

ABSTRACTIONISM - a direction in the art of the XX century, in which the work is built exclusively from formal elements: line, color spot, configuration. It originated in the 1910s, after World War II, became the dominant art movement in the countries of Western Europe and North America. The largest representatives: V. V. Kandinsky, K. S. Malevich, P. Mandrien, R. Delone, F. Kupka.

ABSTRACT EXPRESSIONISM - the course of abstract painting, which arose between 1933 and 1945. in America based on European styles. This title combines two different directions of Action Painting (action painting) and Color Field Minting (painting color spaces). The color scheme and the game of colors are a common feature for both directions. The largest representatives are: D. Pollock, V. De Kuning, X. Hofman, A. Gorka, R. Motherwell, M. Rothko, F. Kline.

AVANGUARDISM is a concept that defines experimental, innovative, modernist initiatives in art. At different stages, different directions acted as discoverers.

ACADEMISM is a direction formed in art academies of the 16th — 19th centuries, based on academization (turning it into a norm, pattern and foundation) of an art school of a particular direction.

Empire style 1st third of the XIX century. in Europe, the final phase of the evolution of classicism.

ANDERGROUND - underground culture as an integral part of the so-called counter culture. Originated in the USA. In the USSR, it became the designation of communities of artists representing art that is not recognized by the authorities.

ANTIQUE ART is the art of the ancient era of Ancient Greece and those countries and peoples of the ancient world whose culture developed under the decisive influence of the ancient Greek cultural tradition: the Hellenistic states, Rome, Etruscans, Scythians, Thracians, Gauls, etc.

BARBIZONSKAYA SCHOOL - originated in the 1830-1860-ies. in France. The largest representatives are: J. Dupre, T. Rousseau, N. Diaz, de la Peña. They built canvases on a combination of a realistically imprinted everyday landscape motive and a sublimely romantic perception of nature as a whole.

BAROQUE - style, originated at the end of the XVI century. in Italy, in Europe it was distributed to the beginning of the XVIII century, in Latin America, and partly in North America and Asia - in the XVII — XVIII centuries. The fundamental feature is synthetics. Baroque art is notable for its pomp, agility, exaltation of images.

BUBNAYA VALET - an association of Moscow artists (1910–1916), who turned to pictorial and plastic searches in the spirit of P. Cezanne, Fauvism and Cubism, popular prints and folk toys. The largest representatives are: V. D. and D. D. Burliuki, P. P. Konchalovsky, A. V. Kuprin, M. F. Larionov, I. I. Mashkov, R. R. Falk and others

Biedermeyer, Biedermeier - style direction in the art of Germany, Austria, a number of countries of Central and Eastern Europe in the years 1815-1848. Reflected the tastes of the burgher environment. The largest representatives in the painting: G. F. Kersting, L. Richter, K. Spitzweg, M. Schwind, F. Waldmüller, I. Tomints.

BUNJINGA - Japanese ink painting school, which arose in the late 17th century. The largest representatives are: Taiga Ikeno, Buson Yesa, Tessay Tomioka.

VERIZM is a trend in Italian painting of the end of the 19th century, its principles were formed under the influence of the theory of French naturalism. The largest representatives are: F. P. Michetti, J. Pellitza da Valpelo, V. Vela.

Renaissance, Renaissance, is one of the greatest cultural and historical eras. It began in Italy in the 13th century. and gave way to baroque at the end of the XVI century. It is characterized by cardinal shifts in the orientation and meaningful pathos of culture and the arts, the proclamation of the real world and man as the highest value. Proto-renaissance - the initial period (1260 / 1280-1320). The largest representatives are Giotto, P. Cavallini, A. Di Cambio, N. and J. Pisano. Early Renaissance (about 1401/1420 — about 1500) —the time for the formation and affirmation of Renaissance principles. The leading schools of this time are Florentine, Venetian, Ferrara, Umbrian. High Renaissance - the period of the highest ascent. The largest representatives are: L. Da Vinci, Raphael, Michelangelo, Giorgione, Titian. Late Renaissance (152O / I54O — 159O) - the final stage. The largest representatives are: Michelangelo, Titian, Veronese, Tintoretto, Palladno. The Pleiad of outstanding Renaissance masters worked in the 1st half of the 16th century. in Germany: A. Dürer, X. Holbein the Younger and others. The culmination of the national line in Dutch art was the work of P. Bruegel the Elder. Renaissance had a decisive impact on the subsequent development of European art.

HYPERREALISM - the direction in European and American art of the I960-1980-ies, using a color photograph or a model to reproduce individual fragments of Reality. The largest representatives are: D. Eddy, R. Estes, R. Goingo, R. Cottingham, B. Schonzai. M. Morley, C. Close, D. de Andrea, D. Hanson.

GOTHIC - a style that emerged in the middle of the XII century. Replaced the Romanesque style, in the XV — XVT centuries. gave way to the Renaissance. Inherited and developed the religious-cult hierarchical character, irrationalism and symbol, and the callegorical nature of thinking. Its features are: the organic connection of fine art with architecture and interior, the complexity and rhythmic richness of the composition, the spirituality and sublimity of images. Late Gothic ("flaming" or international, "perpendicular style"), together with the complexity and underlined verticalism of the decor, introduces features of individuality, greater intimacy and secular elegance. GOHAU, chung gohua - the traditionalist trend in Chinese painting, which arose at the turn of the XIX-XX centuries; painting with mineral and vegetable water colors and black ink, it is characterized by the use of techniques developed in antiquity and the preservation of traditional medieval genres.

GRAFFITI - a movement in art that emerged in the youth culture of the United States and spread in Europe in the 1960-1970s. Graffiti is the art of streets, and artists, mostly young people, use multicolored sprays (paint in cans) as a painting material. The role of the canvas is played by the walls of buildings, public transport, fences. Some representatives of this direction paint with colored chalk, for example, Kate Haring.

GUN-BI - in classical medieval painting and modern traditionalist Chinese painting Guohua is one of two (along with se-i) complementary manners; based on the finest graphical elaboration of details, clear readable line.

DADAISM is a movement that originated in Zurich in 1916 among the emigrants. Intellectual rebellion. The largest representatives are: M. Du-shan, F. Pikabiya, X. Arp, M. Ernst, C. Schwitters.

DECADE - a collective designation for non-traditional phenomena in the art of the 2nd half of the HGH - the beginning of the XX century. Characteristic features - the mood of decline, the motives of death and non-existence, the cult of beauty, unlimited freedom of personality and creativity.

Ancient art - 1) the art of ancient Russia (IX-XIII centuries.), The initial stage of development of medieval Russian art, the time of its addition, the Christianization and the first flowering. It served as a model and base for the development of Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian art schools of the XIV-XVI1 centuries; 2) Medieval Russian art (IX-XVII centuries.).

ANIMAL STYLE - a type of ancient and medieval ornament, dating back to the totem worship of the beast-progenitor. It was distributed to the Scythians, Sakas, Altaians, Thracians, Sarmatians in the I millennium BC. e., the Celts and the Germans - in 1 thousand n. e., in medieval Russian art (mainly in miniature books).

Impressionism - a direction in art in I860 - the beginning of the XX century. Its representatives sought to impartially and naturally capture the surrounding world and everyday life in their mobility and variability, to convey their fleeting impressions. The largest representatives are: E. Manet, C. Monet, O. Renoir, A. Sisley. C. Pissarro, P. Cezanne, E. Degas, B. Mornzo, A. Guillaume, E. Boudin, J. Whistler, M. Liberman, L. Corinth, K. A. Korovin, I. E. Grabar, O. Rodin, P. P. Trubetskoy.

KANO - Japanese school of painting, which developed during the 2nd half of the 15th-20th centuries. She developed the techniques of the school of Tosa and the tradition of monochrome painting. The largest representatives are: Kano Masano-bu, Kano Motonobu, Kano Eytsku.

Karavajism - artistic direction, characteristic of the initial stage of development of realistic painting of the XVII century. The main feature is the monumental world of the everyday world using light and shade contrasts. Created by Caravaggio and his followers: O. Gentileschi (Italy), X. Terbryugten (Netherlands), X. Riberau (Spain).

KINETIC ART - a trend in modern art that makes extensive use of moving structures and other elements of dynamics; took shape in the 2nd half of the XX century. in the USSR in the 1960s, a kinetic group "Movement" operated.

CLASSICISM - style and trend in artXVII - early. XIX centuries., Turned to the ancient art and art of the High Renaissance, as a model. It is characterized by balance, clarity, plastic clarity and harmony. The largest representatives: in painting - N. Poussin, S. Lebrun, C. Lorrain, J. L. Daville, J. O. D. Ingres; in Russian sculpture - M.I. Kozlovsky, F.F. Shchedrin, I.P. Martos.

CONCEPTUAL ART, conceptualism - the direction in avant-garde, originated in (960-ies. The peculiarity consists in refusing to translate the idea into the material. Conceptual objects exist in the form of sketches, projects, texts; the subject of contemplation is the mental form. The most influential union is the English group "Art-language."

KOSTUMBRIZM reproduction of life, mores, types of people, nature, urban and rural streets and interiors, idyllic and irony notes. The largest representatives are: V.P. de Landalus, R. Torres Mekdes, X. A. Arrieta.

CRITICAL REALISM - the direction in the art of Europe and America, which arose in the middle of the XIX century. Focused on the direct image of the daily life of people. The largest representatives are: O. Daumier, P. Gavarni, G. Courbet, J. F. Millet, C. Meunier, A. Menzel, V. Leibl, M. Munchachi.

CUBISM - a trend in French art in the 1900-1910s. Characteristic is the predominance of straight lines, faces and cuboidal forms in paintings. The largest representatives are: P. Picasso and J. Marriage. The most famous groups are “Bato Lavoir” and “Golden Section”.

MAVRITAN ART - a style that was formed as a result of the merging of the artistic traditions of the Arab caliphate, Berbers and Visigoths. In the ornaments, masterly executed complex compositions of geometric and plant patterns, inscriptions are distinguished by a variety of forms and variants, an exquisite combination of linear graphics and color accents.

Mackyayooli - a current in Italian painting of the 1860-1880s The name is given for the style of writing free colorful spots. The largest representatives are: T. Sinorini, J. Fattori, S. Lega.

SMALL DUTCHS - the symbol of Dutch painters of the 17th century, so called due to the chamber character of the work and the small size of the paintings.

MANIERISM as the basis of the artistic image; its external expression is the sum of certain stylistic devices (“beautiful manner”). The “manners” style system includes anti-classical beginnings (elongation of proportions, irrationality of spatial and color relations, serpentine rhythm of movement) and canonization of complex formulas of movement, derived from Raphael And Michelangelo.

METAPHYSICAL PAINTING is a trend in Italian art that emerged in 1916 as a reaction to the radical anti-traditionalism of the futurists. Pictures of "metaphysics" are full of hints, associations, literary and mythological references. The largest representatives are: J. De Chirico, C. Carr, A. Savigno, L. De Pisis, J. Morandi.

MODERN - style in Europe and America at the end of the HGH - the beginning of the XX century. (other names - ar nouveau, art nouveau, secession, liberty, modernism). The inseparability of genres and types of art within the framework of modernity led to a relative lack of independence of painting, drawing and sculpture, and to a revival of the type of the universal artist. Flatness, ornamental character of the whole with illusionistic and naturalistic details included in the fabric of the painting is characteristic of modernism. The sculpture of modernism was distinguished by the fluidity of its forms and the quaintness of its silhouette. Received book and magazine graphics. The members of the Nabi group, the World of Art group and others worked in the Art Nouveau style. The largest representatives were M. Denis, P. Bonnard, E. Vuillard, P. Seruzier, G. Klimt, M. A. Vrubel, V. M Vasnetsov, K.A. Korovin, E. Munch, F. Hodler.

NAZAREANS - German and Austrian artists, members of the Union of St. Luke (1809), representatives of the German school of painting of the Romantic era. Sought to revive medieval religious art.

Naive art - one of the areas of primitive art XVIII-XX centuries. Includes visual forms of folk art, the work of self-taught artists, amateur art. It develops in areas mastered by professional art, but retains its own goals and original technique.

NATURALISM is the direction in European and American art of the last third of the 19th century, programmatically seeking to liken the artistic knowledge to the scientific. Contributed to the formation of critical realism.

NEOIMPRESSIONISM - a current that arose in France ca. 1885 Gave a scientifically grounded character to the techniques of decomposing complex tones into pure colors and writing techniques with separate strokes. The largest representatives: J. Seru, P. Signac.

NEOCLASSICISM - a term denoting various trends in art that arose after the classicism of the 17th century, orienting on the classical examples of art of Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome and the Renaissance and aimed at making them a criterion of modern art. Most often, the term “neoclassicism” is used to designate the flow within the modern style, early functionalism and early avant-garde of the first quarter of the 20th century. Its characteristic feature is its relation to the ancient and renaissance heritage as the highest artistic norm.

NEOPLASTICISM - a current in architectural and artistic art, which arose in 1917-1928. in Holland and related to Style magazine (Leiden). Founder: P. Mondrian.

NEORALISM - the direction in the art of Italy of the period after the Second World War. Characterize the image of the lives of workers and peasants, their struggle for their rights. Characteristic forms of expressive realism: dynamic composition, energetic delineation of volumes, rich color. Representatives: R. Guttuso, G. Mukki, 3. Trekkani, J. Dzigayna, A. Pitstsinato.

Neo-traditionalism - the designation of a wide range of artistic phenomena in the culture of the XX century, associated with the direct reliance on the traditions of art, recognized as a layer of culture, resisting avant-garde. One of the largest directions of the XX century, and in a number of countries dominating. Vivid speeches of neotraditionalism - P. Picasso's neo-Enghrism (1910s), appeal to the tradition of A. Derain, O. Dix, K. Kappa. M. Campigli, association AHRR, social realism.

“NEW REALITY” is the direction in the art of Germany in 1925-1933, which sought to counter the disturbing ecstaticism of expressionism with an objective depiction of reality. Representatives: J. Gross, O. Dicke, A. Kanolt, G. Schrimpf, E. Vigener, C. Grosberg, G. Davringhausen.

NOVECHENTO - a trend in the art of Italy in the 1920s, which sought to restore the continuity of tradition. It formed the official art of the fascist dictatorship. Representatives: L. Dudreville, A. Funi, P. Marussig, U. Oppie, M. Sironi.
NEW WILD - direction in American and European art of the 1970-1980s, which brought to the limit the principle of spontaneity, freedom from any rules and restrictions. Representatives of: Salome, M. Disler, 3. Polke, G. Baselitz, G. Pents, I. Dokupil, I. Vavrin.

OP-ART is a trend that became widespread in the 1960s. She continued the technical line of modernism, used visual illusions, relying on the features of perception of flat and spatial figures. Representatives: V. Vazarelli, B. Riley, X, R. Soto, R. Anushkevich, L. Punz, K. Cruz-Dies.

TRAVELERS - members of the Russian Democratic Association Association of Traveling Art Exhibitions (1870). Followers of realism, put forward a program of folk art (depicting typical aspects and multifaceted characters of social life, often with a critical trend). Exhibitions organized by them in different cities of Russia were a noticeable phenomenon in cultural life. The last (48th) exhibition was held in 1923. The largest representatives are: I. N. Kramskoy, G. G. Myasoedov, N. N. Ge, V. G. Perov, K. A. Savitsky, I. E. Repin , A.K. Savrasov, I.I. Levitan, V.I. Surikov, V.M.Vaznetsov.

POP-ART - a trend in painting that spread in the United States and England in the 1950s. Characterized by the use and processing of images of mass culture. He marked the rejection of abstractionism and the transition to the concepts of a new avant-garde. Artists showed a new mechanized world, presenting things as something beautiful. The beginning of pop art was laid by the activities of the London Independent Group. He gained international fame in the American version: R. Rauschenberg, J. Jones, E. Warhol, J. Rosenquist, R. Lichtenstein, R. Hamilton, T. Wesselman, K. Oldenburg.
ПОСТИМПРЕССИОНИЗМ — собирательное Наименование нескольких направлений французского искусства рубежа XIX—XX вв., декларировавших неприятие эстетики импрессионизма и следующих за ним хронологически. Является связующим звеном между искусством XIX и XX вв,

ПРЕРАФАЭЛИТЫ — группа английских художников и писателей XIX в., следующих идеалам искусства средних веков и Раннего Возрождения (до Рафаэля). Членами «Братства Прерафаэлитов» являлись: Д. Г. Россетти, X. Хант, Дж. Э. Миллес и др

PRIMITIVISM is a broad trend in the art of the late HGH-XX centuries, consisting in following primitive, naive art. Primary art, the traditional art of the peoples of Africa, Oceania, America, fine art of the lower classes and self-taught artists became its guides. Characteristic features - spontaneity, brightness of expression, beauty, simplicity of form. The largest representatives are: A. Rousseau, L. Serafan, grandmother Moeei, I. Generalich, N. Pirosmani.

PURISM - the direction in the French art of the 1920s .; decorative tasks, extremely strict in form. The largest representatives are: A. Ozanfan, S.-E. Jeanneret (Le Corbusier).

REALISM - one of the main trends in the development of world art, suggests stylistic diversity and has its own specific historical forms: the naive life-like rock paintings of ancient eras, the idealization of ancient art, the late Gothic spirituality, etc. Especially intense in Renaissance art. The realism of art of the XIX — XX centuries. marked by social orientation.

REGIONALISM, regionalism is a trend in the art of the USA of the 1920s – 1940s that focused on the image of “authentic America” and was inspired by the ideas of national exclusivity and originality of development. Characteristic is the imitation of American self-taught artists of the 18th — 19th centuries.

ROMAN'S STYLE - the first large-scale artistic style after antiquity, which united all forms of art in vast territories. Its development lasts from the XI century. until the middle of the XII century. The iconography of paintings and reliefs is clearly defined. Characteristic abstraction, historical rigor, flatness and simplicity of form.

ROMANTICISM - the ideological and artistic movement in European and American culture of the end of XVI - beginning of the XIX century. It originated as a reaction to rationalism and the self-assured optimism of the aesthetics of classicism and the philosophy of the Enlightenment. Characteristic appeal to art to Raphael, the analogy of genius, faith in the omnipotence of the artist. The largest representatives in painting: E. Delacroix, T. Gericault, W. Blake, I. G. Fussli, C. D. Friedrich, F. O. Runge, O. A. Kiprensky, K. P. Bryullov, A. A. Ivanov.

SALON ART - a conservative trend in the artistic culture of Europe and America of the 19th - early 20th centuries, the name was due to its support from the Parisian salons. Common features: eclecticism of a creative method based on the norms of academicism and late classicism and using outwardly perceived methods and techniques of romanticism, later realism and naturalism; spectacular beautiful composition and unambiguous content; straightforward interpretation of topics; formal completion; pathos; rejection of innovative art. Representatives: T. Couture, A. Cabanel, A. Bouguereau, J.-L. Jerome, F. Cormont, S. Shaplen, F. Winterhalter, E. Carolus-Durant.

CULTURAL ARTS - a special type of mass artistic culture (not professional and not folk, traditional): the field of free artistic creativity of autodidacts, self-taught people, people who do not have professional training in art, engaged in artistic activities at their leisure. It always existed as a parallel world in relation to professional art; it became an independent practice in the 20th century, when there was a need for a special organization, support for amateur artists. It has a wide social base.

SYMBOLISM - the direction in European and Russian art at the turn of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The masters of this direction were united in their ideas about art as a symbol of unknowable entities, in search of non-allegorical ways of expressing the ideal beginning. Characteristics: polysemy of an image, game of metaphors and associations. It arose as a reaction to the limited positivist aesthetics and late realism. The largest representatives are: P. Puvis de Chavannes, G. Moreau, P. Gauguin, M. Denis, D. G. Rossetti, M. Klinger, E. Munch, A. Becklin, F. Hodler, A., Ryder, M. A. Vrubel, V.E. Borisov-Musatov, N.K. Roerich, members of the Blue Rose Association.

SYNTHETISM - the picturesque system that emerged at the end of the XIX century. in France. It is characterized by a decorative generalization of color spots, the total symbolic character of the images, and the refusal of detailed images. The largest representative: P. Gauguin. Followers: Pont-Avensky school.

SOC-ART is one of the most well-known areas of Soviet art of the 1970s and 1980s, established within the framework of the so-called alternative culture that opposed the state ideology of those years. Using ironically and grotesquely reworking the common symbols and signs of socialist agitation, I debunked their true meaning in the playful, often pathetic form. Since the late 1980s. enters the international arena. The political reorientation of society predetermined its decline.

SOCIALIST REALISM - a theoretical principle and artistic direction that occupied the USSR from the mid 1930s to the early 1980s. official dominance. The goal was to establish socialist ideals in a generally accessible realistic form. The largest representatives are: N. A. Andreev, S. D. Merkurov, I. D. Shadr, V. I. Mukhina, G. G. Ryazhsky, A. M. Gerasimov, B. V. Johanson, A. A. Deineka , D.S. Moore, Kukryniksy.

STROGANOVSKAYA SCHOOL - the direction in Russian icon painting of the end of the XVI - beginning of the XVII century. Most of the icons of this school were created by the Tsarist icon painters in Moscow, who also fulfilled the orders of the Stroganovs merchants. They are distinguished by their small size, miniature letters, complexity of composition, and fantastic landscape backgrounds. and Nikifor SaIs renowned masters: P. Chirin, E. Tom, Nazarin. Moskvitin, Is

SAYBOKUGA - Japanese ink painting school, which appeared at the end of the XIV century. based on Chinese monochrome painting. Representatives: Mokuan, Zesetsu, Sessu, Sasson.
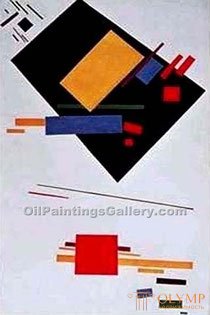
SUPREMATISM - the direction in the avant-garde art of Russia, the founder of which is the painter KS Malevich, a kind of geometric abstraction. Representatives: K. L. Boguslavskaya, I. A. Puni, I. V. Klun.

Severe style - originated in Russia in the late 1950s - early 1960s. Dramatically changed the content of the thematic picture established within the framework of socialist realism. Characteristic features: monumental compositions, generalized laconic forms, energetic rhythm, large color spots. Representatives: N. I. Andronov, A. V. Vasnetsov, G. M. Korzhev, V. I. Ivanov. P. F. Nikonov, T. T Salatov.

SURREALISM is a trend in the art of the 20th century that chose the sphere of the subconscious (dreams, hallucinations) as a source of inspiration and replaced logical connections with free associations. The largest representatives in the painting: M. Ernst, A. Mason, J. Arp, J. Miro, S. Dali, P. Bloom, R. Magritte, P. Delvaux, I. Tanguy.

TASHISM is a current close to abstract expressionism, a painting of action that became widespread in 1940-1950 gt. Representatives of this direction created original compositions from chaotically located smears and spots. Representatives of P. Soulage, J. Mathieu, H. Hartung, J. P. Riopel, J. Bazin, E. Vedova, A. Jorn, C. Appel.

UKIE-E - in Japanese painting and graphics XVII-XIX centuries. direction that reflects the life of the urban population. Representatives: H. Moro-nobu, K. Utamaro, T. Syaraku, K. Hokusai, A. Hiroshige.

PHUVISM, wild - the direction in French art of the beginning of the XX century. Characteristic features: extremely intense sounding of open colors, comparison of contrasting chromatic planes enclosed in a generalized contour, reduction of the form to simple outlines in case of rejection of the cut-off modeling and linear perspective. The largest representatives are: A. Matisse, J. Braque, J. Rouault, A. Derain, A. Friez, A. Marquet, M. Vlaminck, R. Dufy, J. Flandren, K. van Dongen ..

FUTURISM - the direction in Italy and Russia at the beginning of the XX century. Rejected the traditional culture in all its manifestations. “Energy” compositions with figures fragmented into fragments and with sharp corners intersecting are characteristic. The largest representatives are: W. Boccioni, K. Kappa, L. Russolo, J. Severini, J. Balla, E. Prampolini, F. Depero. In Russia there was the direction of cubofuturism (D. Burliuk, O. Rozanova).

EXPRESSIONISM - the direction of the beginning of the XX century. The largest representatives are: the Dresden Most association (E. L. Kirchner, E. Heckel, C. Schmidt-Rotluf, F. Bleil), E. Nolde, M. Pechstein, O. Muller; the Munich Association of the Blue Horseman ”(V. Kandinsky, F. Mark, A. Macke, P. Klee, A. Yawlensky, G. Kampendonk, A. Kubin).

YuHUA - an innovative trend in Chinese painting; opposes gohua; Oil painting 1 m and paints using techniques introduced from the West.

YAMATO-E - in the fine arts of Japan of the 10th — 12th centuries. independent, actually Japanese direction, opposed to Kara-e (meaning "Chinese painting"). Characterized by the reproduction of plots of medieval Japanese novellas, novels and diaries on scrolls, expressive combination of clear silhouettes and bright color spots, interspersed with gold and silver sparkles.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)