Heating water in independent (closed) water heating systems is accompanied by the release of air bubbles from it. Floating and accumulating, they can create air traps and impede the circulation of coolant. In addition, it is necessary to provide devices for removing air at the start of the heating system.
In systems with natural circulation and top distribution, air is removed through an expansion vessel, which is usually connected to the main riser. The main pipelines running from the expansion vessel, laid with a gradient of 0.005 in the course of the water. When the water velocities in these highways are low, air clusters float to the expansion tank even to meet the water flow.
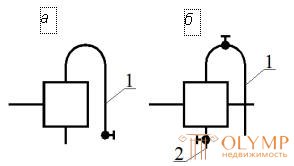
| In systems with forced circulation and top distribution, the water velocity in the mains is significantly higher, and the direction of bubbling is provided to coincide with the direction of water movement (the slope of the pipelines against the water flow). Thus, air clusters are concentrated at the highest points of the system - at the ends of the highways. At these points for the collection and removal of air include the installation of air collectors (Fig. 3.12). Air is released from the air collector to the atmosphere through a valve, which is periodically opened manually, or equipped with a plunger, a device that automatically discharges air into the atmosphere. | |
Fig. 3.12. Air collectors: a - end flow for installation on the last riser; b - horizontal flow; 1 - tube for air release; 2 - a branch pipe with a stopper for the descent of dirt |
In systems with lower wiring air is concentrated in the heating devices of the upper floor. To remove it, air taps (Mayevsky taps) are installed on the upper deaf plugs of these devices, which allow manual discharge of air as needed.
TEST QUESTIONS
1. What kind of heating devices can be used in residential, public, industrial buildings?
2. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of various heating devices.
3. What is the nominal density of the heat flow of the heater?
4. What is the difference between the calculation of the difference between the average temperature of the coolant in the device and the air temperature in the room with one-pipe and two-pipe water heating schemes?
5. How is the calculated area of the heater determined?
6. How is the heat load distributed between two heaters placed in the same room?
7. What are the parameters assigned brand circulation pump in a water heating system?
8. How are the required capacity and head of the circulation pump assigned?
9. In what cases is a hydraulic elevator provided in water heating systems?
10. What are the functions of a hydraulic elevator in a water heating system?
Game: Perform tasks and rest cool.8 people play!
Play game12. What is the design of heaters used in water heating systems?
13. What are the parameters for selection of water heaters for water heating systems?
14. How do lamellar water heaters differ from traditional shell-and-tube water heaters?
15. In which heating systems should an expansion tank be provided?
16. What are the functions of the expansion tank in the water heating system?
17. What is the calculation of the expansion tank?
19. How are automatic expansion systems arranged?
20. Why is it necessary to provide for the removal of air from water heating systems?
21. How is air removal from various water heating systems?
22. In what cases and in what points of water heating systems is the installation of air vents?
23. In what cases is the expansion tank used to remove air?
24. What are the automatic expansion systems have an advantage over expansion tanks?
25. What are the laws of hydraulics used in the hydraulic elevator?
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)