Clay mortars are used for plastering dry premises, structures made of stone, brick, wood, and adobe. Prepare them like this. Clay put in a container. Pour water there, knead the clay and leave it for a day. After a day, knead again and mix until smooth, adding water to a creamy consistency. After this solution is filtered through a sieve. Sand is added to the resulting clay mass in small portions and mixed until homogeneous. The amount of sand depends on the fat content of the clay. For strength, lime mortar is added to clay solutions. These solutions can be used for several days. In the case of thickening they add water and mix everything.
Each subsequent layer of the solution is applied only to a sufficiently hardened previous one. These solutions harden slowly. In order for the applied layers of the solution to thicken and dry before applying the following layers, a large work front is necessary.
Lime mortars are used for plastering stone walls and ceilings with the exception of cornices, socles, parapets. In wet rooms, these solutions are not used. Lime mortars harden faster than clay ones, but for plastering, they also blow a large range of work, especially when they plaster wooden and other surfaces that weakly absorb water from the solution. On brick surfaces due to the rapid absorption of moisture from the solution, hardening occurs faster and the front of work is reduced accordingly. Hardening lime mortar is easy to determine by how white they are.
Lime mortars have a small strength - up to 0.4 MPa. They grab slowly, so they can be cooked in large portions and stored for several days. However, from long-term storage, they lose their plasticity, and they have to add a binder.
The solutions are prepared as follows. The box is drained (liquid) or put (thick) lime paste, filtered through a sieve. Add sifted sand in small portions and mix everything. The operations are repeated until a homogeneous solution of the required fat content is obtained. For homogeneity, the solution is filtered through a sieve. The thick solution is diluted with water. Lime mortar for making lime-gypsum mortar is made thicker.
Lime-gypsum solutions are intended for plastering wooden surfaces of non-moistened premises, as well as stone, fiber-filled, reed and solomite surfaces. Eaves are well drawn from this solution. Lime-gypsum solutions quickly set, so when working with them does not require a large front of work.
Lime-gypsum solutions (zavodki) prepared in small portions (no more than 5 liters), so that they can be used in a matter within a few minutes. The grasping solution cannot be mixed, since in this case it loses its ability to harden and does not acquire strength.
To prepare a portion of the solution, water is poured into the mortar box, gypsum is poured there with a thin layer and everything is quickly mixed until a gypsum creamy dough is formed. Then: remove the lime mortar, mix it again quickly and use right there in the business.
Cement-lime mortars (mixed) are used for plastering external walls, wetted parts of buildings, as well as baths, wet rooms, socles, etc. These solutions slowly set. Apply them in thin layers, so they can be prepared in large portions. Cement-lime mortars are used in the case for an hour, i.e. before the cement sets. These solutions are more plastic than cement, they are more convenient to work with, they are easily leveled with a thin layer and less cement is stratified.
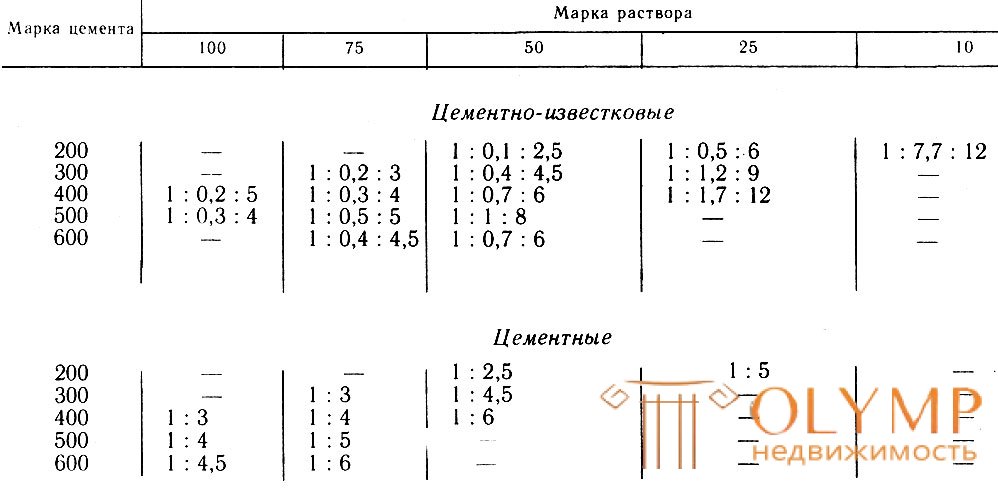
The composition of cement-lime mortars (cement: lime paste: sand) in bulk parts: 1: 1: 6; 1: 2: 8; 1: 2: 9; 1: 2: 11; 1: 3: 12 and 1: 3: 15. The brand of mortar depends on the brand of cement (Table 2).

Table 2. Compositions of cement-lime and cement mortars
Solutions are prepared in different ways. In one case, the dry mix is first made of cement and sand, the right amount of lime dough and water is measured, everything is mixed, milk of lime is obtained, which is filtered through a sieve, and the cement mixture is closed on this lime milk. In another case, a lime mortar is prepared from lime dough and sand. Cement is added to this solution and mixed. If necessary, add water. You can also mix the cement with water, add the obtained cement milk to the lime mortar and mix everything up to complete homogeneity.
Cement mortars are used in wet places. They plaster the lower parts of the foundations in a humid environment, plinths, exterior walls of buildings. These solutions are used for the device insulation layer with the addition of waterproof additives. Cement mortars are durable, but tough, slowly set. To perform work with cement mortars requires a significant scope of work. Solutions used in the case no later than an hour after preparation.
The compositions of the solutions are used from 1: 1 to 1: 6, i.e., from 1 to 6 parts of sand are taken for one volume part of cement. Solutions in the ratio from 1: 4 and more are quite tough, and it is inconvenient to apply them. In plastering, mortar compositions up to 1: 3 are most often used. They are more plastic, well applied and leveled, but more cement is required.
Solutions are prepared as follows. Doze out the cement and sand, mix them up and sift through a sieve. Prepared dry mixture shut with water. The compositions and brands of cement-lime and cement mortars are given in table. 2
Solutions on ground quicklime-kettle are used for the same purposes as lime-dough solutions. The prepared solution is kept for 30-40 minutes and only then applied to the surface - this makes it easier to level and grout.
Solutions from dry mixes are prepared as follows: 1 wt. including Portland cement, 2 fine dried river sand and 0.1 lime powder are mixed with water and used for covering the layer of cement mortar, doing rusting at the joints of reinforced concrete flooring of floors and floor panels, staircases, etc. The strength of this solution compression 5 MPa, the thickness of the applied layers is not more than 5 mm, the covering is not more than 2 mm.
General requirements . All materials for solution preparation are sieved through a sieve. Ready solutions are filtered. When this large particles remain on the sieve and the solution is further mixed, which improves its uniformity. Solutions for spray and soil filter through a grid with cells of 3 x 3 mm; Nakryvochnyh layers in conventional plaster - additionally through a sieve with cells of 1.5x1.5 mm.
Slurry solutions should be stronger than for the soil, as the spray holds the entire thickness of the plaster. For coatings, the solution used is less durable than for the primer.
Clay and lime solutions should have a normal fat content. Lean solutions, in which the aggregate (sand) is abundant, are fragile; fatty solutions, drying, crack, and for their preparation consumes a lot of binders. The fat content of the solution or binders is determined in the laboratory.
Plastering solutions should have workability, i.e., the ability to easily fit a thin dense layer with filling all the irregularities. This property is largely dependent on the mobility of the solution, i.e., the ability to spread under the action of its own gravity. Mobility is characterized by the immersion value of a standard cone.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)