In some cases, in the upper part of the base of the building being erected there may be a weak layer of soil, therefore there is a need to transfer pressure from the building to more dense soils that occur at a certain depth. In these cases, often arranges the foundations of the piles, which are able to perceive large loads compared to the foundations of shallow lay and, moreover, are more economical, since with their impact the volume of labor-intensive earthworks and works decreases.
Piles are called relatively long rods, immersed in the soil in finished form or manufactured in the soil in a vertical or inclined position. A pile structure (foundation) is a group of piles, combined on top with special slabs or beams, called grillages . Rostverka are low or high.
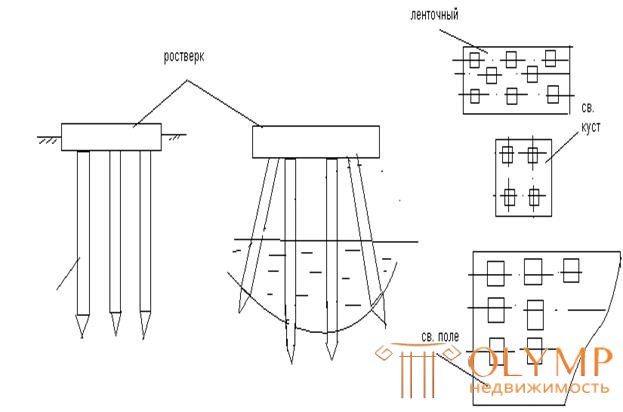
In the practice of modern construction, depending on the constructive solutions of buildings, the following types of pile foundations are used: single piles, used for light structures, when one pile perceives the load from the building column; strip foundations used under the walls of buildings, with the placement of piles can be single-row and multi-row, pile bushes, erected for individual structures (usually columns of frame buildings), solid pile field for heavy structures.

Nomenclature and scope of piles.
In domestic practice, more than 150 types of piles are known, which are classified:
1) by material: reinforced concrete, concrete, lightweight aggregate, wood and steel
2) by construction: solid and composite square, round, rectangular and polygonal with and without broadening, with and without a tip, prismatic and pyramidal (conical), hollow and solid section, screw, piles and columns;
3) by type of reinforcement: with prestressing and non-stressed longitudinal reinforcement, with transverse reinforcement of the trunk and without it;
4) according to the method of manufacture and immersion: prefabricated and monolithic, secondary drilling, bored, including with a sealed bottom;
5) the nature of the work in the ground: piles-pillars, based on almost incompressible soils, and trailing piles, buried in compressible soils.
The pile column is a driven pile with non-stressed square reinforcement, the above-ground part of which serves as a column for the building. The pile-column differs from the corresponding pile by the presence of embedded parts and the increased, if necessary, content of longitudinal reinforcement. For light agricultural buildings developed piles, columns with consoles. Piles-columns are recommended for use in medium-density sands and clayey soils of a refractory and semi-solid consistency.
Bored piles are made in the ground. The reinforcement cage is installed into the drilled well and the concrete mix is laid after the concrete reaches the strength, the pile can perceive design loads.
Ramming pile with compacted base. The compaction of the base increases the bearing capacity of the stuffed piles. The base is compacted by punching a well 2-6 meters long, with a diameter of 40-80 cm. conical pipes with cast club-shaped ramming, or by sealing the bottom of a drilled well with heavy cylindrical rammers with tamping, if necessary, rubble.
Such piles are used in low-moisture resistant clay soils, they can rely on the roof of sandy soils.
In some areas of the country, claydite-concrete piles have been used, in which expanded clay is used as large aggregate, which makes it possible to lighten the weight of the piles by 20-30% and thereby reduce their longitudinal reinforcement and use lighter hammers to sink the piles.
In areas where the forest is a local building material, on sites that are composed of weak soils, as well as tight plastic clay soils and medium density sands, it is advisable to use wooden piles with high groundwater levels. It is allowed to use these piles for capital buildings under the conditions of a permanent position of the heads of the piles below the underground water horizon for not less than 0.5m. Wood piles are made from coniferous timber (pine, larch, spruce, fir) and can be whole and composite single-barrels with a diameter of 18-40cm; solid and composite batch, consisting of 2-4 trunks, with a diameter of 32-40cm; the longest length of solid piling trees is 8.5 m, composite ones - 15 m.
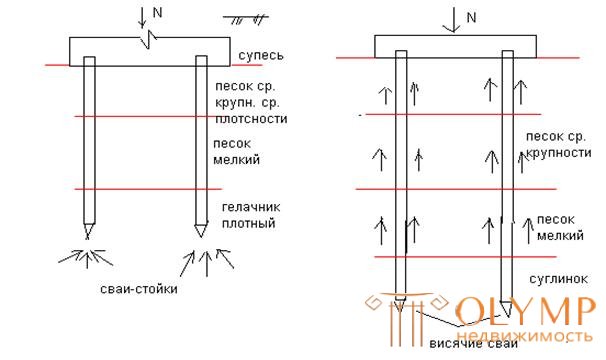
According to the method of transferring pressure from the building to the base, pillars and friction piles (trailing piles) are distinguished. Piles - racks with their lower end can rest on practically incompressible soils: rocky, dense coarse-grained, or dense clay soils. The friction forces on the side surface practically do not arise, and their bearing capacity depends only on the bearing capacity of the soil under the tip of the pile:
F = Rs (where Rs is the resistance of the soil under the tip of the pile.)
Friction piles (trailing) are surrounded on all sides by compressible soils, and the load on the base is transferred both by friction forces along the side surface of the pile Rf and due to the resistance of the soil under the lower end of the pile Rs. The bearing capacity of such piles is determined by the expression
F = R f + Rs
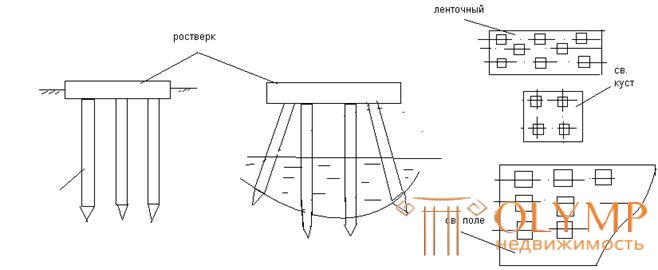
Constructions of pile grillages .
The construction of the pile foundation is completed with a grillage device, that is, a structure connecting the heads of the piles. The heads of the piles should be firmly connected with each other and with the grillage. For this purpose, reinforced concrete piles expose reinforcement not less than 25 cm when working piles for a vertical load and 40 cm when working piles for a horizontal load. Pile heads are embedded in the grillage concrete at least 5 cm and 10 cm respectively. If a reinforced concrete grillage is arranged on wooden piles, then the heads of the piles are sealed for at least 30 cm. In the bridge piers, the heads of the piles are embedded in the grillage of not less than twice the thickness of the pile shaft.
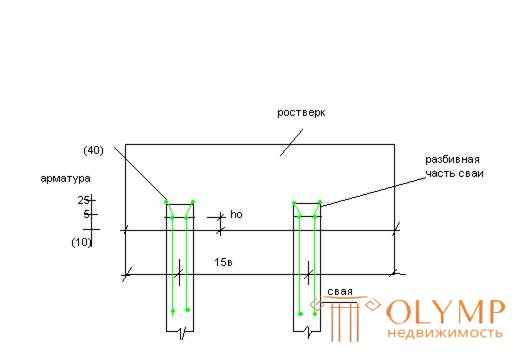
The distance between the axes of the hanging piles should be between (3É6) and (in - the width of square piles or diameter of the round) the minimum distance between the axes of the pillars is 1.5 v; the distance from the edge of the grillage to the outer side of the pile with its free fixing in the grillage is taken when placing the piles: single row - not less than 0.2V + 5cm; two and three-row - 0.3V + 5cm and with a large number of rows 0.4V + 5cm.
Grillages are made of monolithic or precast concrete. Height of the grillage is assigned according to the calculation for pushing in accordance with the requirements of the design standards for reinforced concrete structures according to the formula:
(1) hp = -b / 2 + 1 / 2√b2 + N / k * Rbt,
where:
b- width or diameter of the pile
N-force per pile
k is a coefficient taken to be 1
Rbt is the calculated resistance of concrete to axial tension; usually, by design considerations, hp≥ho + 0.25 m, but not less than 30 cm
(ho- the value of the pile embedment in the grillage)
During the immersion of piles, deviations from the project at 0.3v piles are allowed. Such a deviation of the piles from the design axis causes an additional requirement that the overhead of the pile cap should be at least 0.2V of the pile and not less than 5 cm. Outlets of the pile reinforcement should be welded to the base reinforcement of the pile cap.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)