Other times, different morals - says the proverb. Including the construction with the arrival of the XXI century, the requirements for the quality of housing being built have changed. The 2009 Federal Law “On Energy Saving and Energy Efficiency Improvement ...” dramatically changed the rules of the game in all sectors of the economy and directly affected the construction industry, regulating it with strict energy efficiency standards for buildings being built. New standards do not allow the construction of heated, but not warmed buildings.
In order to meet modern construction requirements and in accordance with new energy efficiency standards, all newly erected heated structures should be well insulated.

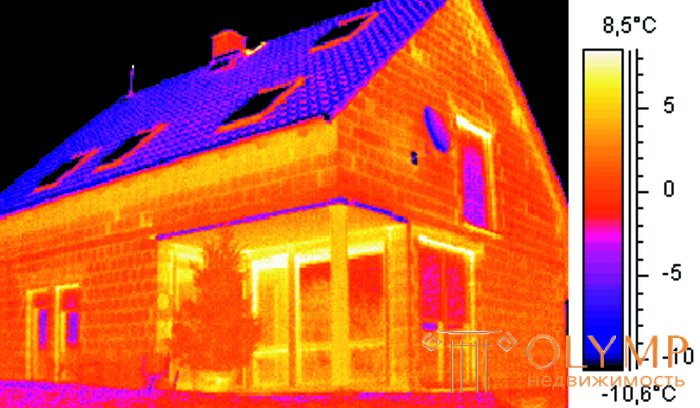
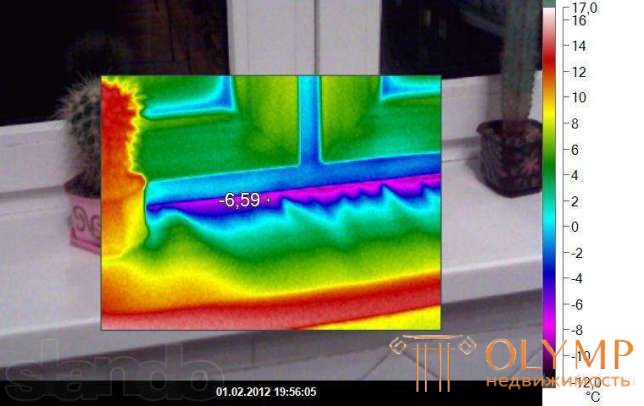
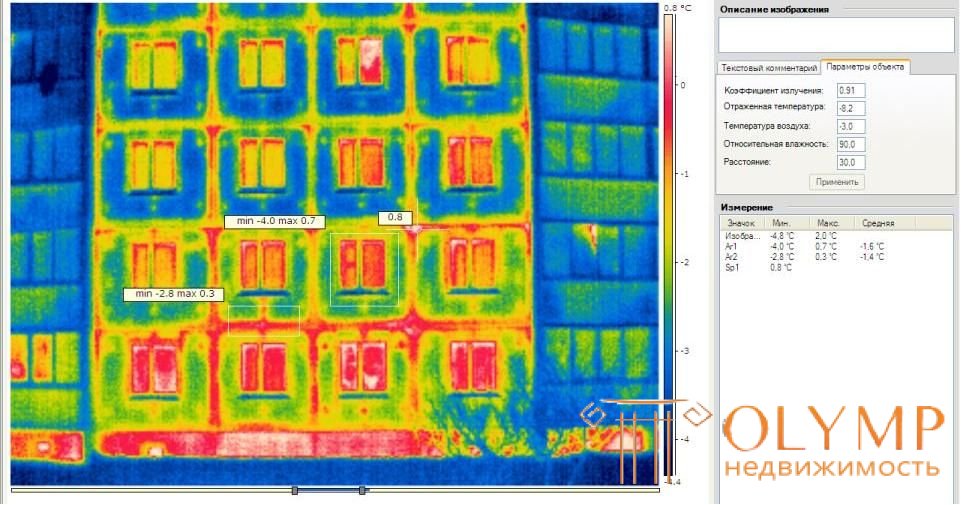
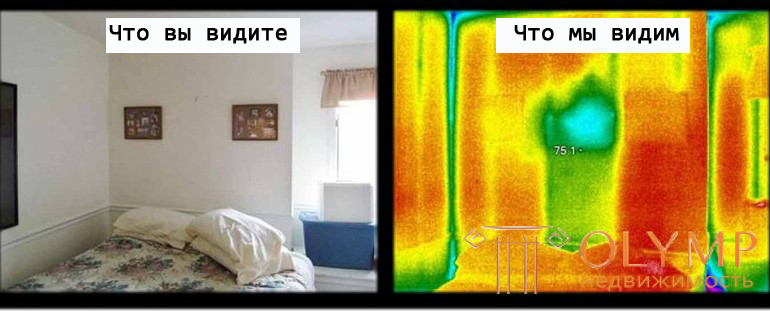
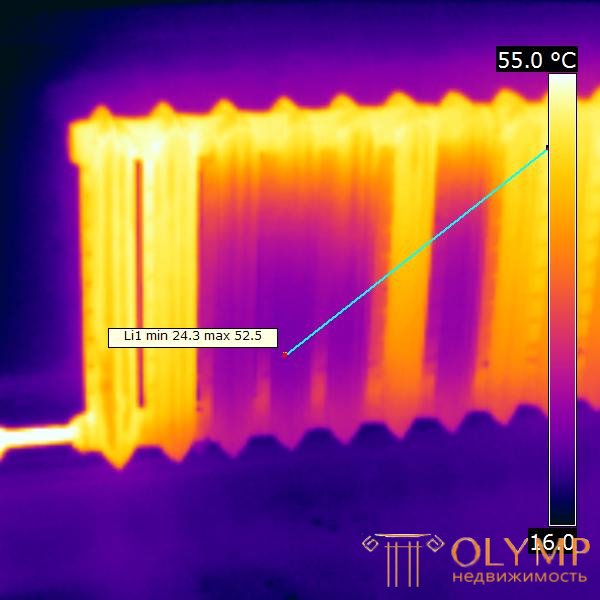
The heat loss of a building is often invisible to the naked eye. Their appearance is due to such reasons as improper operation of heating devices and the structural features of the building and their defects. Excessive heat losses are manifested in increased costs for heating, and often many do not even know about it. Heat loss can be detected using thermal imaging diagnostics. It is this kind of diagnostics that will provide reliable information about the thermal condition of a building or structure.
Thermal imaging is a modern method that allows you to get accurate information about the condition of the building envelope at the time of the diagnosis. In the thermal imaging diagnostics of buildings and structures, a special measuring device is used - a thermal imager. It allows you to monitor the temperature distribution of the surface, which is investigated, in the infrared range. Hot and cold areas are indicated by different colors on the thermogram. Using this data, you can identify places with temperature anomalies. During the thermal imaging diagnostics of buildings, windows, walls, ceilings, underfloor heating, interfloor ceilings, entrance and balcony doors, heating systems are checked and heat loss is examined.

Thermal imaging diagnostics of buildings and structures allows you to:
Thermal imaging diagnostics of residential objects provides monitoring of the condition of the heating equipment and monitoring the construction work. Such inspections of buildings are safe, they save on maintenance, are carried out without de-energizing the equipment in use and without dismantling the structure of the structure. Thermal imaging diagnostics of a residential facility is carried out only in the cold season with good lighting and the absence of foreign objects in the corners, on the floor, and window sills. The temperature difference between the room and the street should be more than 15 degrees Celsius. Only under such conditions it is possible to conduct high-quality thermovision diagnostics.


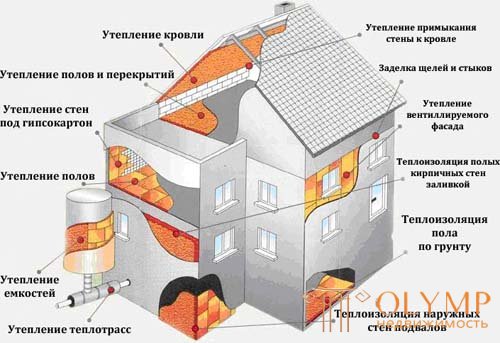
The task and purpose of thermal insulation:
reduce heat loss in winter, reduce heating of buildings in summer;
protect bearing structures from aggressive environmental influences;
reduce the harmful effects of severe temperature drops and their direct consequence - deformation of the power elements, which objectively increases the life of the building as a whole;
Heat insulation materials.
Thermal insulation materials are divided by type of feedstock into organic, inorganic and mixed. The most common insulation, organic and inorganic, with comparable densities are in the same price segment.
Inorganic insulation - various mineral wool and slabs of them (for example, stone wool), expanded perlite, verimiculite, mineral wool (glass wool), aerated concrete, etc.
Inorganic fiber insulation, perhaps the most popular in construction. Their qualities such as high fire resistance and good vapor permeability are valuable, while the air between the fibers is in a static state, which prevents convective heat transfer and makes them good heat insulators.
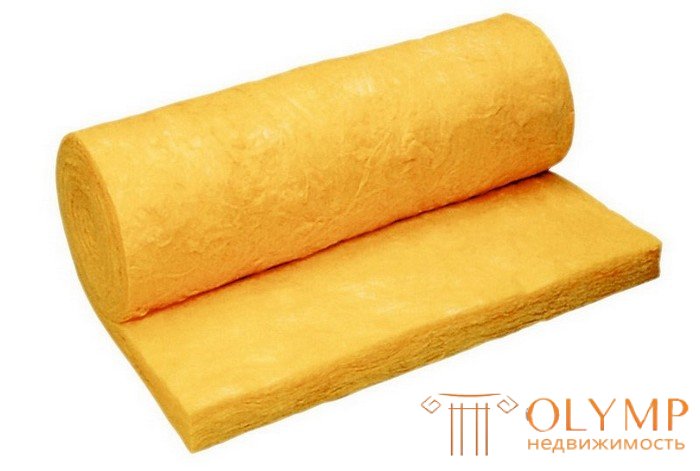 Mineral wool (glass wool) is a good, time-tested insulation, with a thermal conductivity of between 0.035 and 0.045 W / mK, according to this indicator is one of the best thermal insulation materials. Insulation of mineral origin, used for thermal, sound and fire insulation in construction, industry and shipbuilding. Mineral wool is the most popular material on the market, widely used for thermal insulation of houses and structures. Non-flammable, with good dielectric properties and excellent vapor permeability.
Mineral wool (glass wool) is a good, time-tested insulation, with a thermal conductivity of between 0.035 and 0.045 W / mK, according to this indicator is one of the best thermal insulation materials. Insulation of mineral origin, used for thermal, sound and fire insulation in construction, industry and shipbuilding. Mineral wool is the most popular material on the market, widely used for thermal insulation of houses and structures. Non-flammable, with good dielectric properties and excellent vapor permeability.

Of the shortcomings (about strength - which is not, that is not), we can note the hygroscopicity. Mineral wool insulators, without a capillary structure, are themselves afraid of moisture. This is a common shortcoming of all mineral wool insulants. In order to reduce it, manufacturers are hydrophobic fiber. With the passage of time, mineral wool shrinks, especially in vertical structures of buildings, to eliminate this negative effect, mineral wool insulation with a density of 120 kg / m3 and higher is used for walls. Another significant drawback of insulation based on mineral wool is not resistance to rodents, which arrange moves and holes in almost all structures of the building, where there is a mineral wool.
 Stone wool , a vapor-permeable material, its resistance to fire (up to 1000 ° C) is highly valued. Resistant to aging - decay and to the effects of microorganisms and insects. It is used in all external structures of buildings as thermal protection, and in partitions it serves as a sound insulator. The only place where it is not recommended to use is the insulation of the walls of basements and basements. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of stone wool in the interval from 0.035 to 0.039 W / mK. At the same time, large variations in density from 30 kg / m³ to 250 kg / m³ make it possible to use high-density modifications where there are large distributed loads, for example, for sound-thermal insulation of floors.
Stone wool , a vapor-permeable material, its resistance to fire (up to 1000 ° C) is highly valued. Resistant to aging - decay and to the effects of microorganisms and insects. It is used in all external structures of buildings as thermal protection, and in partitions it serves as a sound insulator. The only place where it is not recommended to use is the insulation of the walls of basements and basements. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of stone wool in the interval from 0.035 to 0.039 W / mK. At the same time, large variations in density from 30 kg / m³ to 250 kg / m³ make it possible to use high-density modifications where there are large distributed loads, for example, for sound-thermal insulation of floors.

A significant disadvantage of insulants based on stone wool as well as glass wool is not resistance to the effects of mice and rats, which in it fundamentally substantiate their homes.
 In addition to mineral and glass wool, organic heaters such as polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam are in great demand. Due to the low thermal conductivity coefficient from 0.035 to 0.040 W / mK, low cost and ease of installation, these heaters are one of the most practical insulation materials in our market. They are used for thermal insulation of external walls of buildings, for warming floors in basements, ground floors and floor slabs under a cement-sand screed.
In addition to mineral and glass wool, organic heaters such as polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam are in great demand. Due to the low thermal conductivity coefficient from 0.035 to 0.040 W / mK, low cost and ease of installation, these heaters are one of the most practical insulation materials in our market. They are used for thermal insulation of external walls of buildings, for warming floors in basements, ground floors and floor slabs under a cement-sand screed.
 The main disadvantages are fire hazard and the combustion products are highly toxic, a vapor insulator, which also needs to be taken into account, especially when weathe wood houses.
The main disadvantages are fire hazard and the combustion products are highly toxic, a vapor insulator, which also needs to be taken into account, especially when weathe wood houses.
The main direction of using polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam is the insulation of the walls of basements, ground floors, insulation of floors on the ground, insulation of windows and surrounding areas.

Also a significant drawback of the foam (including extruded polystyrene foam) is the instability to the effects of mice and rats. Even being plastered, the foam remains defenseless in front of rodents, in which they make many moves and holes, thereby destroying the heat-insulating layer of the building.
 Polyurethane foam is also widely used in construction, and, above all, for insulation and repair of roofs. It has even better thermal insulation properties than expanded polystyrene and mineral wool. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material in the range from 0.020 to 0.035 W / mK. Polyurethane foam has a low vapor permeability, which relates it to waterproofing, and this is one of the major drawbacks in the insulation of wooden structures. Resistant to moisture and temperature extremes.
Polyurethane foam is also widely used in construction, and, above all, for insulation and repair of roofs. It has even better thermal insulation properties than expanded polystyrene and mineral wool. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material in the range from 0.020 to 0.035 W / mK. Polyurethane foam has a low vapor permeability, which relates it to waterproofing, and this is one of the major drawbacks in the insulation of wooden structures. Resistant to moisture and temperature extremes.
 It is flammable, when burning emits toxic gases, which also does not contribute to the expansion of its scope. The technology of building insulation using PPU is quite complex and if the technological modes of equipment are not followed, there is a high probability to obtain low-quality material with great shrinkage, especially with regard to insulation of closed cavities where it is extremely difficult to control the process of filling PUF.
It is flammable, when burning emits toxic gases, which also does not contribute to the expansion of its scope. The technology of building insulation using PPU is quite complex and if the technological modes of equipment are not followed, there is a high probability to obtain low-quality material with great shrinkage, especially with regard to insulation of closed cavities where it is extremely difficult to control the process of filling PUF.
But the main reason preventing its widespread use is the high cost, much higher than the price of mineral wool and polystyrene insulators.
Polyurethane is produced directly on the construction site in the form of foam and is applied to the treated surfaces and closed cavities with the help of special equipment. High adhesion coefficient, solidity and high strength of the resulting product make it indispensable for objects with special requirements for insulation.
In everyday life and in construction, for minor repairs and thermal insulation works, its one-component modification is widely used, the so-called assembly foam hardening in the air, in the form of cans with a frother.
 Penoizol is a type of carbamide foam. It is produced at the construction site directly at the object of insulation, and in a liquid form under pressure is pumped into the cavity of walls and floors. That allows you to achieve better results than the insulation of traditional insulating materials, as Penoizol penetrates into all cavities, voids, cracks, creating an effective heat-insulating layer.
Penoizol is a type of carbamide foam. It is produced at the construction site directly at the object of insulation, and in a liquid form under pressure is pumped into the cavity of walls and floors. That allows you to achieve better results than the insulation of traditional insulating materials, as Penoizol penetrates into all cavities, voids, cracks, creating an effective heat-insulating layer.
 It has a group of flammability G2, at a temperature above 200 ° C it is charred, but it does not support combustion and does not emit toxins, in contrast to expanded polystyrene. Rodents do not live in penoizole, which cannot be said about foam and mineral wool, in which mice are arranged like at home.
It has a group of flammability G2, at a temperature above 200 ° C it is charred, but it does not support combustion and does not emit toxins, in contrast to expanded polystyrene. Rodents do not live in penoizole, which cannot be said about foam and mineral wool, in which mice are arranged like at home.
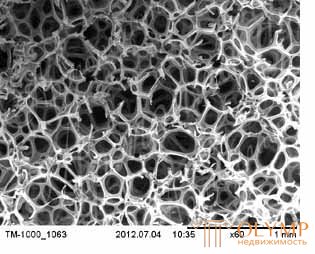
Penoizol " breathing " non-combustible insulation, having a capillary microstructure (dimension 20-30 microns). This feature makes it one of the best heat insulators for wooden buildings and allows you to use it as a heater for wooden houses and structures without restrictions, without fear of the appearance of mold. The basis of the process of moisture transfer inside Penoizol is a capillary structure that effectively pumps moisture through its thickness towards lower partial vapor pressures. At the same time, the capillary structure of penoizol does not allow it to be used for warming those parts of buildings and structures where insulation will get in contact with the ground (for example, the underground part of foundations, screed over the ground), moisture will flow into the material, impairing its thermal insulation properties.
 Due to the fact that penoizol is produced directly at the facility, the material initially turns out to be wet (the water content in the fresh material is up to 300%) and subsequently dries out in the warmed cavities of the building. In the cavity of brick and concrete buildings, penoizol is poured under high pressure, which eliminates the appearance of material shrinkage during the drying process (for 2–3 weeks).
Due to the fact that penoizol is produced directly at the facility, the material initially turns out to be wet (the water content in the fresh material is up to 300%) and subsequently dries out in the warmed cavities of the building. In the cavity of brick and concrete buildings, penoizol is poured under high pressure, which eliminates the appearance of material shrinkage during the drying process (for 2–3 weeks).
When warming the same frame structures, curtain walls and open surfaces (attics, floors), where it is impossible to create a lot of pressure in the wall during pouring, the material is subject to shrinkage (up to 1%) during drying and finishing strength.
For successful struggle with shrinkage in frame structures, specialists of Armoplast company use a set of measures:
- obligatory micro and macro reinforcement of penoizol in frame buildings and open castings
- fast drying of the material is unacceptable, since Penoizol during fast drying does not have enough time to polymerize and gain sufficient strength, which leads to a high percentage of material shrinkage (penoizol must be between vapor barrier and windproof vapor transparent membranes and dry within 2-4 weeks)
- Mandatory use of "correct" components, the so-called " foam - insulated " resin of VPSG and Mettemplast technology.
Thus, observing simple technological requirements, insulating frame and wooden buildings with Penoizol on resins specially designed for it, applying material reinforcement , pumping Penoizol under waterproofing and windproof membranes (this requirement is also necessary for insulation based on mineral wool and eco-wool), this is a negative phenomenon as the shrinkage is completely eliminated, thus obtained fine seamless monolithic thermal insulating layer is further coupled over the entire volume reinforcing mineral in Loknya exclusive shrinkage during the lifetime of the material.



Penoizol allows you to gently zapenivat cavity, enveloping all the elements of structures lying on the path. The thermal resistance coefficient of penoizol is from 0.030 to 0.035 W / mK, which is better than that of mineral wool and polystyrene insulators and allows to obtain less heat loss through the enclosing structures with all other conditions being equal.
 Ecowool is a loose, lightweight cellulose fiber produced from waste paper (80 % ) with antiseptic and flame retardant additives (up to 20 % ). Environmentally friendly material, because the basis of cellulose. It is very practical (compact) in transportation, since manufacturers form it into tightly packed briquettes (300 kg / m³), and at the facility with the help of special equipment they fluff it up to the required density.
Ecowool is a loose, lightweight cellulose fiber produced from waste paper (80 % ) with antiseptic and flame retardant additives (up to 20 % ). Environmentally friendly material, because the basis of cellulose. It is very practical (compact) in transportation, since manufacturers form it into tightly packed briquettes (300 kg / m³), and at the facility with the help of special equipment they fluff it up to the required density.
Two basic ways of laying are applied: dry, with the help of blower installations, and wet laying. In both cases, fluffed-in insulation in a special bunker with air flow is blown into insulated cavities, where it is evenly distributed, penetrating into all voids. This method as well as pouring penoizol under pressure allows repairing or restoring thermal insulation layers without complete disassembly of the facade.
The wet method differs only in the fact that cotton is additionally wetted with water or a solution of water with glue at the moment of blowing.
 When wooded with ecowool density below 50kg / m3, the material has significant shrinkage, especially in vertical structures.
When wooded with ecowool density below 50kg / m3, the material has significant shrinkage, especially in vertical structures.
Eco-wool characteristics:
insulation and noise insulator - with density from 30 to 75 kg / m³, with low air permeability;
thermal conductivity - 0.032-0.041 W / mK - an indicator, as in the best heaters;
The combustibility group - G2 - is the same as that of penoizol, but unlike it, ecowool is moderately flammable (the flame is suppressed by the fire retardants present in its composition).
The material is characterized by good moisture permeability, it easily accumulates and releases moisture in accordance with changes in environmental humidity.
The advantages of this heater certainly can be attributed to the high speed of installation, and the dry method of work on insulation can be conducted in the winter.
 Foam glass . As a heater, it possesses a set of such valuable in construction qualities as strength, rigidity, non-hygroscopicity, does not burn, with high thermal (450 ° C - the beginning of deformation) and chemical resistance. In addition, it is easy to saw - a very valuable property on the construction site. Foamed glass, natural material - this is 100% ordinary glass, however, foamed using a special technology. Hence its chemical and thermal resistance.
Foam glass . As a heater, it possesses a set of such valuable in construction qualities as strength, rigidity, non-hygroscopicity, does not burn, with high thermal (450 ° C - the beginning of deformation) and chemical resistance. In addition, it is easy to saw - a very valuable property on the construction site. Foamed glass, natural material - this is 100% ordinary glass, however, foamed using a special technology. Hence its chemical and thermal resistance.
The structure of the glass foam is similar to pumice stone, with the same closed cellular structure, high surface adhesion (well glued), with zero wind and vapor permeability. In construction, as insulation, it has been used for more than half a century, and the studies conducted on samples of the 1950s did not reveal any significant changes in appearance (destruction), and the insulating properties deteriorated only by a few percent. Гомельский стекольный завод, единственный производитель теплоизолятора на постсоветском пространстве, гарантирует 100 летнюю эксплуатацию.
Из положительных характеристик хотелось бы отметить, стабильность размеров утеплителя, с коэффициентом расширения близким к коэффициентам расширения основных строительных материалов, таких как бетон, металлы.
Основных недостатков два: непаропроницаемый утеплитель, характеристика, противоречащая современной строительной философии «стены и потолки должны дышать», то есть автоматически удалять накопившуюся влагу в окружающую среду. Второй и наверное главный, высокая стоимость, что переводит его, учитывая уникальные характеристики, в разряд специальных.
Пеностекло получило широкое распространение как термоизолятор промышленных печей, дымовых труб, в пищевой, химической и атомной промышленности. Широко применяется в строительстве значимых общественных зданий в основном для термоизоляции крыш, утепления гостиниц, спортивных сооружений. Там где востребованы его уникальные прочностные, термические, гигроскопические, пожаробезопасные и санитарно-гигеенические качества.
На рынке теплоизоляционных материалов под видом «экологически чистых» анонсируются и другие утеплители, иногда достаточно экзотические, в основе своей содержащие целлюлозу, глину, перлит, вермикулит, камыш, лён, солому, овечью шерсть, кизяк и другие. У них достаточно высокий коэффициент теплопроводности по сравнению с вышеописанными утеплителями, поэтому дома нуждаются в более толстом слое теплоизолятора. Большинство таких, для нас экзотических утеплителей, используется локально в разных странах мира, в соответствии с наличием источников сырья и сложившимися традициями строительства.
Утепление дома «экологически чистыми» материалами.
К сожалению, не редко под видом «экологически чистых» материалов рекламируются неэффективные, непроверенные, нестойкие утеплители или утеплители вчерашнего дня. По сути это недобросовестная эксплуатация модного тренда.
Для достижения хорошего уровня теплоизоляции внешних стен, рекомендуется использовать величину коэффициента теплопередачи равную U = 0,35 Вт / м 2 К. Это равносильно в среднем 10 см слою минеральной ваты (280 кН / м 2 ) или 9 см слою пенополистирола (220 кН / м 2).
Чем ниже коэффициент теплопроводности утеплителя, тем качественней теплоизоляция.
Это определение совершенно не корректно при выборе утеплителя.
For proper choice of insulation and the method of insulation it is necessary to have a good knowledge of physical and chemical properties, to know the advantages, disadvantages and limitations in the use of one or another type of insulation. Ideal insulation is a thermos, in reality this does not exist. A good heat insulator is always a compromise between the desired and the available set of properties, price and quality.
When choosing a heat-insulating material, in addition to thermal conductivity, the complex takes into account other quality characteristics, such as: fire resistance, water vapor diffusion coefficient, durability, resistance to moisture, and microorganisms. Where it will be used, in what conditions to work, how to interact with structural elements, what enclosing structures will be applied, where and what cold bridges are expected and much more. The heat loss of a house depends not only on the heat transfer coefficient of the insulation, but also on the architecture of the building, the composition and properties of its structures.
 To insulate different parts of the house, you need to choose a heater that is optimal for these operating conditions. For example, it is better to warm the foundation with extruded polystyrene, despite its high fire risk. Buried in the ground, it will not catch fire, and the rest of its properties are best suited for basement insulation. It is better to make external insulation of walls and ceilings of log houses at Penoizol as the most suitable for wooden housing construction and having the best price-performance ratio.
To insulate different parts of the house, you need to choose a heater that is optimal for these operating conditions. For example, it is better to warm the foundation with extruded polystyrene, despite its high fire risk. Buried in the ground, it will not catch fire, and the rest of its properties are best suited for basement insulation. It is better to make external insulation of walls and ceilings of log houses at Penoizol as the most suitable for wooden housing construction and having the best price-performance ratio.
Knowledge of the thermophysical properties of building materials, their interaction, including insulation, is one of the necessary conditions for competent design and construction of energy-efficient buildings.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)