Principles of modernization of buildings. Modernization is understood to mean such a major overhaul or reconstruction, which is accompanied by the transformation of a building into a structure that meets modern requirements of technical and functional operation.
By upgrading the building, the layout is as close as possible to the requirements of functional comfort. Engineering equipment is improved, equipped with modern systems and installations.
The principles of modernization of buildings depend on their features, laid during the construction, and are subordinated to the chosen strategy.
Building Retrofit Strategy. The modernization is based on three premises:
- - the priority of address design of the composition and structure of apartments in the building;
- - comprehensive orientation towards a market economy;
- - the maximum use of features of the constructive and planning decisions of the structure.
Under the targeted design imply the formation of such concepts of modernization, as a result of which housing should be obtained, designed to meet the comfort requirements of specific categories of residents. It is intended to move from creating apartments for the average user to individual design for specific residents, especially since the redevelopment of the old building always carries with it the signs of originality.
If modernization is oriented towards a market economy, one should strive to entrust financing of repairs to the consumer, and use centralized resources to meet the urgent needs of the city or territorial entities. With the limited resources of the municipal authorities, part of the payment for repairs should be shifted to the legal entities and individuals concerned, and not to the financially insecure part of the population.
It is necessary to take into account the tendency of property stratification of citizens and the formation among residents of various incomes of various comfortable housing requirements. On this basis, to modernize apartments for certain categories of users.
The first category includes the poor and least-affluent citizens who live in apartments on a lease or privatization basis. For them, it is possible to limit comfort requirements to minimum, but decent conditions. They must provide safety and hygiene, combined with a minimum of modern amenities.
The second category includes the main part of the middle class. Residents applying for extended housing services are more comfortable, either own or rented for a relatively higher price than social housing.
This category is not uniform in its composition. It includes not only residents who are economically able to provide themselves with housing that is close to European standards in terms of comfort. There is a less secured layer, which is available only a slight increase in comfort compared with the apartments of the citizens of the first category.
The third - the smallest category of the population - is the most affluent, having the opportunity to rent or own prestigious most comfortable apartments or even private residences.
There is a tendency to directly use Western analogues without adapting to our traditions and conditions. The most important of them is the priority of multi-storey buildings with the entrances common to several apartments on the floor platform of the staircase, but not with separate exits from them to the street.
Built 100-50 years ago in the now prestigious areas of the city, such buildings are subject to primary reconstruction. An autonomous (in a separate apartment) arrangement of apartments for wealthy people in them causes antagonism among the residents of the section.
As you can see, it is necessary to move on to transfer under the expensive housing of buildings entirely, which should, to some extent, relieve tension in relations between neighbors. However, it is impossible to say with certainty that in our society with the psychological stereotype of universal equality there can be no confrontation between the inhabitants of neighboring houses.
On the other hand, the desire of municipalities to shift the burden of renovating dilapidated buildings to non-traditional investors is justified. They will be interested in investing in repairs only if they receive a certain benefit in kind in the form of housing or financial assistance to them, by selling apartments received as property.
The prestige of the area and the comfort of housing prepared for sale may provide incentives for the middle class to acquire it. However, this class has not yet been formed in the country and the demand for prestigious apartments, apartments is not large enough. Therefore, when choosing a modernization strategy, you need to rely on marketing research and the search for consensus with all the participants in the process of urban development and reconstruction of buildings.
The number of stakeholders should include not only city halls, municipalities, prefectures and district administrations, but also directorates of a single customer. It is necessary to further study the opinions of residents of the reconstructed territories, their associations, partnerships and fraternities. It is impossible to exclude the builders - executors of town-planning ideas, implementing them, as well as potential owners and tenants. It is necessary to take into account the architectural and planning features of buildings, their initial purpose and the period of construction.
Modernization of planning elements of buildings.
Planning elements include apartment building communications, rooms, kitchens, lavatories and other components of the apartments. Regardless of the characteristics of the reconstructed house, their modernization is subject to general laws. Consider the features of the most common methods of redevelopment.
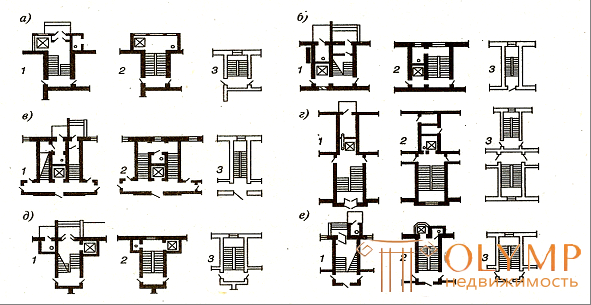
The modernization of the staircase and elevator units is based on the preservation for subsequent use of existing stairwells, especially the front ones. In old apartment houses they are often decorated with stucco moldings, rosettes and paintings, sometimes of high quality. This decor must be preserved for posterity (Fig. 6.1.).

1 - reconstruction, first floor plan; 2 - the same, typical floor plan;
3 - existing layout
Fig. 6. 1. - Reconstruction of stair-elevator nodes
Black stairs are either eliminated as unnecessary, or converted into ceremonial ones, when they want to increase the number of sections in the building when disaggregating apartments. Typically, these ladders do not meet fire regulations and modern operating requirements. Transit treads, width and large slopes of marches do not meet the standards. But the biggest drawback is the lack of elevators, which are often found in front stair nodes.
Marches steep ladders shift, trying to place in the dimensions of the building. However, this technique is not always feasible. The length of the staircase has to be increased due to the installation of glazed balcony-type platforms. This does not violate the decor of the main facades, since the black stairs are located on the courtyard side.
The most serious work arises when it is necessary to increase the width of the marches, when you need to shift walls or move the staircase to another place. Often it can be rebuilt at the expense of neighboring rooms. At the same time fit an elevator and a garbage chute into the building envelope.
These elements of engineering improvement set, providing access to them from the storey site. If this solution fails, they are mounted on the floor, which is less convenient and allowed as a forced one.
Elevator mines are trying to conclude in fireproof structures. It is logical to use the dimensions of the black stairs, if they are adjacent to the front. Then the existing main walls isolate the elevator and the garbage chute . If in the end there is no place for their placement, then use adjacent volumes . This technique is permissible only when non-residential premises, such as kitchens and bathrooms, are adjacent to these engineering elements.
In the practice of modernization, there are often cases when an elevator cannot be placed in the dimensions of a building without a large loss of usable area. Then it is made attached in the form of a balcony system or hung on the facade of a building . Use variant e, the frame of the mounted elevator is fixed to the consoles located in the level of the attic floor. Stops are tied to interfloor platforms.
Of particular difficulty is the placement of the elevator and the garbage chute on the black staircase. There are two possible solutions. First, a side solution, when for engineering equipment use the envelope of the old narrowed staircase. Secondly, choose the central location of this equipment and the bypass ladder.
Elevators are installed in buildings, the floor of the upper floor of which is above the blind area above 13.5 m. These engineering devices are passenger, cargo and cargo-passenger (Fig. 6.2.).
If a foreign-made elevator is used, the dimensions are specified according to the product passports. In those cases when it is impossible to place a standard shaft, an elevator is ordered on an individual project. In residential buildings, freight elevators are very rarely installed. Usually use passenger or cargo-passenger.
The engine room with a drive and control devices is located at the top or bottom of the shaft. In the first case, the design of the elevator is simplified.
The number of bends of the suspension ropes is reduced, which increases the reliability and service life of the mechanism. At the lower location, noise is reduced and system maintenance is facilitated, but the load on the mine is increased.
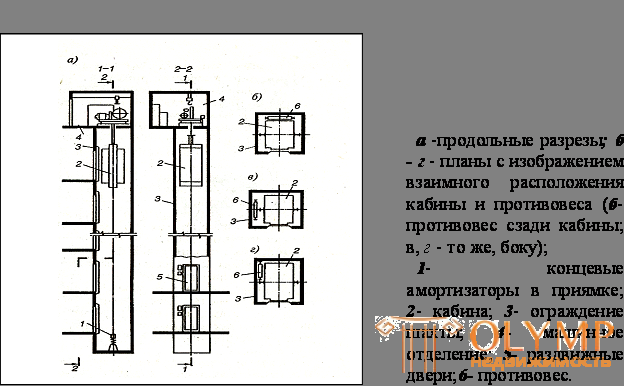
Fig. 6. 2. - Elevator with upper engine room
Garbage chutes, as a rule, are installed next to elevators, but there are also cases when these elements of building engineering equipment are located on different sides of the staircase. Garbage chutes are also mounted on the interfloor platforms, removing the distributors of dirt and odor from the entrances to the apartments.
The chute consists of a barrel with garbage-receiving valves, above the barrel room with a barrel ventilation system and a garbage chute. Vertical barrel added system strengthened by clamping in the interfloor ceilings. However, in practice there are solutions with a trunk hidden in the wall. They were used in houses built 40-50-ies. Twentieth century.
Garbage valves-valves installed across the floor, if the barrel is located on the interfloor area. But solutions are possible with valves on each floor. As a rule, in such solutions they equip the floors.
Nadstvolnye premises garbage disposal located in the attic. They are equipped with a mechanically driven ruff for cleaning the barrel, so these rooms are made at least 2.2 m high to the ruff suspension blocks. Size in terms of designate, based on the possibility of free access to the cleaning system, which is necessary for disinfection of the garbage disposal. Provide a walk around the trunk in width equal to 0.8 m.
The fire chamber on the first floor is fenced off with fireproof structures. Within the limits of the size of the modernized building, it is difficult for it to allocate a place with a floor mark at the level of a blind area, therefore, the added volume is often erected, which is connected with the need to have a place in the yard with unhindered access to the garbage trucks.
The entrance node during the modernization is decided, keeping the existing main entrances, but they strive to make one more from the courtyard. Nowadays, such an entrance to a greater degree ensures the safety of the staircase, if the tenants use it to them. If the entrances are built in the archway under the building, they are completely reconstructed. Provide direct access to the staircase with the courtyard space.
Tambours are installed at the entrances, sometimes the first flights of stairs are reworked for this. If they allow for the movement of persons with disabilities, then use ramps or lifters.
In homes, vestibules are equipped with automatic locking devices with combination locks that prevent free passage to the building. Sometimes they are equipped with television tracking devices.
To accommodate the concierge at the entrance allocate a special room. Planning it is solved in the form of a room equipped with a sanitary unit or even a small apartment. In the wall separating the concierge room from the staircase, install a door and viewing opening, providing an overview of the vestibule and adjacent volumes (Fig. 6.3.).
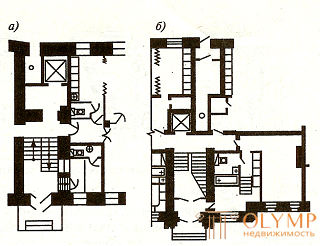
but - rooms with a bathroom; b - small apartment concierge
Fig. 6.3. - Fragment of ground floor plans with accommodation
concierge rooms
Planning elements of the modernized apartment is appointed on the basis of its settlement by one family. The apartment includes living rooms and utility rooms. Rooms are divided into shared and sleeping or individual use.
Utility rooms consist of kitchens, combined sanitary facilities or separate lavatories, bathrooms, front and corridors, built-in wardrobes, balconies and loggias.
The common room, as a rule, is the composition core of apartments, therefore it is endowed with the largest area. This room is designed for all family members to stay, relax and receive guests. It can be used as a dining room, thus, carrying in itself multifunctionality. Therefore, according to the norms, its area should not be less than 16 m.
In social housing, the common room, if necessary, is also used for sleeping. The berth is separated from the main volume by a niche or an alcove. In two-bedroom apartments the common room is made isolated. In the multi-room it can be a pass. The entrance to the banned room is made opposite the door to the common one. This provides the shortest transit route through the premises. Based on the convenience of placing the furniture, the width of the common rooms is prescribed to be at least 3-3.5 m.
In prestigious apartments, the common room is often combined with other function rooms, for example, a winter garden and other active and passive recreation areas. In such apartments, its area is not limited, but on the contrary, they seek to increase as much as possible.
Sleeping and private rooms intended for personal use, recreation or work of one or two family members. The width of the bedrooms take in the range of 2.2-3 m.
In apartments for economically secured residents there are no such rigid restrictions. When the bedroom is trying to arrange a closet and a toilet.
Kitchens are a place where the hostess spends a significant part of the time allotted for the household. This room is considered as production, subjecting the technology of food processing and dishes, cooking. In accordance with this, kitchen equipment is installed, consisting of a hearth (stove, gas or electric stove), sink, cupboards, and hinged shelves. The working front of the kitchen includes a refrigerator, and sometimes a dishwasher and washing machine. The minimum length of such a front is set to not less than 2.7-3 m.
According to Russian tradition, all family members often gather in the kitchen and not just for meals. Based on this, there are three types of planning solutions for kitchens: kitchen-dining rooms, kitchen workers and kitchen niches (Fig. 6.4).
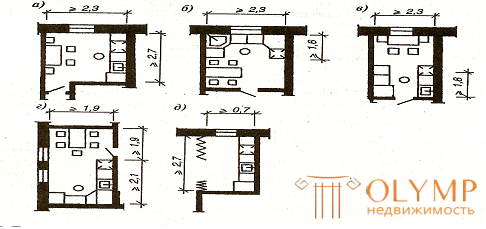
a - g - kitchens in separate rooms; d - kitchenette with electric stove.
Fig. 6. 4. - Types of kitchens in modernized municipal houses
The kitchen-dining room is comfortable as it turns into an extra room. In this kitchen provide a place for a dining table.
The working kitchen is an isolated volume, intended only for cooking. It is located near the dining room or common room. In the partition separating the kitchen and these rooms, often punch the opening for serving dishes.
Kitchen niches are placed in the common room or front. The latter solution is used in hotel-type apartments. The depth of the niche is not less than 0.7 m, and the length is taken along the front of the equipment. According to current regulations, such kitchens are allowed to do only with the installation of an electric stove.
In prestigious apartments, kitchen niches are often located in a special area of the common room. Then it is separated from the main volume by a decorative transparent barrier. His role can play the bar.
In the sanitary unit They combine the rooms in which a toilet, washbasin, bidet, bath and shower tray and sometimes a steam room are installed. If, however, provide for apartments of improved planning, the area of the bathroom increase.
In one-room apartments it is allowed to use a combined sanitary unit, in apartments of a hotel type - reduced sizes (Fig. 6.5.).
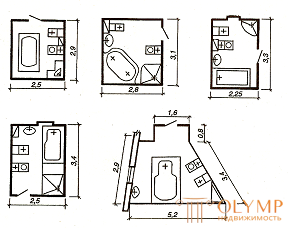
Fig. 6.5. - Нестандартные санитарные узлы, применяемые при модернизации под элитное жилье
В престижных квартирах санитарные узлы выполняют по индивидуальным проектам. В квартирах используют неудобные для комнат места, делая помещения непрямоугольной формы.
Часто квартиры оборудуют двумя-тремя узлами. В парадной части устраивают уборную с умывальником, а в спальной зоне – один-два совмещенных санузла. Сейчас престижность квартиры определяют не по набору комнат, а по количеству санитарных узлов. Иногда их размещают при каждой спальне. В основном узле устанавливают ванную увеличенных размеров типа Джакуззи (Jacuzzi), а в других – обычного размера. Установка первого типа ванн требует проверки на прочность перекрытия под ними.
Коридоры и передняя являются планировочными элементами, связывающими отдельные части квартиры. Они необходимы не только для связи, но и разобщения отдельных объемов. Например, шлюзом-переходом отделяют спальную зону от помещений коллективного пребывания семьи. При этом соблюдают нормативную ширину проходов. В комнаты их делают не менее 1,1 м, в кухни – 0,85 м. До этого же размера можно сократить коридоры, ведущие в спальни, если имеется второй вход из общей комнаты.
Передняя является помещением, откуда начинается квартира. Ее ширину принимают не менее 1,4 м. В престижных квартирах передние делают большими, иногда превращают в холлы, естественно перетекающие в общую комнату.
В передней предусматривают установку вешалки для этого требуется фронт не менее 0,8 м в малокомнатных квартирах, а в трех- и четырехкомнатных 1,2-1,6 м.
Встроенные шкафы и шкафные комнаты-кладовые размещают в коридорах и передних, в наиболее неудобных для комнат местах квартиры.
Модернизация квартир.
Модернизируя квартиры, оценивают несколько факторов.
Ориентацию здания оценивают прежде всего. Закрепленное на местности, оно часто оказывается неблaгoприятно ориентированным относительно стран света, соседней застройки и шумных городских магистралей. Обеспечивая инсоляцию помещений, уменьшая влияние других факторов, планировочное решение варьируют. Квартиры проектируют с окнами не на одну сторону горизонта, а на две.
With этом в неблагоприятные условия обычно ставят комнаты общего пребывания, а окна спальных ориентируют в тихий двор и на наиболее инсолируемый фасад. Следует отметить и такую закономерность: свобода выбора решения обратно пропорциональна количеству сохраняемых внутренних несущих конструкций . Чем больше колонн, пилонов и стен нужно оставить в пределах габарита здания, тем сложнее создать квартиру, соответствующую намеченному замыслу и уровню комфортности.
Планировочные параметры в каждом здании, особенно дореволюционной постройки, настолько индивидуальны, что невозможно рекомендовать стандартные решения, оптимальные для разных периодов постройки (исключение составляют типовые дома второй половины XX в.). Однако в приемах модернизации квартир существуют общие принципы, зависящие от таких планировочных особенностей зданий, как ширина корпуса, шаг оконных проемов, конструктивно-планировочная схема и принимаемая ярусность квартир.
Ширина корпуса существенно влияет на планировку квартир. Так, в узких корпусах шириной до 9 м можно разместить квартиры двусторонней ориентации . Для размещения квартир односторонней ориентации нужно прибегать к планировке, отличной от общепринятой.
As a rule, part of the light front has to be occupied by outbuildings, and pull rooms along two or even three windows along the facade . The same apartments of municipal housing are possible in adjacent buildings, courtyards with narrow buildings adjoining each other and solved jointly. If the levels of the floors in different buildings do not match, then use the options of apartments in two levels, communicating with small ladders.
In buildings with a width of up to 13 m, the layout differs little from the traditional one. Here the design solution is subject to the conditions of orientation and the rhythm of the windows on the facade of the building.
Step window openings , as a rule, different from those adopted in new construction.
For old buildings, a fairly frequent step is characteristic - from 2.2 to 2.6 m. Although in buildings built before 1917, there are approximately 15% of houses with window pitch 3.4-3.6 m. As a rule, in each The structure adopted a constant rhythm of windows, with the exception of those parts of the facades on which the architect emphasized, changing the rhythm and size of the light openings.
A constant small window pitch excludes the possibility of differentiating rooms by width, if the apartment is solved with single-window rooms with a window along the axis of the room. Therefore, partitions shift, which is unprofitable from the point of view of lighting with natural light. Here resorted to two opposing techniques aimed at changing the pitch of windows and the size of window pillars.
In the first case, some windows lay. This allows the partition to be placed anywhere on the wide pier. When laying, it is usually left a niche that does not violate the architecture of the facade, preserves the rhythm of the openings .
The second technique is punching or knocking window openings. Since this technique not only leads to a change in the appearance of the building, but also the carrying capacity of the walls, it is resorted to in exceptional cases. More often, the step is changed due to partial bookmarking of openings .
In buildings with a wide window pitch, they arrange sleeping niches, closets, or use rooms close to the square.
In buildings with a width of more than 13.5 m, apartments have excess depth, sometimes exceeding 7 m. This contradicts the principles of constructing modern planning solutions for apartments in municipal housing. Therefore, the excess depth of the rooms is camouflaged with alcoves and niches, or instead of them they are fitted with wardrobes or closets.
For hygienic purposes, the air is ventilated, providing ventilation, usually natural. For This one of the walls put ventilation ducts. Use and reception when the kitchen is separated from the sanitary facilities. Sanitary equipment is connected to the independent risers of engineering communications. To reduce their number in the house bathrooms adjacent apartments are placed nearby. Another example, if the sanitary facilities of adjacent apartments are put in series, this allows you to place utility rooms in a narrow transverse span (Fig. 6.6).
In wide buildings, the solutions of economical apartments of two-sided orientation are the most complex, since housing should not be located near the longitudinal wall in the shaded part. This space has to be given for utility rooms and their area usually exceeds the regulatory recommendations.
The architectural composition of the apartments depends on the structural design of the building. In single-span bodies, the inner supports do not restrain the freedom to choose the layout. In the two-span apartment you can easily enter modern apartments of municipal housing, if the longitudinal wall is located along the axis of the house or close to it. The solution is more difficult when the longitudinal wall is displaced by a considerable distance.
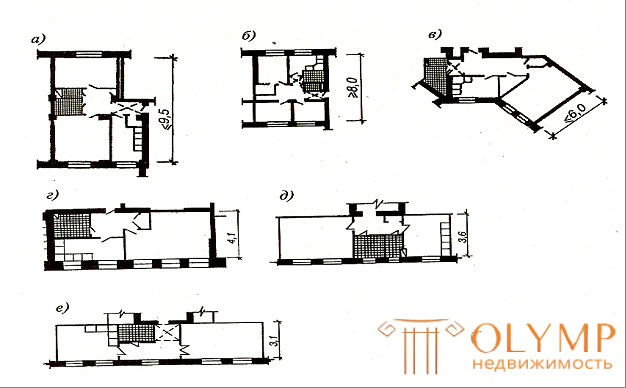
Fig. 6.6 - Examples of planning apartments in narrow buildings with a small transverse architectural and planning step
In three-span cases, the middle span is used to accommodate the back rooms of the apartment or arrange alcoves . Medium support columns are played up here, but such a solution is also possible in buildings where the longitudinal walls in which piercing of openings is acceptable are supported. Otherwise, the average span must be used for outbuildings or extra-residential communications.
Difficult solutions in buildings with internal transverse walls, carrying the load from the floors. These walls so firmly fix the existing layout that it is not possible to change it without partially disassembling them. Planning decisions are entirely dependent on the individual characteristics of the building and therefore recommendations for modernization cannot be given.
The solutions of municipal housing apartments in buildings with walls at an angle different from 90 ° C are not less complicated. In this case, some of the rooms are not rectangular and oblique corners must be masked with cabinets or other utility rooms. In such housing, hallways, kitchens are non-rectangular, and if that is not enough, then a common room. In a large room of complex configuration it is easier to arrange furniture than in a small one.
Similar problems practically do not arise at modernization under prestigious housing. This is another argument in favor of the transfer of tenement houses for pre-revolutionary construction under such housing. In this case, there are no such severe restrictions on the area of apartments and the composition of outbuildings.
The quality of the planning decision of the apartment is not made dependent on the norms. It is due to the designer’s ability to hide corners. Or on the contrary, decoratively beat them.
Bunk apartments are now quite widely represented in the prestigious domestic housing. Usually they use the experience of a two-story cottage construction and place in the first tier of a day stay room, and above them - the intimate part of the apartment. We give an example of a similar solution used in the reconstruction of the house . Presented apartment with three bedrooms. In the first tier there is a day stay zone with a living room equipped with a kitchenette and a sanitary unit with a toilet and a washbasin. The upper tier can be accessed from the hall by a spiral staircase, but another emergency exit is left - directly to the landing.
In domestic practice, there are other methods of organizing space. Apply residential cells with a developed second tier, occupying the area of two apartments at the bottom. The first tier is reserved for guest rooms: a hall, a living room with a kitchenette and a small sanitary unit with a toilet and a washbasin.
The second tier is much larger than the first. In addition to the bedrooms, there is an additional hall, a kitchen-dining room and an office, that is, rooms for the day stay of family members. It is as if a third functional zone is set aside, separated from the lower one — the guest zone (Fig. 6.7.).
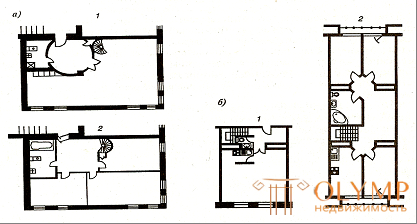
a - with three bedrooms in the upper tier, located in the dimensions of the lower; b - with a developed upper tier located above two apartments of the lower floor; 1 - the first tier ; 2 - the same, the second.
Fig. 6.7. - Bunk apartments in renovated houses
In terms of design, such solutions are somewhat more complex than the first. More massive floors are needed here, as they separate two apartments. Requires increased sound insulation, both from airborne and impact noise.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)