
1. Air exchange rate
The calculation of the ventilation system involves the determination of air exchange. The amount of air required depends on the presence of some factors, such as: the rate of air exchange , the presence of excess heat generation, moisture release, the presence of harmful substances, etc. Read: how to calculate the required room air exchange. of the above. Provided that the greatest value will be the air exchange at the normative multiplicity, then it is the value of the air exchange rate that will affect the air exchange of the room. The calculation of the magnitude of air exchange on the multiplicity and its values will be discussed in this material.

Air exchange rate is the intensity of air exchange, which is determined by the number of air exchanges per unit of time. It is equal to the ratio of the volume of air that is supplied per unit of time to the volume of the room to which it is supplied.
In simple words, this is a number that shows how many times in one hour there is a complete change in the volume of air in a room.
As already mentioned, under the condition when harmful impurities are not taken into account, the air exchange value is calculated according to the standard multiplicity. Whether it is a domestic area or a production area, the formula for calculating the air exchange according to the multiplicity will be the same:
L = Vpom ⋅ Kp (m3 / h),
where Vпом - the volume of the room, m3;
Kp - normative air exchange rate, 1 / h.
The volume of the room should be known, while the number of multiplicity is regulated by the rules. These include building codes (SNiP 2.08.01-89), sanitary and hygiene standards, and others.
 This table shows the values of the air exchange rate for domestic premises: The air exchange rate for industrial premises and rooms with a significant volume:
This table shows the values of the air exchange rate for domestic premises: The air exchange rate for industrial premises and rooms with a significant volume: 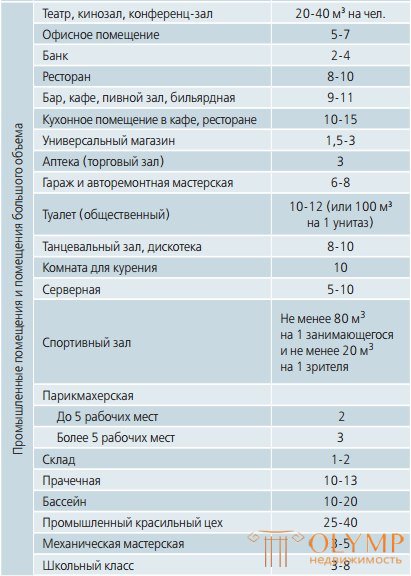
The above data are taken from the directories of the famous Ukrainian company Vents.
As you know, in homes, ventilation systems are designed with natural motivation.
Places for removing air from the premises are the kitchen, bath, toilet, that is, the most polluted areas of the apartment. Fresh air flows through the slots, windows, doors.
Over time, the materials and design of windows will be improved. The current designs are completely sealed, which does not allow to perform the necessary air exchange and to satisfy the minimum rate of air exchange .
Similar problems are solved by installing various air flow systems. These are the inlet valves in the wall, as well as the inlet valves in the windows.
2. Calculation of air exchange
Air exchange - the amount of air required to completely or partially replace the polluted air in the room. Air exchange is measured in cubic meters per hour.
How to perform the calculation of air ? In general, air exchange is determined by the type of air pollutants found in this room.

The basic calculations of air exchange are the calculation for sanitary standards, the calculation for normalized multiplicity, the calculation for compensation of local extracts. There is also air exchange for the assimilation of apparent and complete heat, for the removal of moisture, for the dilution of harmful substances in the air. For each of these criteria, there is a different method for calculating air exchange .
Before starting the calculation of air exchange you need to know the following data:
Air exchange for the multiplicity is determined by the formula:
Lk = k • V (m3 / hour)
where k is the normalized air exchange rate;
V- volume of the room, m3.
The index k for different rooms and the details of the multiplicity calculation are presented above.
Air Frequency Chart:
| Household premises | Air exchange rate | |
|---|---|---|
| Living room (in apartment or hostel) | 3 m3 / h per 1m2 residential premises | |
| Kitchen apartment or hostel | 6-8 | |
| Bathroom | 7-9 | |
| Shower | 7-9 | |
| Restroom | 8-10 | |
| Laundry (household) | 7 | |
| Walk-in closet | 1.5 | |
| Pantry | one | |
| Garage | 4-8 | |
| Cellar | 4-6 |
| Industrial premises and large premises | Air exchange rate | |
|---|---|---|
| Theater, cinema, conference room | 20-40 m3 per person. | |
| Office space | 5-7 | |
| Bank | 2-4 | |
| A restaurant | 8-10 | |
| Bar, cafe, beer hall, billiard room | 9-11 | |
| Kitchen room in a cafe, restaurant | 10-15 | |
| Supermarket | 1.5-3 | |
| Pharmacy (trading room) | 3 | |
| Garage and auto repair shop | 6-8 | |
| Toilet (public) | 10-12 (or 100 m3 for 1 toilet) | |
| Ballroom, disco | 8-10 | |
| Smoking room | ten | |
| Server | 5-10 | |
| Sports Hall | At least 80 m3 per 1 student and at least 20 m3 per 1 spectator | |
| Barber shop (up to 5 jobs) | 2 | |
| Barber shop (more than 5 jobs) | 3 | |
| Stock | 1-2 | |
| Laundry | 10-13 | |
| Pool | 10-20 | |
| Industrial paint shop | 25-40 | |
| Mechanical workshop | 3-5 | |
| Classroom | 3-8 |
Air exchange by heat generation is determined if there is a large amount of heat in the room that needs to be removed.
Calculation of air exchange by heat excess is carried out according to the formula:
L = 3.6 • Qizl / (ρ • c • (tud – tпр)) (m3 / hour),
where Qisl - the amount of heat that is released into the room, W;
ρ is the air density in the room, kg / m3;
c is the mass heat capacity of air;
tud is the air temperature that is removed by ventilation, ºС;
tpr - air temperature that is supplied, ºС.
The desired air exchange for excess moisture in the room can be calculated by the formula:
L = W / (ρ (dyd – dpr) (m3 / hour),
where W is the release of humidity in the room;
ρ - air density in the building, kg / m3;
dud - the moisture content in the air that is removed by the ventilation system;
dpr - moisture content in the air that is supplied.

Air exchange calculation
Air exchange for gas emissions into the room is calculated by the formula:
L = K / (Kgdk – Kpr) (m3 / hour),
where K is the weight amount of gases that are released into the room;
Kgdk - maximum permissible concentration of gases;
CRC - the concentration of gases in the supplied air.
L = GCO2 / (UPDK-UP) (m3 / h)
where GCO2 is the amount of CO2 emitted, l / h,
UPDK - maximum permissible concentration of CO2 in exhaust air, l / m3,
UE - gas content in the supply air, l / m3.
| Norms of permissible concentrations of CO2 in the air, l / m3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In places of permanent stay of people (living rooms) | 1.0 | |||
| In hospitals and child care facilities | 0.7 | |||
| In places of temporary stay of people (institutions) | 1.25 | |||
| In places of short-term stay of people (institutions) | 2.0 | |||
| In the outdoor air: | Settlements (village) | 0.33 | ||
| Small cities | 0.4 | |||
| Big cities | 0.5 | |||
The calculation of air exchange in a room according to sanitary standards (according to the number of people) is determined from the condition of providing a person with the necessary amount of fresh air. For public buildings, sanitary norms provide for the supply of 20 m3 / hour • people during temporary stay of a person in the room, 40 m3 / hour • people during a long stay, and 80m3 / hour • people for the gym.
The formula for calculating the air:
L = n • l (m3 / hour)
where n is the number of people, people;
l - sanitary air supply rate, m3 / h • pers.
For the calculated value of air exchange take the maximum value from the calculations for heat, moisture, the flow of harmful vapors and gases, according to sanitary standards, compensation of local extracts and the normative frequency of air.
Air exchange of residential and public premises is usually calculated by the rate of air exchange or by sanitary standards.
After calculating the required air exchange, the air balance of the premises is compiled, the number of air distributors is selected and the aerodynamic calculation of the system is made. Therefore, we advise you not to neglect the calculation of air exchange , if you want to create comfortable conditions for your stay in the room.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (1)
Спасибо все понятно