Dining table is a subject, without which it is simply impossible to create a harmonious design of a kitchen-dining room. In addition to the direct purpose - eating - it also serves as an aesthetic goal, completing the formation of the image of the room. In addition, many housewives often use it and as a work surface for cutting, processing and cutting products. Therefore, the choice of a dining table should be approached seriously, taking into account several important aspects: dimensions, shape and design. Let's take a closer look at these aspects and take a look at the photos of modern dining tables.
Ergonomics of the dining table When choosing a dining table for the kitchen-dining room, initially it is necessary to take into account its ergonomics. Its height, width and length must meet certain requirements, which provide maximum functionality and comfort during use. For complete convenience when eating a person needs at least 60-70 cm of free space. Therefore, for an average family of four people, the most optimal choice is a table not less than 120 cm long, and not less than 75 cm wide. For holding celebrations, you need a larger model - about 160 cm long; for such a desk, they can comfortably seat up to eight people. Also, when choosing a building, consider the dimensions of the room. In a small kitchen, a too-large table can create obstacles for moving or performing standard procedures; and vice versa, a small table in a large room will create a feeling of emptiness. The shape and design of modern tables. Dining tables are square, rectangular, round, oval and triangular. Square tables are an acceptable solution for a small kitchen-dining room. Often they have a compact size and are designed for two, a maximum of three people. They are convenient because they can be safely moved to the wall, freeing up several centimeters of free space. Clear construction lines add to the severity of the room.
Rectangular dining tables - a classic solution in the interior. They look comfortably in any style and can be placed both in the central part of the room and near the wall. Rectangular models are available in various sizes and designs. They can be solid, folding or sliding. In the last two cases, it is possible to simply solve the problem of space shortage and make the kitchen design extremely functional: if necessary, the table is cracked and then hidden in a corner away from the eyes
Round tables are ideal for families with small children. In their construction there are acute angles that a child can get hurt. Moreover, the round shape of the table-top puts everyone in equal conditions, without distinguishing the owners from the guests, adults from the children. Often, large round models are based on three legs, and small ones - on one center. The only disadvantage of such a decision in the kitchen-dining room is the inability to move the table to the wall.
The oval table is suitable for large families. 6-8 people are comfortably behind it. Likewise round solutions, oval models have smooth lines without sharp corners, which can create a relaxed atmosphere during the meal
Triangular tables - an extraordinary solution in design. They are able to create a superior tandem with a kitchen and a dining room, if the latter lack an expressive point of focus. Even the simplest design room will look exotic with a triangular dining table. Just take a look at the photo below to appreciate the unusual elegance of such a decision.
Dining tables-transformers deserve special attention. They become real salvation for very small spaces. In the unfolded state, they do not differ from solid tables, and when folded they become the most inconspicuous and compact object in the kitchen. Today, there are three types of transforming tables: tabs, books and wings. The design of models with tabs consists of two sliding parts and a third extra, which is inserted in the middle. The table-book consists of a stationary part and a warehouse. In turn, the table with wings has a stationary central part and folding side parts.
Dining tables. Dining household tables are designed to be static and transformable. In any case, the dining table consists of a lid, a base and, if necessary, transforming devices and drawers. Table covers are made of wood chipboards or solid wood. Wood chip plates are veneered with veneer, films, plastic. The edges of the lids are lined or decorated with curly wood veneers. The dimensions of the table lid are determined by the number of seats. The dimensions of the seating area are 500–600 mm in length (width) of the table top, 300–325 mm in depth. The number of seats increases depending on the chosen scheme of transformation of the table cover. There are sliding, retractable and hinged trans-formed table covers.

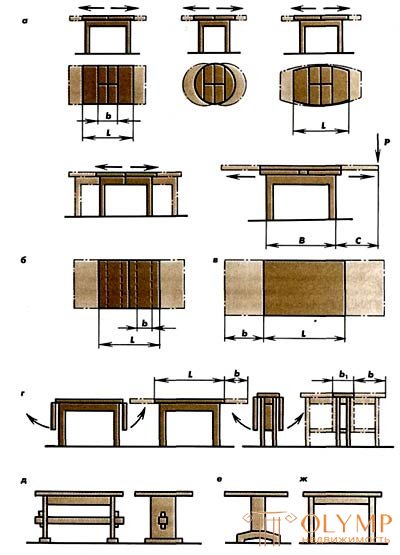
Fig. 1. Dining tables: a-d - schemes of transformation of the lids; g - g - schemas of the sub-table; g - l - connections of parts of the sub-table; m - o - transforming device
In tables with a non-movable underframe and sliding covers (Fig. 1a) after the transformation, the size of the cover increases by one folding element. The number of seats after transformation is increased by two. In tables with a sliding base and sliding covers (Fig. 1 b) after the transformation, the size of the cover can be increased by one, two and three loose elements. The number of seats during the installation of three loose elements is increased by six. In tables with retractable bottom covers and a non-sliding underframe (Fig. 1c), the size of the cover after transformation can be increased by one or two covers. The number of seats is increased by two or four. The dimensions of the table covers, transformed according to the schemes shown in figure 104 g, are increased by raising the hinged covers. The number of seats after the transformation is eight to twelve. The width of loose elements b in transformable tables must correspond to the size of the seat, that is, be at least 500-600 mm. In addition, tables with an unmovable underframe must take into account the overhang of the cover C after transformation relative to the table legs, which characterizes the stability of the dining tables. The stability of the dining tables is the ability to resist tipping over in adverse operating conditions (the greatest overhang of the table cover and the load on the edge of the cover). Dining tables that have a permanent overhang of the lid (tables that are untransformable and with a sliding underframe), as well as tables that do not increase after the transformation of the overlid, are stable. When designing, the stability of dining tables can be calculated using the formula: PC = (B / 2) * Q, where P is the vertical load equal to 10 daN (kgf) for tables weighing up to 15 kg and 15 daN (kgf) for tables weighing over 15 kg; C is the overhang of the table cover, mm; B is the length, width of the table base, mm; Q is the weight of the table, kg. Based on the condition that the table does not overturn, the maximum permissible overhang of the cover can be determined: C less = (B / 2P) * QIf the calculation turns out that table stability is insufficient, it is necessary to reduce the overhang of the table cover or to increase its mass by using parts of a larger section, a larger mass, etc. The table base is a wooden support. In the tables of non-transformable support, there are side racks connected by the tsargs and the middle bar (Fig. 104 d), or the central rack (Fig. 1e). In the tables, a transformable support consists of four legs and the kingfom (Fig. 1 g). The legs can be square, rectangular and round in shape. The dimensions of square legs in cross section should be at least 45x45 mm, rectangular — 60x45 mm, round - 0 50 mm. The width of the tsarg 90-100, thickness not less than 19 mm. The supports, consisting of four legs and tsarg, are also used in untransformable tables with a drawer. The upper part of the substructure, where the tsargs are located, is called the tsarist belt. In non-transformable tables in the royal belt is a drawer. To install a box in one of the table's sides, a rectangular cutout is made into which the box enters. The box is installed on the guides of the L-shaped slats, connected with the tsargami spikes. Transforming devices are placed in transforming tables in the stern zone. Substrate parts are made of coniferous wood, chipboard, glue round pillars are glued from plywood or veneer. median connection on the thorn "dovetail" (Fig. 1 h). The middle bar with the side posts is connected with wedges (Fig. 1 and). The layers of the sides and the middle bars should be located vertically. The wider side bars and bars, the more
rigidity of the table. The slope of the wedge is 1:10, width b from the end of the bar to the wedge is at least 50 mm. Klin-new connection is used not only as a constructive, but also as a decorative. When developing the design of the under-table of a table consisting of four legs and sides, the main attention is paid to the rigidity of the joints providing the rigidity of the tables as a whole. The rigidity of the dining tables is characterized by - resist vibration by external forces. It depends on the stiffness of the junction and attachment of the legs, the correct choice of sections of the legs and table flanks. Tsargs between themselves and legs with tsargs in non-detachable underframes are connected with a single non-through spike semi-threading on glue. In folding joints, tzargs are connected with wooden or metal bulls, legs are attached to the seals with special ties, standard bolts or studs with a nut (Fig. 1k) . Wooden lugs are connected to the tsargs on straight box spikes or on the dovetail thorn. Metal lugs attach sharps to the flanks (four screws are placed on each joint). The thickness of non-standard metal bosses 4 mm, width 70 mm. Standard stamped lugs are made of stiffeners from steel with a thickness of 2 mm. The spiked straight joint is the strongest and toughest, therefore it is recommended for dining sliding and non-sliding tables of all sizes. Compounds on the dovetail spike and metal bosses are about twice as inferior in stiffness to straight spike compounds. Such compounds are used in sliding and non-sliding dining tables, with the exception of banquet tables. For fixing the legs in tables with bent-glued tsargoy (Fig. 1 l), standard screws and nuts are used. Dining tables by industrial enterprises are made with a folding sub-base (with removable legs) to reduce the size of the table taken up by transport. Dining tables in home workshops can be made with non-collapsible and underframes. The rigidity of the tables, in which the legs with tsargami are connected by a single non-through thorn with a semi-weave, is higher than the rigidity of similar tables with matching connections of the legs with the tsargs. In addition, during the operation of the dining facilities in collapsible joints, the nuts are self-unscrewing, which reduces the rigidity of the joints. Nuts need to be periodically screwed in. The transforming devices of the dining tables are running bars and pivoting pins. The running bars, screwed with screws to the table top, move into the sleeves of the tsarg (fig. 1 m) or guide bars (fig. 1n) attached to the tsargam. The connection of several guide bars forms a rocker guide (Fig. 1o). In order to prevent the ridge from coming out of the groove in the bars of the rocker guide, the joint is fixed with a metal angle bracket. Rubbing surfaces of running bars are made of hardwood hardwood. Tables are static. Dining untransformable (static) table on the side racks is shown in Figure 1 a. The table is made of solid wood of coniferous species. The thickness of the side posts is 25 mm. At the bottom of the rack is mounted on spiked joints; a support bar, which increases the stability of the table. Edges racks curly. In the upper part of the side pillars there are two tsargami, connected with the posts on the dowels or the angular middle joint on the thorn “dovetail”. The middle bar is connected to the side racks with the help of wedges. The table cover can be of a frame or shield structure. The bars of the frame with a cross section of 25 x 90 mm are connected with angular spike joints on the “us”. On the inner edges of the frame, a quarter is taken into which they insert a 8-10 mm thick plywood file. The veneer is coated with a film material or cloth. To prevent the panel from jarring during operation, when facing, the glue mortar is applied from the inside only around the edge of the panel with a strip of 20-30 mm. File to the frame attached turntables. The frame to the side racks is installed on the dowels with additional fastening with metal squares. Panel covers glue from coniferous sawn timber. Cover thickness 20-25 mm.
To close the connections of the side pillars with the lid, bars with a thickness of 30-35 mm are screwed on the inside of the lid on the screws. In addition, the bars provide stability of the covers when warping and are a decorative element.

Fig. 2. A set of furniture for the equipment of the dining area using the dining table: a - general view; b - design racks; in - fastening the cover; d - e - mounting of the supports to the rack. Figure 2a shows a set of furniture for the equipment of the dining area using a dining table with a round lid on the central rack. Round tables can not be blocked with other pieces of furniture, there should be a free zone around them. Therefore, dining tables with a round lid are used in rooms with a large area or on terraces. Table stands are made from solid wood of softwood or hardwood. They have a square or round shape (Fig. 2 b): The base of a square stand is a glued timber section of 120 mm thickened in the lower and middle parts. The thickening of the timber is used to increase the stability of the rack and for aesthetic reasons. Racks of round shape consist of segments connected to the insert rail. The table cover with a diameter of 1000-1200 mm is made of solid wood. Cover thickness 30-35 mm. The cover can be made of solid wood or chipboard thickness of 18-20 mm. In this case, to increase the stability of the lid and for aesthetic reasons, bars or rounds with a thickness of 30-35 mm are screwed on its inside. The lid is fixed with screws to the cross-piece, embedded into the rack (Fig. 2c). The working surfaces of the lid of tables of solid coniferous wood should be de-tarted. The supports of the table are a cross (fig. 2 d) or extension legs (fig. 2 d). The character of the connection of the rack with the supports must be well thought out, since with one-sided load on the table cover there are significant loads on the connections of the rack with the supports. Square stands with a crosspiece can be connected to a through spike with wedging with a wedge on the glue. Round racks to the crosspiece attached to shkantah. The diameter of the dowels is 14 mm, the number of dowels for one connection is at least four. Spacer legs are attached to the rack on the dowels with a diameter of 14 mm with an additional fastening with a metal bracket. The tables are transformable. Tables with sliding covers and a non-sliding under-cabinet are made with a rectangular and round under-underlay (round shelf). Figure 3a shows an example of a table structure with a rectangular underframe. To sliding covers
The tables are attached running bars - 4 and 7, which move in the grooves of the tsarg. The insertion element 6 consists of two shields connected by loops. One shield of the supplementary element is attached to a pivotal rolling pin 2 rotating in the side bar. In the folded position, the insert element rests on the support bar 3. During the transformation, the inset element rotates together with the rolling pin and lies on the longitudinal bar. Then the second half of the supplementary element leans back on the loop and lies on the other side. The shkanta 5, installed at the edges of the loose element, four shkanta on each side, enter into the corresponding slots of the sliding table covers. Before and after the transformation, the sliding covers of the table are connected to each other and the inset with hooks J. Hooks protect against accidental release of the dowels from the sockets, as a result of the cheek and the folding element can descend down under the load of objects on the table. A round barrel and a loose-leaf element, stored freely in the sub-base, is shown in Figure 106 b. The sliding bars 8, which are moved in the grooves of the guide bars 10 connected by spikes to the hinge 9, are attached to the sliding lids 8. The insertion element 6, consisting of two shields connected by loops, is freely stored in the base on the supporting bars 3 connected to the bars. In the structures of tables with a round side, the supplementary element can be pivotal - attached to the pivotal rolling pin (Fig. 3c)
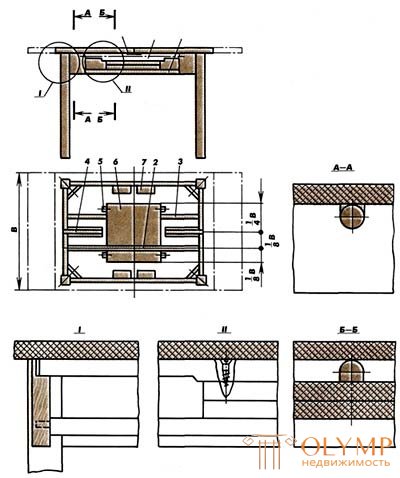
Fig.3. Dining tables with sliding covers and a non-sliding base: a - rectangular; b-in - round (round tsargoy); 1 - hook; 2 - rolling pin; 3 - support bar; 4, 7 - running bars; 5 - shkant; 6 - supplement; 8 - sliding covers; 9 — round pike; 10 - guide bar. The process of making dining tables with a rectangular non-separable basement from pre-prepared parts includes the basic operations performed in the following sequence: forming spikes and sockets in legs and legs; sidewalls under the “dry”, gluing spiked joints of the sidewalls, assembly of the underholding “dry”, gluing and processing the underframe, fastening the support bar, attachment of loose elements
on the hinges, fastening the rolling pin and running bars, installing the insert in the base, checking the transformation effort. When marking the legs, they are sawed off after the base assembly is assembled. For this purpose, the length of the legs at the top of the table should be 40-50 mm longer than the project. If the length of the legs of the under-cabinet corresponds to the design length, then in the places of mating of the tsar with the nests of the legs during assembly, the wood may split, as a result of which the nature of the connection is broken. The glued sidewalls are crimped in zvings and check the correctness of the assembly of the sidewalls with a ruler diagonally. Then the underframe is collected “dry” and glued together in zvings. Compressed in zwingi under-so, checked diagonally and set on a horizontal floor. After the glue dries, the ends of the legs protruding over the tsar are sawed and the understrap is brushed off.In order to ensure the best sliding of the covers on the tsarg during transformation, it is advisable to glue the stripes of cloth (cloth) over the tsarg. Card hinges are used for hanging attachments. After hanging, the buttonhole should protrude to the front surface of the insert. The table covers and the insert element are placed on a flat floor, face down, and a floor is placed on them. Aligning the overhangs of the lid and the inset element along the substructure, fix the running bars to the covers and the rolling pin to the supplementary element. Putting the table on the legs, check the force of trans-formation of the caps. If necessary, the running elements of the transforming devices are waxed or soaped. When making tables with a collapsible rectangular base, first with the help of lugs they connect the tsargs, then the legs are attached to the tsargs.In the future, the process of manufacture is similar to the process of making a table with a non-separable underframe. The production of tables with a round barrel has some peculiarities. Tsugu bent-glued closed loop glued from plywood. The legs are attached to the tsargs with standard screws with a semicircular head. The running bars move in the grooves selected in the king-bars and guide bars. Two support bars are attached to the guide bars with screws, on which the insert is freely stored. If the insert is attached to a pivotal rolling pin, then it rotates in the lugs, screwed to the round tsar with screws.selected in the king-gakh and guide bars. Two support bars are attached to the guide bars with screws, on which the insert is freely stored. If the insert is attached to a pivotal rolling pin, then it rotates in the lugs, screwed to the round tsar with screws.selected in the king-gakh and guide bars. Two support bars are attached to the guide bars with screws, on which the insert is freely stored. If the insert is attached to a pivotal rolling pin, then it rotates in the lugs, screwed to the round tsar with screws.
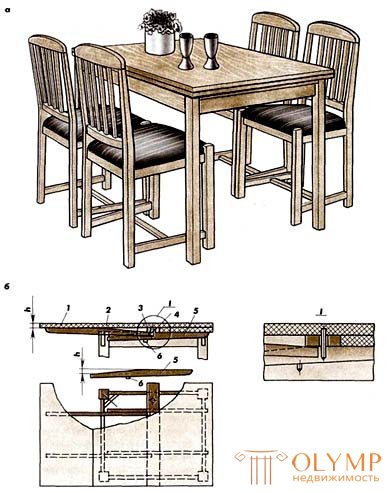
Fig. 4. Dining tables with a rectangular (a) or square (b) underframe: 1 - retractable bottom cover; 2 - top cover; 3 - the bridge; 4 - shkant; 5 - running bars; 6 - shkanty-stops.
Dining tables with retractable lids are made with rectangular (fig. 4a) and square (fig. 4 b) underframes. In both cases, the tables have similar con-structural solutions. The tables have two lower covers 7, which are pulled out from under the upper cover 2. The running bars 5, which are moved in the slots of the tsar, are attached to the lower covers. To the other two sides there is a cross bar, called bridge 3. In the bridge there are two openings in which the dowels 4 are loosely inserted, fastened in the top cover. The running bars have a wedge-shaped shape, due to which the lower lids are set-up on the level of the upper table cover when extended. In the running bars there are bolts-stops 6, which prevent the full extension of the lower lids. In the extended position, the running bars rest against the bridge below. The bridge is fastened to the ready underframe with screws.The width of the bridge depends on the width of the retractable wings, which is determined by taking into account the stability of the table against overturning. Attaching to the retractable covers running bars on the holes in the bridge, mark the installation location of the top cover dowels. Having installed dowels and having put forward the lower covers, plan the locations of dowel stops. Tables with sliding covers and sliding underframes (Fig. 5 a) are resistant to rollover, since the overhang of the cover in the transformation process remains constant. However, after the transformation, the table covers bend by h, which depends on the gaps in the mating connections of the transforming devices and the magnitude of the transformation. It is believed that the table is made with sufficient accuracy, if the deflection of the cover after the transformation is not more than 5 mm. If the deflection of the table cover is more than 5 mm,then in the design of the table provide folding leg, eliminating the deflection of the cover of the table. The legs are made of T-or U-shape of coniferous wood or aluminum pipes and attached to the transforming devices on hinges or brackets. Folding legs are used in tables that can be transformed into five or more loose elements.
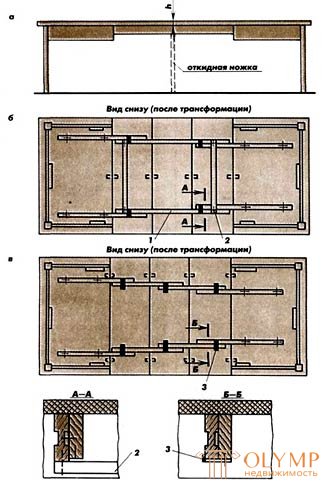
Fig. 5. Dining table with sliding covers and sliding underframe: a, b - rocker guide with running gear; c - rocker guide of individual bars: 1 - middle bar; 2 - transverse bars; 3 - fixing metal square.
Kulisnye guides tables with sliding lids and sliding basement-it is performed in two versions. In the first variant (Fig. 5 b), the middle bars 1 are connected with screws into the running box with cross bars 2. The box must be sufficiently rigid, therefore two trishurips are put on each joint. Extreme running blocks kulisnoy guide attached to the half-cap. Kulis-ny guides with a running box used for tables, transformed no more than three loose elements. The inserts are located on the transverse bars of the entrance box. In the second variant, the link guide is connected from separate bars (Fig. 5c) fixed by metal elbows 3. Such link guides are used for tables that can be transformed into four or more loose elements (banquet tables ). Inserts are stored separately from the table. Before proceeding to the manufacture of a dining table with sliding covers and a sliding underframe, it is advisable to make a drawing (bottom view) of the table before and after the transformation on a scale of 1: 2. If the size of the table after transformation is significant, it is possible to make a drawing of half the table to the axis of symmetry. In the drawing, draws lids, loose elements, underframes, rocker guides, stops, limiting the movement of the bars of the rocker guide, fixing the squares
The table is made in the following sequence. The finished underframe is cut into two equal parts, to which with the help of lugs or squares half-covers are attached and to them (half-covers) the extreme running bars of the rocker guide. Then the leveling elements with half-lids (legs up) are formed on the level floor and the extension is mounted. In accordance with the drawing, stop fixing squares with screws with screws. Putting the table legs on the floor, check the correctness of the installation and the force of transformation. Then mount the hinged leg. Depending on the design and method of attachment, the folding leg can retract itself when the table is moved and folded when it moves apart. Tables with hinged covers, transformed according to the scheme shown in Figure 4g, have two hinged covers that are connected to stationary card loops . To keep the covers in a horizontal position, travel bars or retractable legs are used. The travel bars are moved in L-shaped guide bars attached to the stationary cover and grooves cut in the side bar. Running bars nominated under a fixed cover, which is attached to the base. The movements of the running bars are limited by stops made of plywood, nailed to the running and guide bars by dyami. Retractable legs are a frame attached to the pedestal of the frame or shield design. On each side of the stand put two frames. So that the frames do not slide on the lid after the table is transformed, they are attached to the hinged lid. The stop is a bar with a thickness of 20 mm in which a groove is cut with a depth of 10 mm and a width equal to the thickness of the frame. After opening, the top bar of the frame goes into the groove. In the upper bar of the frame under the stop make a cutout or frame set below the plane of the stationary table cover 110 mm. Tables of this design are called thumbs. They are usually used as an additional side table for dining. Folded tables-cabinets serve as supports for various items.
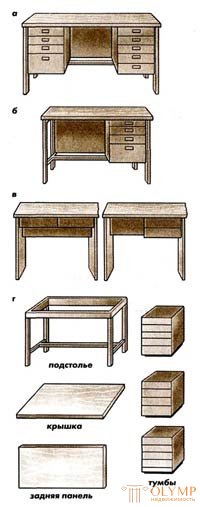
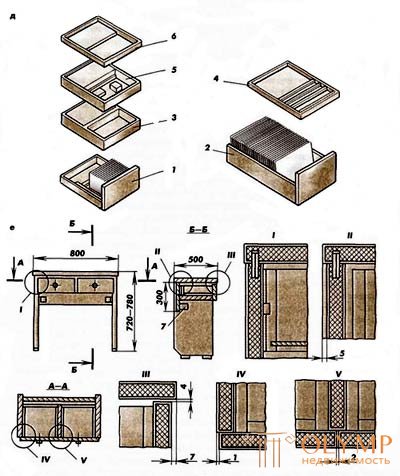
Fig. 6. Writing tables: a - dvukhtumbovye; b - single-room; in - with drawers; e - drawers for equipment for thumbs; е - a design of a desk with drawers: 1, 2 - boxes for vertical storage of books and folders; 3, 5, 6 - boxes for papers; 4 - boxes for writing materials; 7 - metal square
Writing tables can be dvukhtumbovym (Fig. 6 a), single-pomer (Fig. 6 b), with drawers (Fig. 6 c), which are installed in one or two rows. In the second case, the cover is used for fastening the vice when performing electrical installation, plumbing and other work. The desks with thumbs include a lid, a stand, a rear panel, and pedestals (Fig. 6 g). The minimum dimensions of the desks of the desks with thumbs in length and width are: dvuhtumbovy 1400x700 mm, one-curved 1 000x600 mm. Covers are made of solid wood or chipboard. The thickness of the lids 20-30 mm. The covers are fixed to the underframe on the shkanta.The base of the desks are made of solid wood. It consists of four legs, sides, lateral and middle projectile. The width of the parts of the base is 60 mm, the thickness is 25-30 mm. The parts of the base are connected by spikes on the glue. The distance between the middle blade and the tsarg should be 2-3 mm greater than the height of the stand. The rear panel of solid wood or chipboard is fixed between the rear legs. It is used in cases where the table set the back panel to the passage. When installing the table to the wall, the back panel can be not used. The tables of the tables are equipped with drawers (fig. 6 d) or shelves. Thumb walls are made of boards or frames with panels. The joints are non-separable on the dowels with glue. Vertical wall thumbs through passage. In tables with a back panel, the back wall of the pedestal is made of an invoice of plywood or solid fiberboard. The initial value for determining the internal dimensions of the table drawers are the dimensions of the items for which the boxes are intended to be stored, and how these items are stored. The width in the light of the boxes 7, 2 for vertical storage of books and folders 340 mm, height not less than 265 mm. The internal dimensions in terms of boxes 3, 5, 6 for papers and notebooks must be at least 340x240 mm when storing papers in one foot and at least 340x480 mm when storing them in two feet; the internal height dimension must be at least 65 mm. Uca
These sizes do not apply to the drawers 4 for pencils, pens and other written accessories. The sizes of these boxes are determined experimentally, by measuring the items for which they are intended to be stored.
Curbstones, equipped with shelves, have a hinged or sliding curtain, opening up or down the door. The contents of the pedestals, equipped with shelves, are less accessible, but compared to the pedestals with drawers. In this regard, in the manufacture of writing tables, you should give preference to drawers with drawers. Writing tables are assembled in the following sequence: In the ready underfold between the middle progock and tsarms, install the stand and fasten it with screws to the tars and thread. If the table is single-sided, then the cabinet is installed on the left or right of the sub-base. If there is a rear panel in the design of the table, it is positioned before installation of the pedestals and fastened with screws or screw ties to the rear legs. Then a cover is attached to the base on scans with glue. In order to prevent the cover from moving away from the underside, it is necessary to provide additional fastening of the cover to the basement of the squares of the screws. The design of the writing table with drawers installed in one row is shown in Figure 6e. The side supporting walls of the table are connected to the horizontal back, middle, and dividing walls with a cover on the dowels with glue. The rigidity of the design of such tables is provided mainly through the use of a wide (not less than 300 mm) rear wall and additional fastening it with metal angles 7. When installing the boxes in two rows, the guide plates for installing the boxes are attached to the middle partition and side support walls. Between the dividing and side walls, the lower impassable shield covering the drawers is installed on the dowels. The middle dividing wall is additionally attached to the lid with metal angles. In desks with drawers directly under the lid, the overhang of the lid relative to the front wall of the drawer should be minimal. the best viewability of the contents of the box when pushing it
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)