
 By design distinguish the following types of wicker furniture:
By design distinguish the following types of wicker furniture:
The main technical requirements for the material and design of furniture. In the manufacture of wicker furniture used: thick simple single weave with a specific pattern or without it; openwork weaving in combination with other very different types; type-setting weaving in one, two and three rods with a continuous or partial braid of individual elements of the product, or without the use of a braid. The materials used are whole willow rods and sticks, planed ribbons, a rogozovaya pigtail, Kugu, a straw braid and other materials.
The materials used for frames, frames and other supporting parts of wicker furniture should be smooth, clean, without any boughs, spalls, rot and cracks, with healthy wood of uniform color. Willow twigs, peeled from the bark, should be clean and smooth, without knots, cracks and any wood defects.
Connection nodes and parts . The design, the connection of components and parts must ensure the quality of the product, ease of assembly, ease of operation, compliance with modern appearance.
All elements weave on the picture. Braid and blanking parts should be uniform density, without gaps. The front surfaces of products that do not undergo plexus should have a glossy surface, without bark residues, they should be well leveled and thoroughly cleaned so that there are no dents, tears, chipping, burrs, chips.
Details of homogeneous materials used in one product or headset (natural color or colored) are selected for tone and color. Heterogeneity of tone and color is allowed on one product in no more than three places, each with an area of up to 0.5 dm2. The assembled product must be durable, rigid construction and keep in operation the original shape and size. It should stand on a horizontal surface steadily, without distortions and rocking (exceptions are rocking chairs and rocking couches).
Wicker furniture frames made of barked willow sticks or planed sticks from other tree species replacing them should conform to the sample with allowable deviations (depending on its size) + 3-5 mm. The discrepancy of uniform parts in diameter in the product should not exceed 2 mm and is allowed in no more than three places on the product. The deviation of the bent parts from the correct form is allowed no more than 5 mm.
In the production of wicker furniture used prevailing in practice types of fasteners and joints of furniture sticks, plates and rod racks. These connections are divided into detachable and one-piece.
The connectors include connections that allow you to repeatedly assemble and disassemble products without much difficulty. This method of connecting components and parts in the production of wicker furniture because of its specificity is used very rarely.
Split connections are divided into rigid and hinged . Tough ones include joints on couplers and studs, and hinged joints on hinges and hinges. Permanent joints are usually on glue and nails. Very often in one product both types of these compounds are combined.
The permanent joints on the glue are thorny and smooth fugu . Spike connections are subdivided into corner, connections along the length and edges.
Corner joints - the largest group of spiked joints. They are terminal, middle and box. The end corner joints, in turn, are subdivided according to the types of spikes: insert flat through-through spikes — ordinary, double, and “whiskers”; on semi-secret - wedge-shaped, flat; non-through - flat with semi-darkness, with darkness, "on the mustache" and "on the mustache" inserted; non-through round - at a right angle and "on a mustache".
Median corner joints are: through flat - single and double; non-through - flat, round, trapezoid, into the groove and the comb.
Box corner connections : through - group flat, group trapezoid, trapezoid in groove and tongue, round; semi-secret - group trapezoid, group flat, trapezoid in the groove and the crest, flat in the groove and the crest, group wedge-shaped "on the mustache", a quarter on round spikes.
For frame parts, willow sticks, twigs, bamboo are used; Deciduous or coniferous wood is also permitted. Parts of the frame are made in one, two or three rods.
The rods are interconnected. With a total length of the frame part along the perimeter of more than 5 m, it is allowed to make it a composite of two sticks. In this case, two conditions must be observed: the connection points must be located in places inaccessible for viewing during normal operation; the second condition is that it should not reduce the strength of the product.
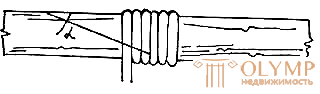 |  |
| Fig. 1. Connection details on the "mustache" | Fig. 2. Connection of parts abutting |
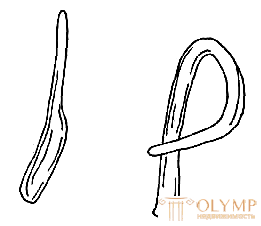
The ends of the sticks and twigs are connected "on the mustache" (Fig. 1) and necessarily nails. The length of the "whisker" must be at least five times the thickness (diameter) of the part. The joints of parts and assemblies made of stick material, as well as the fixing points of the parts with nails, are embedded with thin willow tapes or cords made of polymeric materials. Frameworks can be wrapped with willow, peddig, cord or ribbons made of polymeric materials with the obligatory execution of the pattern given by the project.
Seats chairs and chairs tightly fasten with frames; The cross bars of the seats should provide cushioning. The rods are fastened to the elements of the frame with ends, cut "on the mustache", by the method of girth, strengthened with nails, the joints are tied with willow ribbons or cords of polymeric materials. As an additional limitation to the precipitation of the seat, it is allowed to use wicker mesh, textile braid or other equivalent materials.
When designing wicker furniture in all kinds of parts, components are used end-to-end connections (Fig. 2). The following connection methods are distinguished: a simple lining of one part to another, cutting wood by one third or a quarter of the thickness of one part, respectively, the width of the other; cutting a recess in the face of one part according to the diameter of the shield of the other.
The inset joint (Fig. 3) is made with trimming to form plates at the part applied to the end. The inset joint with undercut and rounding is used to connect the ends of parts in rounded corners. Mounts wrapped with ribbons of willow or other materials. The length of the winding should cover the junction by two or three turns with a tape width of not more than 10 mm. The connection of two parts for an oblique cut (Fig. 4) is the most common type of connection in wicker furniture.
 |  |  |
| Fig. 3. Connection of parts inlay | Fig. 4. The connection of parts on the oblique cut | |
It is used for the manufacture of closed parts ring, trapezoid, oval and other shapes. The joints are wound with ribbons of willow or another material, and the length of the curtain should overlap the oblique cut by two to three turns on each side (Table 1).
Table 1. Dimensions of nails and elements of the joints of the parts on the slanting cut
Diameters of parts to be joined | Cut length | Nail pitch | Nail sizes | |
Diameter | Length | |||
10-15 | 30-45 | ten | 1.0-1.2 | 16-20 |
16-20 | 45-60 | 15 | 1.2-1.4 | 20-25 |
21-25 | 60-75 | 20 | 1.2-1.4 | 25-32 |
26-30 | 75-90 | 25 | 1.4-1.6 | 32-40 |
31-40 | 90-120 | thirty | 1.4-1.8 | 40-50 |
Table 2. Dimensions of nails and elements of the connection details of the method of girth, mm
Diameters of parts to be joined | Coil length | Nail sizes | The thickness of the bow | |
Diameter | Length | |||
10 - 15 | 60 | 1 - 1.2 | 16 - 20 | 2 - 3 |
16-20 | 65 | 1.2-1.4 | 25-32 | 3-5 |
21-25 | 90 | 1.4-1.6 | 32-40 | 5-7 |
26-30 | 100 | 1.6-1.8 | 40-50 | 7-9 |
31-40 | 110 | 1.8-2.0 | 60-50 | 9-15 |
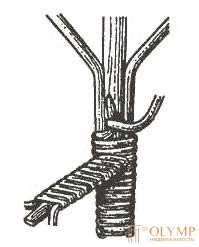
In the form of a collar, the girth method (Fig. 5) connects the shock-absorbing parts of the joints frames of chairs, armchairs and sofas. The attachment sites are wrapped in ribbons of willow or other material (Table 2).
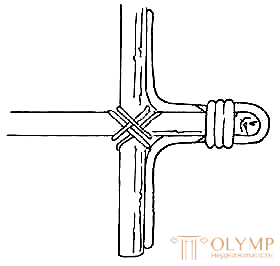 |  |  |
| Fig. 5. Connection method of girth | Fig. 6. Corner joints : a - shoots (left); b - podlozhkami (right) | |
The fastening of corner joints by shooting and podnuchkami is used in all types of wicker furniture (Fig. 6). Attachment sites must be wrapped with ribbons of willow or other material according to a pattern of at least three to five turns. The ends of shoots and podluchek should be cut and rounded.
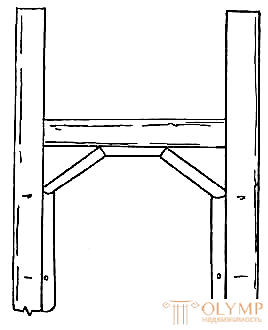
To give wicker furniture durability and stability, they use prokhozh, which can be in the form of a cross and semi-base, ring-shaped, I-beams and other forms.
The details of the projectile are joined and fastened with nails. Joints close up willow ribbon. The cross-shaped projectile is joined in the middle part by cutting 0.5 diameters of the stick (Fig. 7, a), the I-beam is transversely girded with longitudinal sticks (Fig. 7, b), with ring-shaped and figured parts and projectile fastened to the legs with nails. Whets are set at a height of at least 120 mm from the floor.
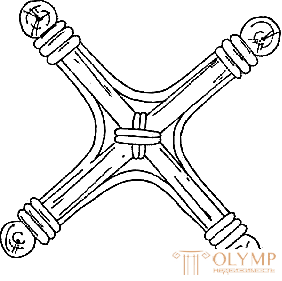 | 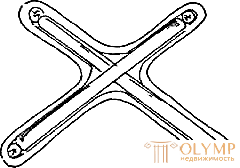 | 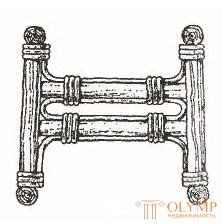 |
Fig. 7. Races : a - in the form of a cross; b - dvutavrovaya | ||
For furniture products made of willow material, the armrests and backrests are made of solid single sticks, in conjunction of two (three) sticks or twigs. The armrests can be reinforced with curly inserts of various shapes, as well as continuous, openwork or combined weaving. The ends of the shooters and podluchek set butt to the footboard (Fig. 8, a), a at the lower ends of the legs cut into a cone and round. In wicker furniture with soft elements or with a complex design, armrests are twisted and braided.
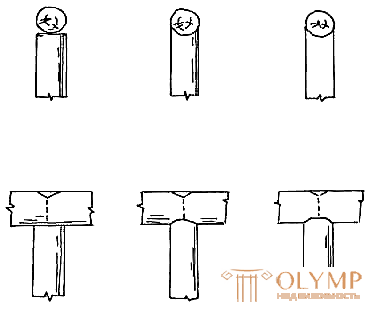 |  |
Fig. 8. Connection details : a - simple; b, c - angular | |
The most common type of corner joint is shown in Fig. 8, b. According to this method, the end of one part is cut to a third or a quarter of the thickness of the stick according to the diameter of the other part, impose it on the end of the last and fasten with a nail. Another type of corner joint (Fig. 8, c) is also used, in which the end of one part is cut off obliquely, and on the other side - “by the side”, impose on the end of the first part obliquely cut off and the junction is fastened with nails.
With the details of glued plywood, slabs or solid wood, wicker elements are connected with the help of nails and screws. In the production of wicker furniture and some other types of products it is necessary to attach the pillar bar to the sticks of the frame. There are three types of fasteners (Fig. 9): prolonged loop, ordinary and double loop.
 | 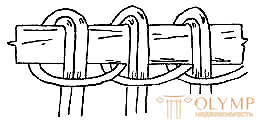 |
| Fig. 9. Types of fastening of the pillars to the stick : a - a tightening loop; b - single; in - double | 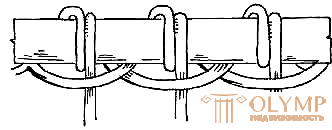 |
Furniture produced in natural color or painted. In one product, a combination of different types and classes of coatings (finishes) is allowed. The coating should be uniform in tone and gloss, and meet the standards of finishing. Paint coatings must be durable, water, light and heat resistant, appropriate for the purpose of the product, without sagging and loose films, cracks, roughness and gaps, drips, stucco, grips, dirt and open pores.
When considering the basic requirements for the design of furniture, it should also be noted that in the manufacture of many craftsmen, especially beginners, make mistakes. In particular, the presence of excessive willow ties, quickly drying, leads to the fact that the furniture is loosened.
Significant defects appear from the bonding of individual elements of furniture with iron nails. At the same time, nails are often driven to places where they are often useless. Not only that, nails hammered into damp wood quickly rust, rust overeats a rod or tire and furniture spreads to pieces. In addition, when drying wood, nails are squeezed out of it and tear clothing.
All these defects of wicker furniture can be eliminated if instead of nails, fasten the corresponding parts with screws (screws) that are not squeezed out of wood. The use of screws does not increase the cost of the product, at the same time, this replacement allows you to give it a lighter and more beautiful shape, the ease and elegance constitute the main feature and charm of wicker furniture. When fastening parts with screws from the master, intelligence and skill are required to correctly determine the place for the screw. These qualities are often not enough for beginners, and they drive in dozens of extra nails, believing in the advisability of such fastening. Replacing iron nails with wooden nails is also impractical, because no matter how carefully they are driven in, the wicker and tire often split, which is not the case when fixing parts with screws.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)