Finishing an apartment, office, home - a very important thing. The right choice of finishing materials will provide a solution to some of the problems that may arise later. High-quality finishing materials will allow in a shorter time to cope with the finish, rather than low-quality.
What kind of flooring has been invented lately - linoleum, carpet, corrugated flooring, raised floors, etc., etc. And yet the most attractive for apartment owners, cottages, offices remains the word "parquet" (translated from French "lath"). Miniature plates of a certain shape, carefully fitted to each other, coated with a special varnish or rubbed to a shine create a beautiful, durable, warm base in any room. Until recently, natural parquet made of various wood species did not have any serious competitors. However, having a lot of advantages, he had one major drawback - the high price.
Durable, beautiful and durable, environmentally friendly, natural material with low sound and thermal conductivity, the parquet still has a number of arguments not in its favor. The main ones are its price and the need for periodic maintenance (repolishing, varnishing, mastic, etc.). That is why material substitutes for piece parquet began to appear. The first of these was a three-layer parquet or floorboard - the essence of the name of the same flooring, cheaper and more technological than the classic piece parquet. This type of coating is completely made of natural wood and retains most of the attractive qualities of its predecessor. The dimensions of the parquet board are many times larger than the size of the slats of the piece parquet, which makes it possible to arrange the floor with much less time and money, and using the “floating” installation method, these advantages become even more tangible. The main disadvantage of this type of coating is a shorter life cycle, since the thickness of the top layer of hard wood is significantly less than that of piece parquet.
Probably, that is why about twenty years ago a fundamentally new substitute for parquet appeared - laminated flooring, laminated parquet, or simply laminate.
Most modern laminates have a four-layer design. It is based on a high-density HDF carrier. This is a plate with a thickness of 6-10 mm, having a density of 800-1100 kg / m3 (depending on the magnitude of the expected loads) and higher strength and moisture resistance compared to other wooden plates. To obtain a picture on a laminate, first a fragment of one or another kind of wood is photographed, then the image is transferred onto paper, which is impregnated with melamine resin. The decorative paper thus obtained is placed over the HDF slab and covered on top with an overlay, a durable protective film of non-woven cellulose material, which is also impregnated with melamine resin. To make the overlay more resistant to abrasion, aluminum oxide is sprayed onto its surface. A stabilizing substrate is placed below the HDF slab to compensate for the stresses created by the two upper layers. All this together is pressed on short-cycle presses at high temperature (~ 2000 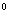 C) and under pressure of about 40 kg / cm
C) and under pressure of about 40 kg / cm 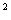 . Due to the effects of temperature and pressure, a chemical reaction occurs between melamine resin, decorative paper and the constituent elements of the HDF board, also impregnated with melamine resin. The result is a new composite material - what we call laminate. The obtained sheets of laminate are sent to the warehouse, where they must be conditioned to remove press "shocks". After exposure, the sheets are cut into panels, the dimensions of which usually lie in the range of 190-300 mm (width), 1180-2000 mm (length), and milling on the ends of the tongues and grooves (tongue and groove) necessary to connect the panels. Everything, the product is ready to be laid in apartments, offices, shops, museums, hotels, even gyms - this is not a complete list of objects where laminate is used. It turned out to be a worthy analogue of the parquet, which retained its main positive qualities - ecological cleanliness and specificity of the design, but with a lower price, enhanced durability, resistance to scratches and dents. And, importantly, it can be washed.
. Due to the effects of temperature and pressure, a chemical reaction occurs between melamine resin, decorative paper and the constituent elements of the HDF board, also impregnated with melamine resin. The result is a new composite material - what we call laminate. The obtained sheets of laminate are sent to the warehouse, where they must be conditioned to remove press "shocks". After exposure, the sheets are cut into panels, the dimensions of which usually lie in the range of 190-300 mm (width), 1180-2000 mm (length), and milling on the ends of the tongues and grooves (tongue and groove) necessary to connect the panels. Everything, the product is ready to be laid in apartments, offices, shops, museums, hotels, even gyms - this is not a complete list of objects where laminate is used. It turned out to be a worthy analogue of the parquet, which retained its main positive qualities - ecological cleanliness and specificity of the design, but with a lower price, enhanced durability, resistance to scratches and dents. And, importantly, it can be washed.
Each manufacturer has its own secrets for making laminate, but in all cases it has at least four layers:
- - protective top (durable film of special resins);
- - decorative (resin-impregnated paper with a pattern printed on it);
- - basic (carrier of high density fibreboard - HDF);
- - stabilizing lower (waxed or resin-impregnated paper).
The top coating of melamine or acrylate resin can be either single-layer or multi-layered, it can include microscopic mineral particles (corundum), it is additionally treated, for example, with electron beams, covered with a non-electrifying film on top, etc. This coating provides the laminate with such properties as resistance to abrasion, resistance to stains, chemicals, the action of sunlight, resistance to all kinds of mechanical damage.
The decorative layer stands out as an element of purely formality: when pressed, the resin of the upper layer impregnates the paper image and forms a whole with it.
The basis of most laminates is a high density fibreboard 6.7-7.7 mm thick (high density flag, abbreviated HDF). It is distinguished by high mechanical strength (in particular, fracture), water resistance (1.5–2 times higher than that of fibreboard), and also lower content of formaldehyde resins.
It is this carrier plate that provides the material with impact resistance, resistance to pressure and long-lasting loads.

By abrasion resistance (which is evaluated by testing on Taber) laminate is divided into 6 classes.
Most of the laminate on the Russian market is from Germany, including products made by Perstop Flooring AB, one of the world's first developers of laminate flooring.
The main properties of the laminate:
- abrasive resistance (abrasion resistance);
- resistance to long-term loads (pressure, collapse);
- impact resistance;
- resistance to scratches and cracks;
- immunity to stains;
- resistance to chemicals;
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation, fading (light resistance);
- heat resistance (heat resistance, resistance to the action of a burning cigarette);
- environmental Safety;
- hygiene (ease of cleaning);
- ease of installation (assembly);
- thermal conductivity (the possibility of laying on a heated floor).
The main disadvantage of the vast majority of floor coverings, including laminate, is water fear.
The most important quality criterion, of course, is the wear resistance of the material. Any type of laminate was originally designed for certain operating conditions, the intensity of the load. Each meets the requirements of its class. Three "lower" classes - 21, 22, 23 - designed for "moving a small number of people." They are desirable to use only in the residential sector. The three "higher" classes - 31, 32, 33 - include laminated coatings that can withstand loads in public areas with different "attendance", these are the so-called "commercial laminates."
Although most of the drawings of laminated floors imitate precious woods, there is a laminate “under the stone” - marble, granite. It can also mimic metal and dyed surfaces. Recently a laminate with “fantastic motifs”, ornaments and even with the image of some objects has come into fashion. Plates of laminate "under the tree" are usually long, like boards. Large squares are most often used for laminates with "stone" and "metal" decor, and small ones - for ornaments and other decorative elements. Plates of different shapes when laying easy to combine.

Laying laminate flooring is quite simple. The main thing to remember is that it should not be glued to the floor. The laminate is assembled in the so-called “floating way”: the plates are fastened according to the principle “spike into the groove”. For a long time, two requirements were mandatory: the use of a special proprietary adhesive for gluing the ends of the plates and the use of a “substrate” of corrugated cardboard or cork for leveling the surface under the laminate and for the floor not to be “echoing”.
Now there are collections of laminate glue-free bundles with locking connection. Their volumes are increasing. The company ALLOC, for example, uses a lock of aluminum, it is installed on a heavy-duty laminate Fibo-Trespo. Another lock, Fiboloc is cut in the middle of the fiber of high-pressure laminate. Laminated boards are joined by snapping their edges into one another. The design of the lock allows you to quickly and firmly connect the boards to each other. As for the substrate, a series of Witex Silit Comfort laminates recently appeared, in which the substrate is already included in the coating structure. Laminate flooring confidently took up a position among the floor coverings (in Europe - 8% of sales), displacing linoleum and carpeting. And there is no doubt that his popularity will grow.

Laminate flooring floating on a rough floor of any solid material (concrete, chipboard, wood, tile, etc., but the heavy carpet is better to remove). That is, the panels are not attached to the base of the floor, but are connected to each other along the end. This type of installation implies the unquestioning observance of two basic rules. The first is that between the laminate and fixed objects (walls, door thresholds, pipes, fireplaces, etc.), as well as when moving from one coating to another (for example, from tile to laminate), it is necessary to leave gaps. Their value is calculated based on the fact that the expansion of the laminate is about 2 mm per 1 m length. We are talking about the natural "movement" of wood and materials from it, which occurs when temperature and humidity fluctuate. At high humidity (more than 70%), wood fiber particles swell and the laminate expands, at low humidity (less than 40% - in our apartments during the heating season it is extremely small) in combination with high temperature, the floors, on the contrary, shrink and dry out. And the second rule: in doorways, as well as if the floor has a length of more than 10-12 m and a width of more than 8 m, it is necessary to arrange expansion joints (or transitional thresholds, which is one and the same). They are necessary for the same natural "life" of wood coatings. The seams are easy to disguise with special expansion profiles in the color of the coating, only they need to be fixed not to the laminate, but to the base of the floor.
The base under the laminate should be flat (the maximum allowable level drop is ± 1-3 mm per 1 m, more significant differences must be eliminated before laying, using special mixtures or leveling plates), solid, dry (maximum - 60% humidity at 18 ° C) and clean. Before installing the coating on the cement floor or the surface of ceramic tiles should put steam vapor-proof layer - plastic film about 0.2 mm thick, film joints with an overlap of 20 cm at the joints. If the noise absorbing substrate is not included, be sure to purchase it additionally. This layer will dampen the noise of steps, as well as level minor irregularities. The substrate can serve as polyethylene, cork, wool-felt cardboard, as well as "professional" materials.
Laminate, especially in the cold season, is better to bring a couple of days before laying - it must “settle”, acclimatize, get used to the temperature and humidity in the room. It is better to store it during this time in the closed packing. As a rule, 5-10% is added to the required amount for possible trimming.
The slats are placed in the direction of the light falling from the window - with this arrangement, the joints between the panels are less noticeable. In long narrow corridors they are usually recommended to be mounted perpendicular to the length of the room, regardless of the direction of light, for visual expansion of the space. The minimum allowable distance between joints in adjacent rows is 200 mm. It is necessary, first of all, to increase the strength of the connection of the panels, as well as for decorative reasons. As a rule, baseboards set 15 minutes after the end of the main work. They are usually attached to clips or screws, but not to the laminate, but to the wall. By color, baseboards can be combined with flooring or with doors.

For many manufacturers, the joints or even the entire slab in the manufacture is impregnated with waterproof compounds. Edges, for example, are usually waxed. In cheap collections, the joints can be further coated with a water-repellent gel (for example, from the German manufacturer CLICKGUARD). It seals and seals the seams of precisely glue-free joints, protecting the material from moisture and preventing its swelling.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)