
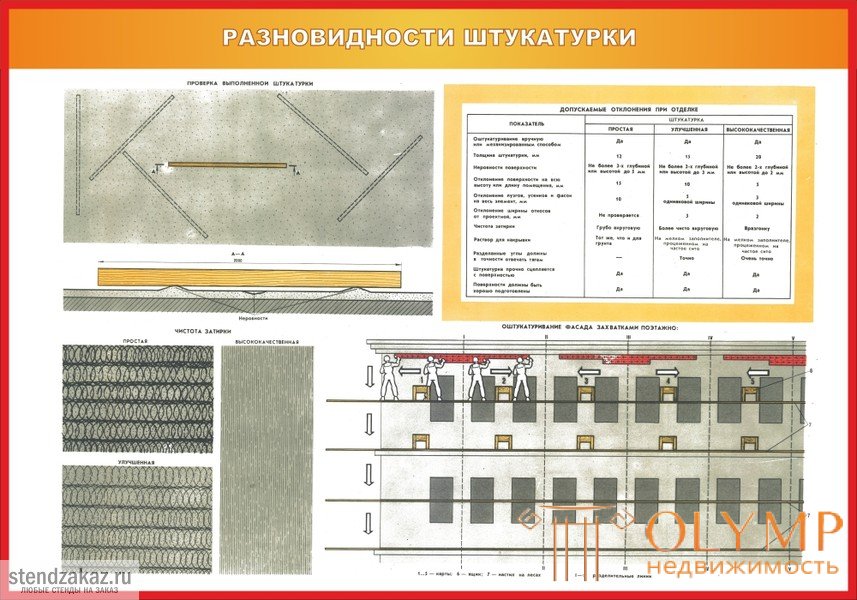
The accuracy of the implementation of various plaster (Table 1) must meet the requirements of SNiP or ENiR, which also determines the thickness of the plaster. The thickness of the plaster should be, mm: idle up to 12, improved to 15, high-quality 20. On smooth brick surfaces the thickness of the plaster can be up to 10 mm, and on smooth concrete surfaces up to 2-3 mm, i.e. cover with grout. On the surfaces of straw, reed and fibrolite, the thickness of the plaster should not exceed 20 mm without additional preparation. On wooden surfaces, it is desirable to arrange a layer of plaster with a thickness of 20 mm or at least 15 mm from the level of the outlet drains, since thinner layers of mortar are easily torn from the warping of stuffed drains, and the dran itself “prints” onto the surface of the plaster.

Table 1. The accuracy of the plaster
The plaster should firmly adhere to the surface, not peel off, have a well-worn surface, without external defects.
Surface irregularities are detected by applying a rule or a pattern 2 m long in different directions vertically, horizontally, and diagonally to the surface.
Vertical and horizontal plaster is controlled by a rule or a cord, that is, by tightening the cord with indentation to the thickness of the plaster and arranging brands and beacons for this cord. Surfaces under the improved and high-quality plasters are fixed, brands and lighthouses are arranged.
If the deviations are greater than the norms given in table. 1, they are eliminated (cut off the solution or additionally impose).
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)