
The facade of the building is exposed to the most intense impact of atmospheric precipitation and is the first to take on all the “climatic shocks: increased humidity, temperature changes, exposure to wind, frost, heat.
One of the most promising methods to solve these problems for any region, reducing heat loss and giving the building a beautiful and original look that has persisted for many years, is building a ventilated facade design using wall cladding materials and additional insulation.
Such a facade combines quick installation, high quality thermal protection, durability, attractive appearance. There is no need to repair the old wall, and in case of damage to the individual panels, they are easily replaced. It is also important the absence of wet processes, which allows you to work at any time of the year.
Ventilated facades are known in Russia relatively recently. But in a number of countries (for example, in Germany, Finland), sufficient experience has been accumulated in their use: in public, administrative and industrial buildings, as well as in the reconstruction of houses of mass development.
The concept of ventilated facade originated in Germany. Having just appeared in Russia, ventilated facades immediately gained popularity, both among architects, builders, and among customers. And there are reasons for this.
The hinged facade is a structure consisting of cladding materials (plates or sheet materials) and a substructure, which, in turn, is attached to the wall so that there is an air gap between the protective and decorative coating and the wall. For additional insulation of external structures between the wall and the lining can be installed insulating layer - in this case, the ventilation gap is left between the lining and insulation. Typically, cladding materials, for construction and thermal insulation, are produced by different companies, although they can work in close contact with each other and recommend customers materials from their partners or even purchase components from them.
Auxiliary elements of the systems of ventilated facades include:
- sealing tape between the panel and the profile of the facing structure;
- decorative corners and inserts for closing the ends and gaps between the panels;
- perforated metal structures for ventilation of the system from below and above: rivets, cleats, dies, etc. for fastening the panels to the profiles.
The facing construction can be mounted both on the carrier and on the self-supporting (in the frame version) wall made of various materials (concrete, brick). Ventilated facades are used not only in new construction, but also in the reconstruction of old buildings (Fig. 14.1.).

Fig. 14.1. - The design of the hinged ventilated facade
The use of mounted structures allows, on the one hand, to “dress” the facade in modern finishing materials, and on the other, to improve the thermal performance of the enclosing structure and protect it from harmful precipitation.
In the ventilated facade, the individual layers of the structure are arranged as follows:
- enclosing wall;
- heat insulation;
- air gap;
- protective screen.
Such a scheme is optimal, since the layers of various materials are arranged as their heat transfer indices decrease, and the vapor permeability resistance increases from the outside to the inside.
Another advantage of outdoor insulation is an increase in the heat storage capacity of the wall array. Thus, according to the data of the TsNIIEP dwelling, if the heat supply source is disconnected during external insulation, the brick wall will cool down 6 times slower than with the inner layer of thermal insulation of the same thickness. Installing insulation outside also reduces the cost of repairing damaged walls.
The combined use of the hinged facade and the heat-insulating layer significantly increases the sound insulation characteristics of the building envelope, as the facade panels and heat insulation have sound-absorbing properties in a wide frequency range (for example, the sound insulation of a lightweight concrete wall increases by 2 times when the hinged facade is installed using finishing panels) (Fig .14.2.).
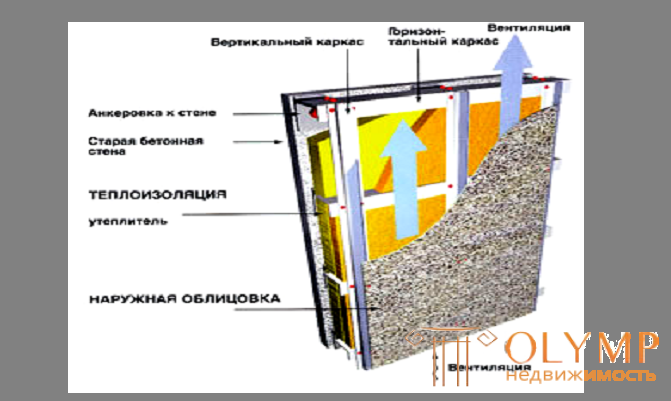
Fig. 14.2. - Ventilated facade design
The presence of an air gap in a ventilated facade makes it fundamentally different from other types of facades, since due to the pressure drop this gap works according to the “principle of the exhaust pipe”. As a result, atmospheric and internal moisture is removed from the enclosing structure. Vented air gap also reduces heat loss, as it is practically a temperature buffer. The air in it is about three degrees higher than outside.
When designing the facade structures with a ventilation gap, special attention should be paid to the possibility of free air circulation. For tall buildings, it is necessary to calculate the air circulation in the air gap in such a way as to maintain a balance that ensures an unimpeded and efficient air flow over the entire inner surface of the wall.
The outer screen of finishing materials protects the thermal insulation layer located behind it, as well as the enclosing structure, from weathering. In summer, it performs the function of a sunscreen, reflecting a significant portion of the heat flux falling on it.
Thanks to a specially designed installation scheme of the ventilated facade to the wall, the structure has the ability to absorb thermal deformations that occur during daily and seasonal temperature changes. This avoids internal stresses in the lining material and the supporting structure, which eliminates the appearance of cracks and the destruction of the lining.
To ensure fire safety, the system of hinged facades includes materials and products classified as difficult-to-fire or fireproof, preventing the spread of fire.
You can highlight the main advantages of ventilated facades:
- ample opportunities for the use of modern facade finishing materials;
- high heat and sound insulation;
- ventilation of internal layers - removal of atmospheric moisture and moisture formed due to diffusion of water vapor from the inside;
- protection of the wall and thermal insulation against weathering;
- non-leveling of thermal deformations;
- the lack of special requirements for the surface of the bearing wall (the system itself hinged ventilated facade allows you to align defects and surface irregularities, which is often difficult and expensive to do with plaster);
- long maintenance-free period (25-50 years depending on the material used).
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)