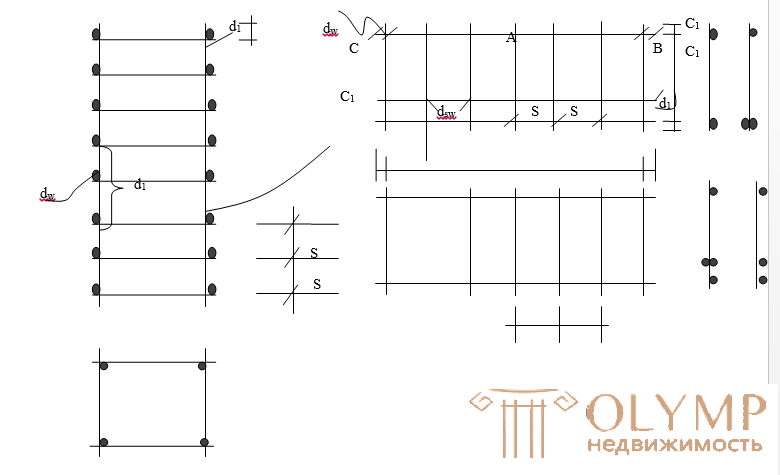
Spatial frames are formed from separate flat frames.
There is a definition of the ratio between the diameters of the rods being welded (see the textbook Kuvaldin or t.3 "Printouts")
“Sw” Distances in Flex Elements
determined by calculation, compressed depend on the diameter of the longitudinal reinforcement
Anchoring and fittings joints
For reliable anchoring in concrete, stretched smooth rods of knitted frames and nets are provided with semicircular hooks at the ends. The force of adhesion of compressed rods with concrete is much greater than the force of adhesion of stretched ones. Therefore, the compressed smooth rods of knitted frames may not have hooks. In welded meshes and frames made of smooth rods, hooks are not needed, because for each rod, rods of the perpendicular direction are anchors that prevent it from slipping in concrete. The rods of a periodic profile in all cases are made without hooks, since the nature of their surfaces ensures reliable zanking. The length of the anchoring zone of working rods depends on the type of construction and the nature of its work under its load. So, longitudinal compressed rods db. laid over the section where they are no longer needed according to the calculation, the length is not <15d, but the smooth rods of knitted frames without hooks on the ends are not <20 d in length.
Protective layer of concrete.
Protective layer of concrete for working reinforcement should ensure the joint operation of reinforcement with concrete at all stages of the structure operation, as well as protection of reinforcement from external atmospheric, temperature and other influences.
For longitudinal working reinforcement, the thickness of the protective layer must be at least the diameter of the rod or rope and not less than:
1) In slabs and walls with thickness up to 100mm inclusive - 10mm.
2) In slabs and walls with a thickness of> 100mm, as well as in beams and edges with a height of less than 250mm - 15mm.
3) In beams and edges with a height of 250mm and ≥ and also in columns - 20mm.
4) In foundation beams and in prefabricated foundations - 30mm.
5) For lower reinforcement of monolithic foundations: in the presence of concrete preparation - 35mm, in the absence of concrete preparation - 70mm.
6) The thickness of the protective layer for transverse, distribution and structural reinforcement should be no less than the diameter of the specified reinforcement and no less: for h <250mm - 10mm
7) The ends of the longitudinal working rods of the non-stressed reinforcement should be separated from the end of the element at a distance not less than specified in t. 38 SniP 21 · 21-75 and not less than 10 mm.
The ends of prestressing reinforcement, as well as anchors. protected by a layer of mortar not <5mm, or concrete not <15mm. 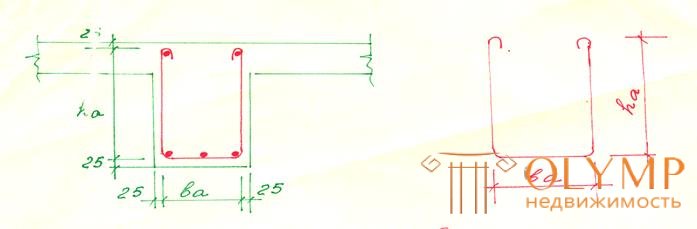
L yoke = 2ha + ba + L
Additive for 2 hooks L take when the diameter of the rod covered by the clamp
10≤d≤25mm respectively
28≤d≤40mm 150 and
Questions for self-test.
1. What is concrete?
2. What is reinforced concrete
3. The advantages of reinforced concrete.
4. The disadvantages of reinforced concrete.
5. What types of reinforced concrete structures do you know?
6. What concrete concrete do you know depending on the volume of the mass?
7. What is the main characteristic of concrete strength?
8. What strength classes do you know?
9. What is a waterproof brand?
10. What is an oros-resistant brand?
11. What is concrete creep?
12. What is concrete shrinkage?
13. Types of reinforcement by the nature of the surface.
14. Types of valves according to the nature of work.
15. What do the grades of hot-rolled reinforcing steel mean?
16. What types of bar reinforcement do you know?
17. What wire classes do you know?
18. Decipher P3, P19, K2x7.
19. What are flexible and rigid fittings?
20. What are the grids, frames?
21. What is a protective layer of concrete for?
22. What is the distance from the end of the longitudinal reinforcement to the end of the beam?
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)