Diagnostics is the process of determining the technical condition of the structures being examined, it consists in identifying defects in structures, ascertaining the reasons for their formation and the effect on the performance of structures.
The survey is a set of measures to determine and assess the actual values of the monitoring parameters characterizing the operational state, suitability and operability of the objects of the survey. This is a process that includes the monitoring, testing, analysis and evaluation of structures. The survey is carried out in connection with the possibility of reconstruction, technical re-equipment, major repairs, in connection with the detection of defects, after an accident or a long break in construction and installation works.
The purpose of the survey is to ascertain the operational qualities of the structures for making a decision on the feasibility of repair and reconstruction, finding out the causes of the accident, and predicting the behavior of structures in the future.
A defect is a separate inconsistency of structures with any parameter, it is an imperfection, inconsistency with standards, specifications, and design standards. Defects are established by regulatory documents or projects.
Stages of the survey and scope of work.
1. Preparatory work.
2. Preliminary (visual) examination.
3. Detailed (instrumental) examination.
4. Calculation of loads and impacts.
5. Verification calculations of structures and their elements.
6. Registration of the survey results in the form of a separate report.
Preliminary inspection of buildings .
A preliminary survey is an analysis of the available documentation and a thorough inspection of the building. Particular attention is paid to such characteristics as:
- - age of the house and its belonging to the historical environment of the city;
- - material and technical condition of bearing structures,
- - structural design of the building and restructuring carried out during operation,
- modifying the scheme of work structures;
- - analysis of the conditions of maintenance of elements of the building, fixing all deviations from the rules of operation.
On the basis of such an analysis, they reveal the causes of the appearance of existing defects, investigate the heat-humidity and aeration regimes of the attic and basement rooms. Establish the quality of maintenance of facades and ceilings. As a result of a preliminary survey, sites for the necessary opening of structures for their examination are determined. Make up a task for technical inspection.
The composition of the technical survey includes a detailed study of the architectural-planning and volumetric solutions, structures and engineering equipment of the building. The purpose of this survey is to develop a technical opinion on the strategy for repairing and restoring the carrying capacity, damaged structures, and measures to ensure the safe operation of the structure in the future.
During the examination, they seek to reveal the actual scheme of work of the elements included in the unified building box system. In it, most of the structures work not independently, but in interaction with others. This affects the redistribution of loads due to an increase in the rigidity of the body of the building as a whole with time, the appearance of homogeneous nodes, the inclusion of partitions in the operation of floors, etc.
The quantitative assessment of these factors, which have a favorable effect on the work of structures, is a serious task, the solution of which goes beyond the framework of normative and reference documents used to calculate the structures of new construction.
On the other hand, the use of the reserves of strength that have arisen during the operation of the building, is an urgent task of design. When developing a project - repair and reconstruction - it is tempting to use these reserves. Therefore, a detailed survey arises the need for a scientific study of the work of structural elements.
The survey of space planning solution aims to obtain detailed data on the architecture of the building and its facades. In the process of examination, the dimensioned drawings of floor plans, sections and facades are compiled.
Floor plans are on a scale of 1: 100 with an accuracy of measurements + 0.01 m. On these plans indicate the purpose and nature of the use of the premises,
cause the dimensions of structural elements and sanitary equipment. Details that cause additional load on the supporting structure, especially noted. Cuts in the scale of 1:50 or 1: 100 make the most characteristic places of the building. In this case, a cut along the staircase is required. In the drawings put down vertical marks, thickness and details of the main structures. Vertical binding of window openings and architectural divisions of facades is given.
The facades of the building are performed on a scale of 1: 100. To facilitate the work using photographs of the building and its architectural details. They also take photographs of the adjacent houses, which will help to later link the facade with the neighboring building.
The general plan of the site is on a scale of 1: 500. It shows the adjacent buildings, green spaces and sections of adjacent streets.
Bearing and enclosing structures are examined for information about their strength and reliability. The main load bearing elements are thoroughly examined: foundations, walls, pillars and columns, floors and roofs. As a result, after carrying out calibration calculations, make up a technical conclusion, where they give an assessment of the strength of the building and its elements. Determine the allowable load on individual structures. Recommend measures for their restoration and strengthening.
In the process of examination of soil grounds reveal the following data:
1) physical and mechanical properties (porosity, humidity, specific cohesion, angle of repose);
2) the uniformity of the base and the degree of use of the value of permissible pressure under the base of the foundations;
3) uneven pressure at different sites, the nature of the sediment and deformations.
Foundation designs are examined by determining the following parameters:
- - geometric dimensions of structural elements, including supporting parts;
- - strength and wear of materials of supporting structures;
- - humidity, uniformity and durability of masonry, concrete or concrete;
- - the presence of reinforcement in the elements of the foundations, its condition and degree of wear.
As a result of the survey, they make up a description of the foundations and the underlying rocks, perform measurement drawings, including details of the basement floors. Measurements are made with an accuracy of ~ 0.01 m. In the description indicate the permissible pressure on the base under the building, the actual specific load under the sole, obtained by calculation. They characterize the design and structural scheme of foundations, their constructive solution, deformational changes and the quality of materials.
The walls of the building are examined in the following order. First of all, analyze the design scheme of the entire structure, identifying the bearing and self-supporting walls. After that, proceed to the study of structures. The scope of the survey depends on the type of repair. Particular attention is paid to the examination of cracks, signs of weathering, swelling or peeling of walls from the vertical.
Cracks are measured by probes, which lead to the laying or physical methods, such as pulsed. Gypsum beacons are placed on the cracks in especially important places. Watching them, judged on the dynamics of the process of cracking. Apply and rapid methods, such as sensors that capture even a slight movement of masonry.
During the examination it is important to establish the solidity of the walls. Channels, pledged openings, other voids or delaminations that appeared during operation, can be easily identified by penetrating radiation or ultrasound.
Armature and metal embedded parts are determined by electromagnetic methods. They can also set the cross section of the metal. As a result of the survey, dimensional drawings of the building plans are made. Dimensions are stamped with an accuracy of + 0.01 m. These drawings complement the executive scans of the walls. They show all the channels and places of mortgaged openings. The location of the cracks, their nature and interconnectedness, the depth and duration of the formation are indicated. Note the fittings and metal fasteners.
Overlaps are such parts of the building, the technical condition of which largely determines the overhaul strategy of the entire structure, therefore, these structures are examined very carefully. In some places open the floor and cladding ceilings. In the occupied apartments, such an opening is difficult, and therein lies a certain complexity of engineering surveys.
During the survey, the following overlap characteristics are established:
Studying the design and structural scheme, consider the possibility of joint operation of bearing elements of floors, the role of intermediate supports, to which a part of the load that is not provided during construction can be transferred. They also determine the influence of the embedment of beams, since over time they can turn into a rigid support capable of perceiving moments.
Identify the location and cross section of metal beams, reinforcement and steel embedded parts. Use electrophysical methods. For these purposes, designs are opened less frequently, since with modern technology, non-destructive methods give very accurate results.
The technical condition of the structural elements and the quality of the materials used are established by sampling and subsequent laboratory analysis. Samples are drilled with special drills in the least loaded sections of the structure.
The deflections of the floors are examined by leveling and measuring the ceiling and the supporting beams by deflectors. At the same time check the suspension in the center relative to the supports.
Floor deformations are examined by cracks in the ceiling. They appear as a result of uneven sediments of the building box, shrinkage in the construction itself, dynamic and static loads exceeding the normative ones.
In the direction and depth of crack opening, the carrying capacity of the overlap is evaluated. Sometimes for such an assessment it is necessary to study the dynamics of the process of cracking. Then install "beacons".
When examining the dimensioned drawings. They are applied to the place of opening, the axis of the beams and girders. Lead cross-section over the ceiling, fix the location of the cracks and the affected nodes of the elements. Dimensions are stamped with an accuracy of plus or minus 0.01 m.
Ladders are examined by determining the following data:
1) the material and design features of the marches and platforms, the constructive solution of the junctions;
2) the nature of the deformations of the bearing elements, cracks and damage to the steps, the plates of the platforms, the places of the embedding in the walls;
3) march slopes and the presence of zabezhny steps.
These structural elements of the building are examined by the methods used in engineering surveys on the floors. The results of the survey are applied to floor drawings and dimensioned floor plans.
Partitions examined by inspection, tapping and sensing. At the same time, deformations of these non-supporting structures, cracks and expansion are detected. Examine the presence of loads from the floors, as a result of unintended project deflections of beams and girders. In buildings where floors will not be changed, it is established which of the partitions can be disassembled and which cannot.
Check soundproofing properties. In places of increased sound conductivity establish the causes of defects in the places of junction to adjacent elements. If they detect the penetration of sound waves over the entire plane, then study the sound-insulating layer.
The wooden partitions check the quality of the wood. It is analyzed for fungus and other biological damage.
Balconies operate in the most adverse weather conditions on the structure. Precipitation, alternating temperature drops, gases contained in the air, have a destructive effect on materials, cause corrosion of steel parts. In this regard, there is a need for regular inspection of these parts of the building with the highest probability of destruction.
Inspection of balconies is to inspect structures. Wherein:
Roofs and roofs are examined, first of all, by establishing the design scheme of the truss system. After that, the materials of which these structures are made are examined.
Inspection of roof structures is carried out to identify deformations in the structures and integrity of the coating; to assess the causes and consequences of the occurrence of these defects.
In roof systems and trusses determine the values of deflections, curvatures and torsion of squeezed elements, sagging of puffs and violation of knots of interfaces.
Check the presence and condition of waterproofing between wooden and stone structures. Identify biologically affected wood and metallic elements that are susceptible to corrosion.
When examining roofs determine the state of the waterproofing layer. Detect defects in it, establish leaks. Particularly inspect the junction to the vertical structures passing through the roof, and inspection of drains.
In the roll roofs check the adhesion of the individual layers of waterproofing carpet among themselves. They are inspected at high points of the roof, since it is known that the mastic under the action of insolation and the associated increase in temperature softens and can flow down. The quality of adjoining the carpet to the funnel bowl is determined by the internal drain. The condition of the drain is also evaluated, which can be littered with debris with a sliding mastic.
The technical conclusion is made up reflecting the results of a detailed survey. The conclusion consists of four parts: architectural, constructive, technical and economic, and conclusions.
In the architectural section , dimensional drawings, a general plan of the site, facades and floor plans, longitudinal and transverse sections are shown. A brief description of the building’s architecture and adjacent buildings is attached to this.
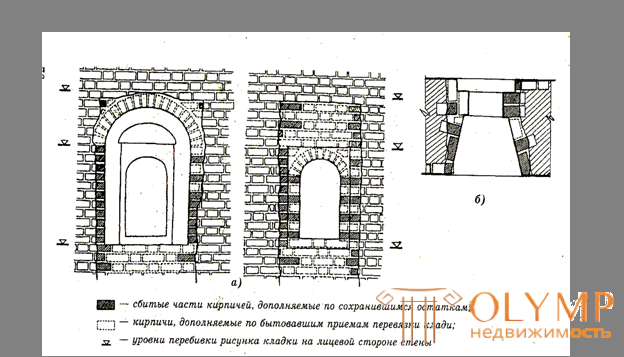
Architectural and planning survey reveals changes in the original plan, the presence of extensions, outbuildings, superstructures, the presence of smoke vents in the walls, laid and interrupted openings. It establishes the presence in the houses of laundries, boilers and other services or industries, causing the weighting of the operation mode of building structures. As a result of this survey, a measurement drawing is drawn up (Fig. 7.1.).

Fig. 7.1. - An example of the examined design
For buildings of architectural and artistic value, facades are presented in the form of photographs, dimensional drawings are carried out. According to archival and historical documents and compared with in kind, they give an opinion on the preservation of the original appearance of the house. Provision is also made for activities that are permissible at this site, based on the preservation conditions of monuments and elements of the historical environment of the city. The explanatory note includes documents on the preliminary coordination of repair with the city and municipal authorities.
The constructive part of the technical conclusion contains the drawings of all the structural parts of the building, a description of their technical condition and deformations with attached photographs.
The data of laboratory and field tests by non-destructive methods, as well as calibration calculations of structures are given. In this part of the conclusion, the preserved archival materials characterizing the constructive elements of the examined house are also given.
In the technical and economic parts reflect the physical and moral deterioration.
buildings, the nature of the planning of apartments and their engineering equipment. Illuminate the landscaping of the adjacent territory and the ecological state of the environment. Based on these data, determine the estimated cost of reconstruction and economically sound measures. Based on these technical and economic indicators, make business plans.
The conclusions contain recommendations on the possible fate of the building as a whole and its individual elements. They are the starting point for developing the same business plans and designing a complete overhaul or renovation.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)