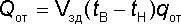
When calculating the required power of boiler plants that provide heated buildings with coolant and selecting the diameters of heating networks, as well as calculating the annual fuel consumption, buildings heat losses are taken according to standard or individual building designs, heating system designs.
In the absence of design data, the design load on the heating system is defined as the sum of the heat consumption rate for reimbursement of the main heat losses of the building without taking into account the infiltration and the rate of heat consumption for ventilation of the buildings, taking into account the infiltration. In industrial buildings, during the operation of which the rolling stock is introduced and withdrawn regularly, the cost of heat for heating the rolling stock and restoring the temperature conditions in the heated room that are disturbed when the gate is opened are additionally taken into account.
The rate of heat consumption to compensate for the main heat losses of the building Qot, W is determined by the formula
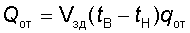 ,
,
where Vzd - the estimated outer volume of the building, determined by the passport of the building, m3; tv is the calculated internal temperature, ° C. If the building includes several rooms with different internal temperatures, the tv value is taken as the average or the volume of the building is divided into several volumes, including rooms with specific tv values. Qot values are calculated for each volume independently, and then summed up; tn - design temperature of outside air, ° С; qot is the theoretical specific heating characteristic of the building, kJ / (m3h ° C), i.e. the value of heat loss through external fences, referred to 1 m3 of the calculated volume of the building and to 1 ° C are the differences between the internal and external temperatures. In determining qot taken into account:
● building type (production or non-production);
● the value of the estimated outdoor temperature;
● height or number of floors of the building and the presence of the overhead light;
● material and thickness of external walls;
● specific external perimeter of the building P (i.e. the length of the perimeter of the building, referred to the building area;
● glazing of the building w, i.e. the ratio of the total area of all openings (windows and doors) to the total area of the external walls.
The value of q is taken from the table. 1 and 2.
Continued 14
Table 1
Values of specific heating characteristics
for non-production buildings at tн = –30 ° С
|
Relative perimeter P |
Glazing w |
qot kJ / (m3h ° С) for buildings with wall thickness, bricks |
||
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
||
|
Single-story buildings |
||||
|
0.1 |
0.1 |
1.533 |
1,462 |
1,382 |
|
|
0.3 |
1.609 |
1,529 |
1,462 |
|
0.2 |
0.1 |
2,150 |
2,008 |
1,848 |
|
|
0.3 |
2.302 |
2,142 |
2.020 |
|
0.3 |
0.1 |
2,768 |
2.554 |
2.314 |
|
|
0.3 |
2,995 |
2,755 |
2.579 |
|
0.4 |
0.1 |
3,385 |
3,100 |
2,780 |
|
|
0.3 |
3,688 |
3,368 |
3.137 |
|
0.5 |
0.1 |
4.003 |
3,646 |
3.247 |
|
|
0.3 |
4.381 |
3,982 |
3,696 |
|
0.6 |
0.1 |
4.620 |
4.192 |
3,713 |
|
|
0.3 |
5,053 |
4,595 |
4.255 |
|
0.7 |
0.1 |
5.237 |
4,738 |
4.179 |
|
|
0.3 |
5,767 |
5,208 |
4,813 |
|
0.8 |
0.1 |
5,855 |
5.284 |
4.645 |
|
|
0.3 |
6,460 |
5,821 |
5.376 |
|
0.9 |
0.1 |
6,472 |
5,830 |
5.111 |
|
|
0.3 |
7,153 |
6,434 |
5,930 |
|
1.0 |
0.1 |
7,090 |
6.376 |
5,578 |
|
|
0.3 |
7,846 |
7,048 |
6,489 |
|
Two-story buildings |
||||
|
0.1 |
0.1 |
1,159 |
1,088 |
1,008 |
|
|
0.3 |
1.235 |
1,155 |
1,100 |
|
0.2 |
0.1 |
1,772 |
1.630 |
1,474 |
|
|
0.3 |
1,928 |
1,768 |
1,655 |
|
0.3 |
0.1 |
2.394 |
2.176 |
1,940 |
|
|
0.3 |
2,621 |
2,381 |
2,213 |
|
0.4 |
0.1 |
3,011 |
2,726 |
2.407 |
|
|
0.3 |
3.314 |
2,995 |
2,772 |
|
0.5 |
0.1 |
3,629 |
3.272 |
2,873 |
|
|
0.3 |
4,007 |
3,608 |
3,326 |
|
0.6 |
0.1 |
4.246 |
3,818 |
3,339 |
|
|
0.3 |
4,700 |
4.221 |
3,885 |
|
0.7 |
0.1 |
4,864 |
4,364 |
3,805 |
|
|
0.3 |
5.393 |
4,834 |
4,444 |
|
0.8 |
0.1 |
5,481 |
4,910 |
4.271 |
|
|
0.3 |
6,086 |
5.447 |
5,002 |
Continued 14
table 2
Values of specific heating characteristics
for industrial buildings with tn = –30 ° С
|
Relative perimeter P |
qot, kJ / (m3h ° С) for buildings with wall thickness, bricks |
|||||||
|
No ceiling light |
With overhead light |
|||||||
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
|||
|
Building height 4–6 m |
||||||||
|
0.03 |
1,121 |
1,092 |
1,079 |
1,987 |
1,953 |
1,928 |
||
|
0.05 |
1.252 |
1,205 |
1,180 |
2.113 |
2,066 |
2.033 |
||
|
0.07 |
1,382 |
1,319 |
1,273 |
2.243 |
2,180 |
2,134 |
||
|
0.10 |
1.579 |
1,487 |
1,424 |
2.440 |
2,348 |
2,285 |
||
|
0.15 |
1,903 |
1,768 |
1,672 |
2,764 |
2,629 |
2.533 |
||
|
0.20 |
2,230 |
2,050 |
1,915 |
3,091 |
2,911 |
2,776 |
||
|
0.30 |
2,885 |
2,612 |
2.407 |
3,734 |
3,473 |
3.272 |
||
|
Building height 6.1–8 m |
||||||||
|
0.03 |
0.857 |
0.819 |
0,802 |
1,474 |
1,441 |
1,428 |
||
|
0.05 |
0.987 |
0,941 |
0.907 |
1,600 |
1.554 |
1,529 |
||
|
0.07 |
1,117 |
1,054 |
1,008 |
1,730 |
1,667 |
1,621 |
||
|
0.10 |
1,315 |
1,222 |
1,159 |
1,928 |
1.835 |
1,772 |
||
|
0.15 |
1,638 |
1,504 |
1.407 |
2,251 |
2,117 |
2.020 |
||
|
0.20 |
1,966 |
1,785 |
1.651 |
2.579 |
2,398 |
2,264 |
||
|
0.30 |
2,621 |
2,348 |
2,146 |
3.221 |
2,961 |
2,755 |
||
At other design outdoor temperatures, the coefficients a taken from Table 1 should be applied to the values of specific heating characteristics at tн = –30 ° С. 3
Table 3
Correction Factor Table a
by the value of the calculated outdoor temperature
|
tн, ° С |
0 |
-five |
-ten |
-15 |
-20 |
–25 |
–35 |
–40 |
–45 |
-50 |
–55 |
|
a |
2.05 |
1.67 |
1.45 |
1.29 |
1.17 |
1.08 |
0.95 |
0.9 |
0.85 |
0.82 |
0.8 |
The heat consumption rate for the ventilation of the building Qvent, W, is defined as
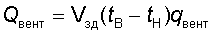 ,
,
where qvent is the theoretical specific ventilation characteristic of the building (specific heat consumption for ventilation), kJ / (m3h ° C), taking into account the standard air exchange in the building, is taken from the table. 4 and 5.
End 14
Table 4
Values of specific ventilation characteristics
for industrial buildings
|
Purpose of buildings (workshops) |
Building building volume, thousand m3 |
qvent, kJ / (m3h ° С) |
|
Iron foundries |
Up to 50 |
4.20 |
|
Thermal |
To 10 |
5.04 |
|
Blacksmith |
To 10 |
2.52 |
|
Mechanical |
to 10 |
1.05 |
|
10 to 50 |
0.63 |
|
|
Woodworking |
Up to 5 |
2.10 |
|
Repair shops |
To 10 |
0.63 |
|
Electric depot |
From 10 |
1.05 |
|
Diesel Depot |
Up to 5 |
1.26 |
|
From 5 and up |
1.05 |
Table 5
Values of specific ventilation characteristics
for non-production buildings
|
Purpose of buildings |
Building building volume, thousand m3 |
qvent, kJ / (m3h ° С) |
|
Residential buildings |
- |
0.42 |
|
Dormitories, hotels |
- |
0.84 |
|
Administrative |
Up to 5 |
0.38 |
|
5.01–10 |
0.34 |
|
|
More than 10 |
0.29 |
|
|
Clubs |
Up to 5 |
1.05 |
|
5–10 |
0.97 |
|
|
More than 10 |
0.84 |
|
|
Cinemas |
Up to 5 |
1.81 |
|
5–10 |
1.64 |
|
|
More than 10 |
1.60 |
|
|
Kindergartens, nurseries |
Up to 5 |
0.46 |
|
More than 5 |
0.42 |
|
|
Schools |
Up to 5 |
0.38 |
|
5–10 |
0.34 |
|
|
More than 10 |
0.29 |
|
|
Polyclinics |
Up to 5 |
- |
|
5–10 |
1.05 |
|
|
10–15 |
0.97 |
|
|
More than 15 |
0.92 |
|
|
Businesses catering, dining |
Up to 5 |
2.94 |
|
5–10 |
2.73 |
|
|
More than 10 |
2.52 |
|
|
Garages |
Until 3 |
- |
|
3-5 |
2.94 |
|
|
More than 5 |
2.73 |
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)