In 1955, the CPSU Central Committee and the USSR Council of Ministers adopted resolutions “On measures for further industrialization, improving quality and reducing construction costs”, “On eliminating excesses in design and construction”, which gave a comprehensive analysis of errors that hinder the rise in the quality of architecture and construction. In the light of the fulfillment of the resolutions, measures were taken to restructure architectural and construction organizations, a program to improve the activities of scientific and design organizations was defined, systematic work began on the development of standard projects for residential apartments designed for family occupancy.
Along with the development of construction according to standard designs of buildings for various purposes, unique public buildings are being constructed, among them - the Central Stadium named after VI Lenin in Luzhniki (A. Vlasov, I. Rozhin, V. Nasonov, and others), the Soviet pavilion at the International Exhibition in Brussels in 1958 (Y. Abramov, A. Boretsky, V. Dubov, A. Polyansky), Palace of Pioneers and Schoolchildren (V. Egerev, V. Kubasov, F. Novikov, B. Pal-lui, I. Pokrovsky and M. Khazhakyan), the Yunost Hotel in Moscow (Y. Arndt, T. Bausheva, V. Burovin and T. Vladimirova), International Pioneer Camp Artek on the Crimean coast (a team of architects led by A. Polyansky).
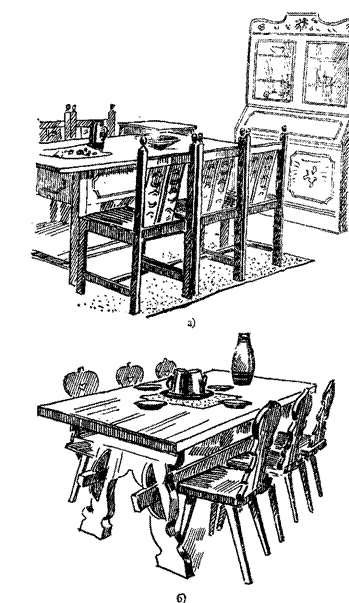
A special place among public buildings belongs to the Palace of Congresses, located on the territory of the Moscow Kremlin (1961, M. Posokhin, A. Mdoyants, E. Stamo, P. Steller, M. Shchepetilnoz). The building is distinguished by a clear and strict composition, monumentality of forms. Significant achievements in the solution of the interior. The decorative curtain of the Palace of Congresses was made according to the sketch of the artist A. Mylnikov from chased metal - against the background of the rising sun there is a scarlet banner with a portrait of V. I. Lenin. In the interior decoration is widely used wood. The panels, walls, interior doors, panel art parquet and furniture are decorated with precious woods: mahogany, Pacific and Anatolian walnut, ebony, oak, beech, ash and hornbeam. The walls of the meeting room are lined with vertical ash wood slats. The parquet in the banquet hall is made in the form of a geometric ornament consisting of diamond-shaped figures and ribbons, narrow veins and perpendicularly set patterned inserts. The set is made of maple, oak and hornbeam. The drawing of the parquet of the lobby foyer is a combination of large squares of light oak with narrow stripes of stained oak and white maple.
Furniture is solved (the author of the furniture of the Palace of Congresses K. Blomerius) in a style of unity with the architecture of the building and corresponds to the purpose and nature of the decision of the interior of a room (Fig. 85). The conference room armchairs are lined with polished Pacific walnut, upholstered in red and equipped with special reclining stands.
Soviet architects pay special attention to residential development. One of the most favorable solutions was found by Lithuanian architects V. Čekanaus-Som and V. Bredikis in the Lazdinai region in Vilnius (1974). A model residential area of Moscow, Chertanovo-Severnoye, is currently being built, in which improved living conditions and developed forms of public services are being created.
One of the main tasks of Soviet architecture is the creation of residential buildings with comfortable single-family apartments. Homes with small-sized apartments of the late 50s have been replaced by more comfortable and spacious apartments of the projects of the 70-80s. The proportions of living quarters have improved, many of them are approaching the outlines in terms of the square, the area of bedrooms has increased, kitchens have increased, hallways have become more comfortable, it became possible to place built-in wardrobes and other equipment and amenities in the corridors, the sleeping place disappears rooms specialize.
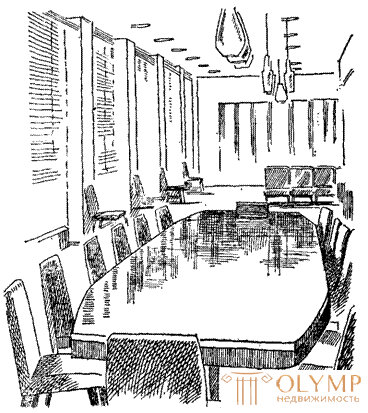
Fig. 1. Cabinet (Palace of Congresses, 1961)
Work on the improvement of single-family apartment in our country went in an organic connection with the development of new progressive types of furniture and the improvement of the material and technical base of the furniture industry.
In December 1956, the All-Union Conference of Furniture Industry Workers was held, preceded by an exhibition of furniture. The exhibition showed prototypes of furniture designed by the USSR Academy of Construction and Architecture, the Moscow Higher School of Industrial Art (formerly Stroganovsky), and the design bureaus of ministries and departments. The exhibition helped outline the future development of design and industrial production of furniture.
The sets of sectional furniture H-30 and H-62, developed by the Central Furniture Design Bureau, received the most approval at the exhibition. A set of H-30s (by E. S. Orlova-Bocharov) of five main types of sections, the combinations of which could give more than 20 different items of cabinet furniture, was also presented at the Moscow exhibition of construction equipment in 1957 and shown in a model apartment in the pavilion USSR at the World Exhibition in Brussels in 1958
In 1958 the First All-Union competition for the best samples of household furniture was held, the main purpose of which was the creation of new models of furniture for standard apartments. Furniture sets were designed with regard to the rational use of space (floor space occupied by furniture should not exceed 28–33%).
For the first time, sectional furniture was shown at the competition, consisting of a series of individual volume elements-sections of various sizes and shapes that can be combined with each other and in height and with locking, creating different versions of cabinets.
The sets of sectional furniture laid the foundations for a comprehensive solution to the interiors. Sectional furniture is divided into four main groups: a separate section is a complete element, independent of the others.
Elements adjoin each other side walls; the lower sections serve as the basis on which the upper sections are mounted; the sections are installed on a special base, solved in the form of a frame on legs or skids; hinged sections.
The design feature of shelving furniture is the presence of variously solved supporting racks: in the form of thin bar structures, metal tubes with devices for spreading between the floor and the ceiling, wooden supports on which shelves and sections are hung. The advantages of the racking design are the ability to preserve spatial connections between different parts of the room, an increased degree of universality.
Versatile and collapsible furniture is economical and rational, easily transported, assembled from flat unified elements. In contrast to the sectional, it does not have double walls.
One of the most rational types of modern furniture is partition cabinets, which can simultaneously serve as walls and cabinets for various purposes. According to the constructive type, they are divided into sectional ones (they consist of separate sections of cabinets and are blocked both horizontally and vertically); universally collapsible (have a small number of planar elements and boxes with common walls for adjacent compartments); frame (include planar elements and boxes).
The competition showed built-in wardrobes, which are usually arranged in wall niches, the ends of corridors and rooms, transverse partitions. Wardrobes and built-in wardrobes for fixed furniture free up the space of housing from bulky mobile wardrobes, making it possible to more freely decide the interior.
Transforming furniture was widely presented, combining furniture products with several functions.
Transformations are most often exposed to beds, which can turn into bed chairs, sofa beds, and also tables (dresser-table, sideboard-table, toilet-desks, etc.).
A special group of modern household furniture is kitchen furniture, the quality of which largely determines the degree of convenience of the apartment. Kitchen furniture is divided into stationary and mobile and consists of desk-cabinets, cabinets, sinks, wall cabinets.
Fig. 2. Furniture for a common room (First All-Union Competition, authors K. K. Blomerius, B. I. Singer, 1958-1959)
The competition gave valuable material and gave impetus to a radical restructuring of furniture companies, as well as for the production of apartment furnishings, showed the need for a comprehensive solution of such interior elements as fabrics, lighting fixtures, wallpaper, decorative furniture, etc.
Among the top awards were furniture for the common room (authors Aus, Kala, Umberg) and samples of furniture by authors K. K, Bloomerius, B. I. Singer, and others (Fig. 2). The competition had a great influence on the work of architects, artists, designers, on the formation of tastes of wide circles of the population.
Along with the growth of housing construction in the country, the demand for furniture grew, the manufacture of which developed based on the application of methods of typing and unifying elements, the appearance of furniture products was improved, the production of new construction and finishing materials increased.
The Second All-Union Competition for the Best Furniture Samples for Residential and Public Buildings (1961) was attended by furniture industry enterprises, design bureaus, design and research organizations, and some higher education institutions.
Fig. 3. The rack in the room (Second All-Union Competition, author Yu.V. Sluchevsky)
Furniture, approved at the competition, differed convenience and beauty. The desire for rational use of living space contributed to the emergence of modern forms of furniture and new interior solutions (Fig. 3). The best works in the competition included a set of furniture for a three-room apartment (the authors are Lilia and Algis Stepulenisa), which was distinguished by well-found proportions, a successful selection of fabrics, and high-quality wood trim. A rational solution of children's furniture was presented by the Standard factory (Fig. 4).
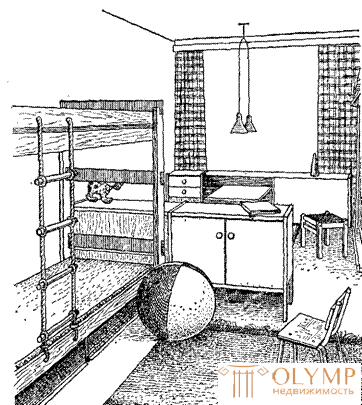
Fig. 4. A set of furniture for the children's room (Second All-Union Competition, Estonian SSR, 1961)
The furniture set developed by a team of authors led by artists A. M. Gurevich and A. Shevchenko differed in their high merit. The set was made of stained ash, combined with polished birch cabinet doors. The color of the upholstery fabric was in harmony with the tone of the wood.
The second All-Union competition showed that furniture designers began to study modern architecture more deeply, to work more attentively on the proportional structure of furniture products, their shape and decoration. The second competition for new samples of furniture revealed a wide variety of solutions, taking into account the features of new types of apartments.
The 60s were a period of revival of the activities of architects and artists in the field of interior and furniture for public buildings (palaces, theaters, cinemas, office buildings, educational institutions, catering enterprises): the Oktyabrsky concert hall in Leningrad (1966, V. Kamensky , A. Zhuk, G. Vlanim, J. Verzhbitsky), cafes “Vana Toomas” and “Tuliac” in Tallinn (1966, V. Tamm, V. Azi), cafe and hotel “Neringa” in Vilnius (1961, A. and V. Nasvitisy) (Fig. 89). In the furniture of the hotel "Neringa" natural wood is one of the main means of its artistic solutions.
Since the 1960s, the production of furniture for public buildings for various purposes has been growing in our country, its assortment has been expanding, and the quality of products has improved. The purpose of a public building is the determining factor influencing the decision of the main groups of furniture. Thus, furniture for children's institutions should be sized to meet the age-specific features of children; its decoration or lining should meet certain hygienic requirements. Children's furniture should be more generalized and concise than the furniture for adults.
The main furniture of the auditoriums - chairs, the design of which should include their installation in rows along the ramp, the possibility of reclining seats, maximum comfort to the viewer.
Furniture for hotel buildings is distinguished by an expanded composition and a diverse design and artistic solution. The degree of comfort, design and technical and economic indicators of hotels determine the number, the equipment of which is necessary to rationally use the floor space and create maximum comfort. Thus, the composition of furniture products, the choice of their type, the direction of the general architectural and constructive solution of furniture depend on the purpose of a public building.
In 1963, a number of institutes were created, which are scientific and design centers for the construction of residential and public buildings and furniture design. One of the main areas of work of the institutes was the comprehensive improvement of mass-produced furniture.
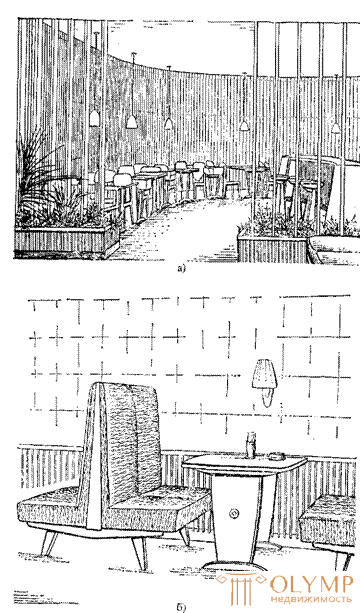
Fig. 5. The interior of the cafe (a) and the furniture in the restaurant (b) of the Neringa Hotel in Vilnius (authors A. and V. Nasvitisa, 1960-1961)

Fig. 6. A set of cabinet furniture for the general room "Sunrise", developed by the group of authors under the leadership of S. A. Selivanov
In connection with the increase in the volume of mass construction, the increase in the welfare of the population of our country, the production of furniture for residential and public buildings is constantly increasing, new, more sophisticated furniture samples are being developed. In October 1973, the USSR Ministry of Forestry and Woodworking Industry, together with the State Committee for Civil Engineering and Architecture under the USSR State Construction Committee, announced the Third All-Union Competition for the Best Samples of Mass Production Furniture for New Apartment Types. Lithuanian set 833 (head of the group of authors V.P. Tsukermanen) was awarded with awards among the sets of furniture for common rooms. A characteristic compositional feature of the set is the vertical rhythm of the protruding side shields and the use of decorative vertical layouts made from solid hardwood wood glued to the plane of the doors. Prizes for the common room were also awarded - “Relief”, “Caravel”, “Tuning fork”, “Sunrise” (Fig. 6); for bedrooms - "Birch", "Sonata", "Necklace", "Autumn" (Fig. 7).
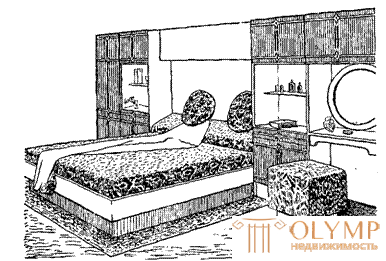
Fig. 8. Set “Autumn” for the bedroom (head of the group of authors Yu.V. Sluchevsky)
The search for contemporary artists is currently taking place both in the creation of new forms of furniture (Fig. 9) and in the traditions of folk art (Fig. 10).
The third All-Union competition showed that the variety of functional processes in the common room and the desire to individualize housing are the reason for the steady tendency to develop not the headsets, but functional groups of furniture, that is, upholstered furniture, cabinet furniture and other things separately. The group of cabinet furniture (wall) is most significant in the spatial and substantive organization of the common room.
The multifunctional purpose of the wall, its saturation with various equipment and devices caused the complication of its internal structure and composition: the alternation of open and closed tiers, the introduction of different-sized similar elements (doors), the free placement of open niches. Plastic body products enriched by the introduction of color. It should also be noted the growing desire to emphasize and identify the vertical division of body products, to saturate facial surfaces with decorative means made by various artistic and technical methods: wood carving (genuine and imitation), pasting with film with ornament, etc. Modern upholstered furniture becomes more sculptural, varied in finishing materials.
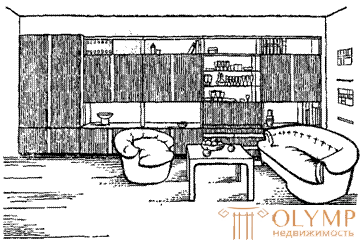
Fig. 9. A set of furniture (the author of the project B. N. Prokopenko)
In the furniture for the bedrooms intensified the search for a variety of artistic solutions. Instead of bedside pedestals, developed solutions of bedside blocks appear, which include open niches, shelves, and drawers in various combinations. In the sets of furniture for the room of a teenager or a child, they strive for the variability of elements and the possibility of combining them, as well as using colors more widely, especially light and bright colors.
Cabinets are usually designed with cabinets with closed compartments of an emphasized vertical construction, sometimes even decorative elements are introduced.
The third All-Union competition showed a significant increase in the professional skills of designers. At present, Soviet furniture makers continue to develop progressive trends that have emerged in the best pieces of furniture noted in past competitions.
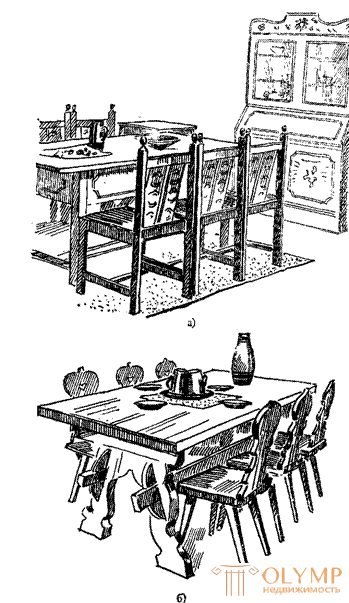
Fig. 10. Modern furniture, designed using forms of folk art: a - a set of furniture for the dining room (by E. Orlova), b - a set of wooden furniture for restaurants
Значительным событием в развитии советской архитектуры и всех с ней связанных отраслей является создание в Москве сооружений и комплексов, предназначенных для проведения XXII Олимпийских игр. В короткие сроки без снижения объемов жилищно-гражданского и промышленного строительства построены и реконструированы 70 олимпийских объектов, многие из которых являются уникальными и не имеют аналогов в практике отечественного и зарубежного строительства. Среди них крупнейший крытый стадион на 45 тыс. мест, крытый велотрек в Крылатском, первоклассный гостиничный комплекс в Измайлове, новый телерадиокомплекс в Останкине, Олимпийская деревня и др.
Осмысление опыта строительства и оборудования олимпийских объектов требует большого и кропотливого анализа, не входящего в задачи настоящей работы. Однако уже сейчас можно отметить огромные успехи советских строителей, архитекторов и художников, выразившиеся в применении новых, наиболее рациональных и прогрессивных конструктивных решений, выразительных объемно-планировочных архитектурных приемов как в решении внешнего облика зданий, так и их интерьеров.
Олимпийские сооружения возведены с применением современных конструкционных и отделочных материалов. Достойное место среди них занимает и древесина. Так, полотно дорожки велотрека в спортивном комплексе «Крылатское» покрыто высококачественной лиственницей и имеет следующие параметры: длина 333,3 м, ширина 9 м, угол наклона виражей 42°, угол наклона прямых участков 11°, их длина 37,07 м. Древесина применена и в отделке интерьеров таких сооружений, как гостиничный комплекс в Измайлове, гостиницы «Салют», «Космос», «Спорт» и др.
Одно из наиболее значительных объектов олимпийского строительства — Олимпийская деревня, расположенная в юго-западной планировочной зоне Москвы. Квартиры, в которых размещались спортсмены, участники игр, были оборудованы специальной мебелью, выполненной из светлой лиственницы. В решении мебельных изделий присутствовало стремление придать им своеобразную трактовку, выраженную лаконичными средствами и ассоциирующуюся с представлением о здоровье, чистоте и красоте.
Бурное строительство различных типов гостиничных зданий явилось причиной развития, проектирования и изготовления мебели для гостиниц, в которой поиск новых форм шел по пути синтеза удобства, технической целесообразности и индивидуальной образной характеристики. Например, мебель для жилых номеров отеля в центре международной торговли и научно-технических связей с зарубежными странами (авторы М. Посохин, В. Кубасов, Б. Скокан, Г. Чернов) характеризуется высокими эксплуатационными, техническими и художественными качествами.
Further development of furniture in our country is due to the fact that furniture is increasingly becoming the main element in the organization of the architectural and planning structure of buildings. The furniture ties with the functional and technological process are strengthened, its compliance with ergonomic requirements, expressed in a scientifically based choice of size, color, texture and other means of functional and aesthetic solutions of furniture products, is growing, compliance with the conditions of mass production and the materials used is enhanced.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)