
The cradles (fig. 6) are made of metal or wood and suspended on steel ropes. Winches for lifting cradles installed on the ground or on the cradles themselves. The passport indicates the load for which the cradle is designed. When finishing works apply self-lifting cradles with electric drive. Lifting height of cradles from 15 m and above, load capacity from 120 kg and more. Lifting capacity must correspond to double rated load.

Fig. 6. Cradle
The cradle must be tested for a static load exceeding the calculated load by 25%. In addition, it is tested by uniformly lifting and lowering with a load exceeding the design load by 10%. For additional testing, it is recommended to lift the cradle with the load half a meter from the ground and leave it in this state for 2-3 hours. It is strictly prohibited to overload the cradle. After the test is drawn up.
Each time before starting work, the cradle, ropes and blocks must be inspected. Defects are eliminated and only then proceed to work.
The cradles on which the winches are installed lower and raise the plasterers themselves. When the winches are placed on the ground, the cradle is raised and lowered by the workers located near the winches. The winches installed on the ground are pressed with a load twice the mass of the cradle along with plasterers and materials.
The blocks of cradles are fixed to the consoles-fingers, fired from the walls under the eaves or hanging from the roof. Consoles are wooden from thick logs or steel from rails, I-beams or channels. All of them must be pre-designed for the appropriate load and fixed on the overlap parts, rafters or other sturdy structures.
All cradles must be grounded.
Scaffolding is used to work at a small height both inside buildings and on facades. Usually use inventory scaffolding of metal pipes. They are easily assembled and disassembled, have lifting devices, which makes it possible to raise or lower them to different heights. The flooring is a wooden shield.
Consider the most commonly used collapsible scaffolding.
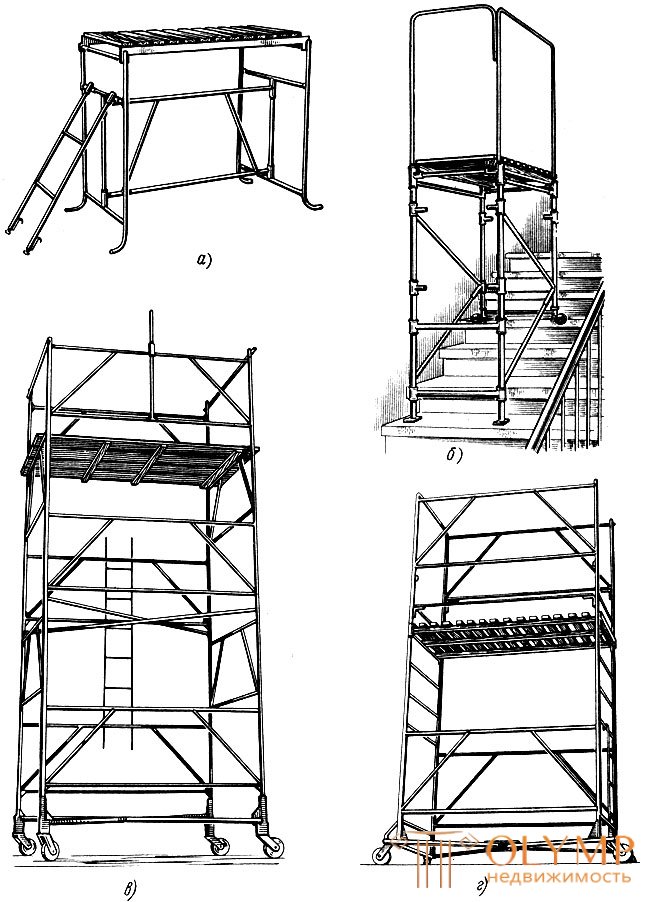
The folding two-high table (Fig. 7, a) has a retractable platform, which makes it possible to perform work in rooms with a height of 2.5 to 2.7 m. The table area can be raised to a height of 1155 mm. The size of the platform is 974 x 530 mm. Mass of the table with a shield of 15.4 kg.
In the case of continuous scaffolding, several tables are placed and floor boards are laid between them.
A folding universal table (Fig. 7, b) is used for working in rooms with a height of 2.5 to 2.7 m. It is also convenient for working in stairwells, since one pair of its legs can be pulled out and set the table on the steps, that the ground will be horizontal. So that the table does not roll down from the steps, one pair of its legs is made without wheels, which creates the necessary braking.
The height of the table platform is 1360 mm, length 1100 mm, width 560 mm. The mass of the table with the shield flooring and fencing 20, 15 kg.
The movable collapsible tower tour (Fig. 7, c) is intended for work in rooms 6 m high. The height of the tower, counting from the floor to the level of the site, is 4 m; dimensions of the working platform for a free-standing tower 2 x 2 m, load capacity 2 kN. The total mass of the tower is 414 kg. If necessary, complete scaffolding install several towers, and between them put the transitional shields. These towers have wheels and easily move along the front of work.
Universal collapsible mobile scaffolding (Fig. 7, d) is made of thin-walled pipes. Height of a working flooring from the level of a floor of 2200 mm; length of the platform is 1950 mm, width is 1000 mm. The scaffolding is mounted on wheels, which allows them to move freely along the front of work.
When plastering ceilings or scaffolding beams, it should be made so high that there is a distance of 15-20 cm between the worker’s head and the ceiling.
Ladders and stepladders . At small repair of various surfaces apply ladders and step-ladders . They are durable, lightweight, they can be transferred from one place to another. From ladders they work only on the walls, from step-ladders — both on the walls and on the ceilings.
According to the design, the ladders should be such that the legs during work are rigidly loosened and not moved.
Legs of ladders happen not sliding and sliding. The lower ends of the stairs are provided with stops in the form of sharp metal spikes, tips. For the concrete bases tips make rubber, for wooden or earth - metal.
Small and repair work inside the premises is carried out from wooden stairs-tables (Fig. 8, a). Materials and tools can be placed on their wide platforms. Also used folding dural ladder tables.
In the stairwells it is convenient to work on step-ladders with retractable legs (Fig. 8, b).
For the convenience of working on the stairs, attachment platforms are attached to their steps (Fig. 8, c). They are made of angular steel. The top of the site has a boardwalk. Two platforms can be attached to one ladder: one for a worker, and another for a material.
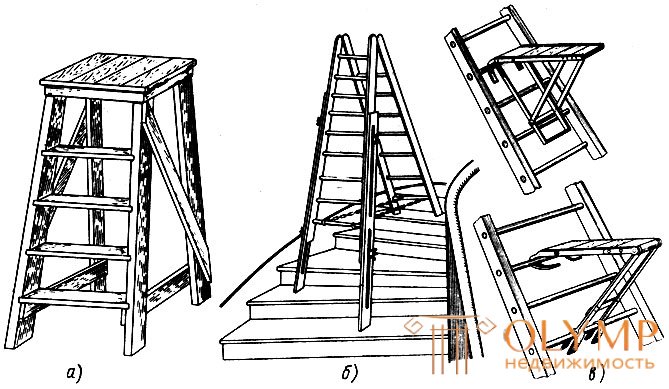
Fig. 8. Ladders: a - a ladder-table, b - a ladder step-ladder with retractable legs, in - ladders with side platforms
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)