GLAVGOSENERGONADZOR LETTER FROM APRIL 29, 1997 No. 42-6-9-ET
On the introduction of the "Temporary guidelines on the use of RCD in electrical installations of residential buildings."
ANALYSIS OF THE CAUSES OF UZO OPERATION
Technical description of the RCD.
In the electrical network with a grounded neutral when building equipment protection against electric shock using the principle of separation of the differential (leakage) current to earth. 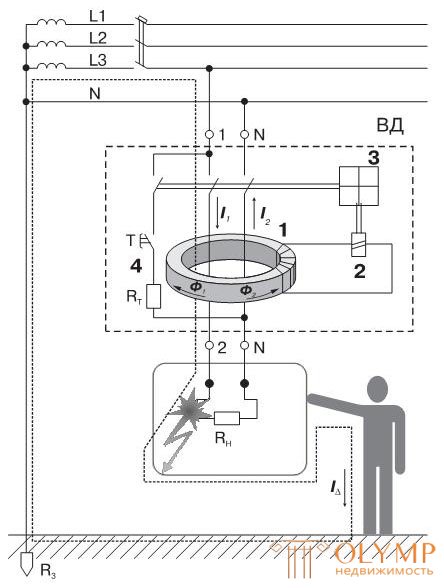
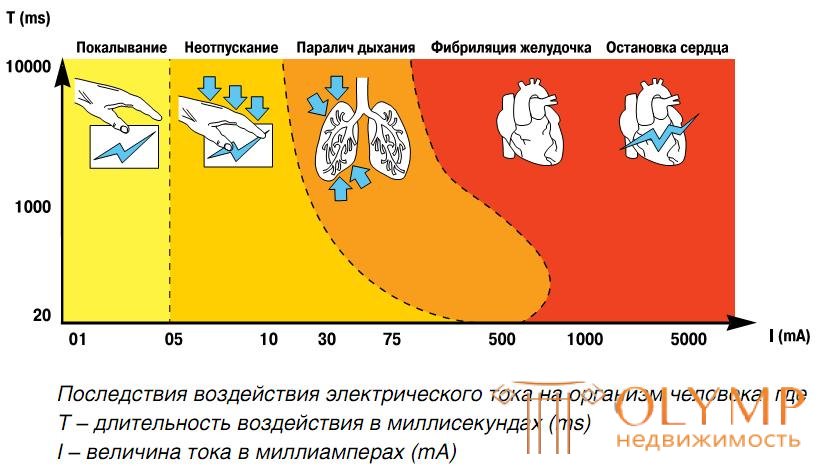
This current iΔ is the difference between the total current i1 flowing into the load from the network and i2 flowing from the load towards the network. The difference is formed in the case of contact with the current-carrying part of a person standing on the floor connected to the ground.
A current transformer 1, the primary winding in which the phase (phase) and neutral wires go together in the direction of the load and the secondary wire is wound over the magnetic conductor, are used as a sensor that emits the specified difference in currents.
A winding 2 of a coil of a miniature electromagnetic relay, an electromechanical release 3, is connected to the secondary winding.
In normal operation, the load magnetic fluxes F1 and F2, formed by the phase and zero conductors, are compensated and the resulting flux is close to zero. In the secondary winding, the voltage is zero.
The principle of operation of an electromechanical trip unit is inverse to the principle of operation of a conventional relay. Its anchor is pressed to the yoke and is held in this position by the attraction of a special “blocking” magnet, and the force of attraction of the magnet is somewhat greater than the force of the special “return” spring tending to tear the anchor from the yoke.
If the resulting differential current of a person exceeds a certain value at which the electromagnetic flux created by the coil of the release 2 becomes sufficient to compensate for the flow of the blocking magnet, the spring will tear the armature from the yoke (pick-up setting). Anchor mechanically affects the control mechanism of the RCD. There is a disconnection of the power contacts of the RCD and the disconnection of the load (consumer) from the electrical network.
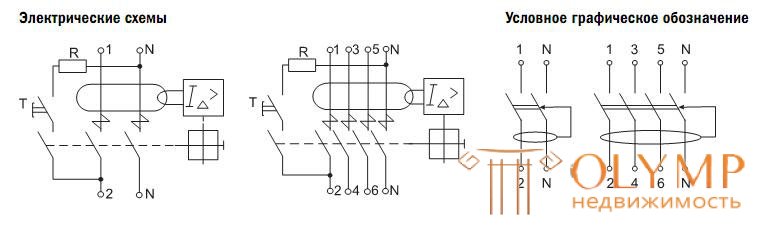
To check the operational state of the RCD, a circuit is provided that contains a “TEST” button and a limiting resistor RT, which simulates the appearance of a differential current. When the button is pressed, the RCD device connected to the electric network is triggered, and a red sector appears in the window of the visual control, informing about the disabled state of the control mechanism.
Recommendations for use
various grounding systems.
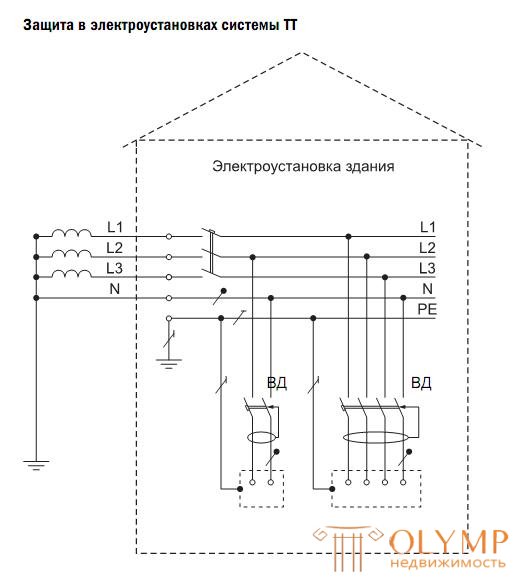
In the TT system, all exposed conductive parts of an electrical installation are connected to a ground that is electrically independent of the neutral point of the power source.
GOST R 50669-94 prescribes the use of the TT system as the main one in the case of connecting these electrical installations to the input distributing devices of the neighboring (capital) building.
In GOST R 50571.3-94 in p. 413.1.4 it is indicated that in the TT system, overcurrent protection devices can be used to protect against indirect contact only in electrical installations that have grounding devices with very low resistance.
In this case, a guaranteed power outage of an electrical installation should be carried out when a voltage of no more than 50 V appears on the exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation.
In real conditions, it is very problematic to automatically turn off the power supply of an electrical installation of a TT system using automatic circuit breakers for several reasons (the need to ensure a high ratio of short circuit current, low resistance to grounding device, etc.). An effective solution to the problem of automatic power-off is the use of sensitive RCDs.
Clause 1.7.59 of ПУЭ (7th ed.) Contains the requirement of obligatory application of VD to ensure electrical safety conditions in the TT system. In this case, the setpoint (rated tripping differential current) must be less than the value of the fault current to grounded open conductive parts at a voltage of 50 V relative to the zone of zero potential.
This means that in electrical installations of individual houses, cottages, country (garden) houses and other private structures, where it is not always possible to perform a grounding conductor with the required parameters, it is necessary to use a TT system with an obligatory installation of RCD. In this case, the requirements for the resistance value of the earthing significantly reduced. 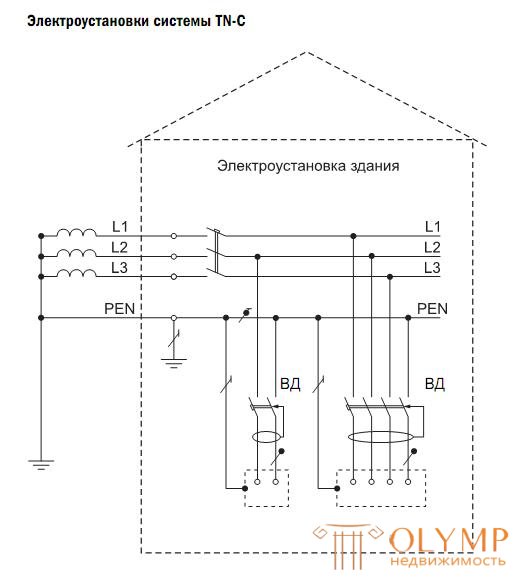
In electrical installations of the TN system, all exposed conductive parts of electrical installations must be connected to the grounded neutral point of the power source through protective conductors. The main electrical safety condition of the system ТN is that the value of the current in case of a short circuit between the phase conductor and the open conductive part exceeds the value of the response current of the protective device in a normalized time. In the case of use as a protective device of the RCD, the value of the short-circuit current should be replaced by the value of the rated tripping differential current of the device I∆n. At the same time, the task of ensuring a low value of the “phase-zero” resistance, which must be solved when using overcurrent protection, is replaced by a test of the operation of the RCD and protective conductor.
Monitoring the resistance of the “phase-zero” circuit should be made only at the input terminals of the RCD.
The most used type of TN system is the TN-C system. In this case, the PEN conductor is used as a protective conductor, which simultaneously performs the functions of the working and neutral protective conductor.
In the 7th edition of the ПУЭ, there is an instruction: “It is not allowed to apply RCDs that react to the differential current in four-wire three-phase circuits (TN-С system).
If it is necessary to use RCDs to protect individual power consumers that receive power from the TN-C system, the protective PE conductor of the power receiver must be connected to the PEN-conductor of the circuit supplying the power receiver, to the protective switching device. ” This means that, as an exception, for protection of individual electrical receivers, PUE allow the use of RCDs in the TN-C system, subject to certain conditions - connecting open conductive parts of receivers to the PEN-conductor from the power source relative to the RCD. 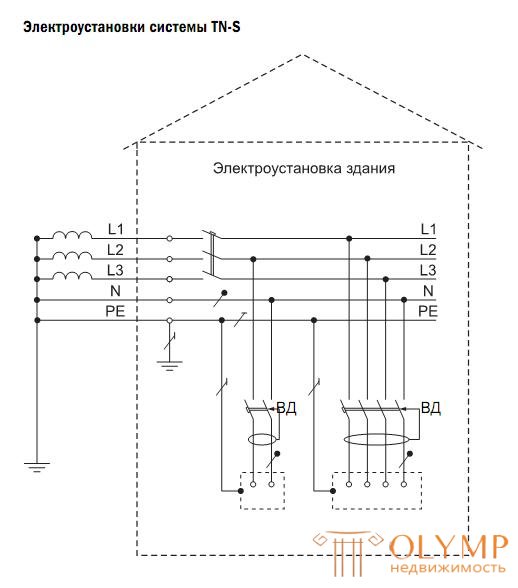
More modern and in most cases safer is the TN-S system, where they use an independent protective conductor PE and a neutral working conductor N, which are laid separately, starting from the output of the power source. This system has been used for a long time in telecommunication networks (this eliminates interference in low-voltage networks that occur when part of the operating current flows in the ground in a TN-C network).
The use of RCDs is mandatory, except for the specified special cases (for example, the fire alarm supply circuit). 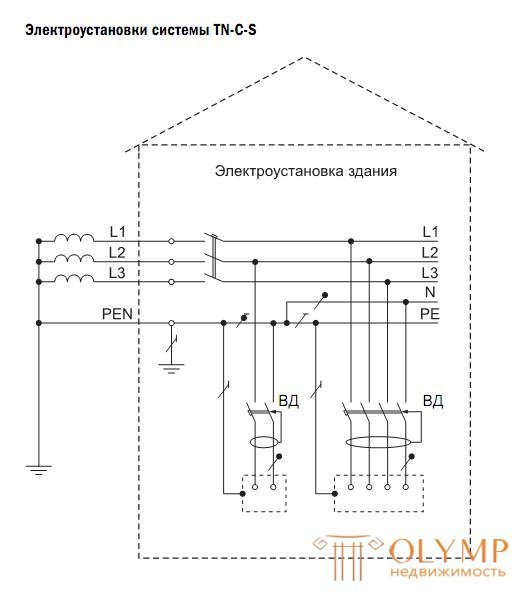
When dividing, for example, in a group panel, in the electrical installation of the TN system of the PEN conductor into separate conductors PE and N, the TN-CS system is formed. At the same time, as in the TN-S system network, PE and N conductors must be laid separately, and their connection after the separation point is unacceptable.
This system is currently the main one, which can be performed in a separate part of the electrical installation during the reconstruction.
Recommendations for use
at various sites.
Residential and public buildings.
To increase the level of protection against fire when shorting to grounded parts at the input to the apartment, individual house, etc. An RCD is required with a response current up to 300 mA (ПУЭ, 7th ed.). If in a household electrical installation there are single-phase and three-phase circuits of plug sockets, then it is necessary to protect three-phase circuits with four-pole RCD, and single-phase - with double-pole RCD. These recommendations also apply to public buildings, for example, public utilities, schools, administrative buildings, etc.
Bathrooms and shower rooms.
For sanitary cabins, bathrooms and showers, it is required to install an RCD with a triggering current of 10 mA, if a separate line is allocated to them, and a triggering current of 30 mA in other cases (for example, when using a single line for a sanitary tub and kitchen) (GOST R 50571.11-96 ).
Construction sites.
Construction sites are characterized by a significant number of accidents caused by electric shock. This situation is explained by the fact that the electrical wiring used on construction sites is temporary, and the electrical equipment is operated in difficult conditions. In this case, most of the electrical equipment and hand-held power tools are used in an external environment that is not protected from moisture, and the staff, as a rule, do not receive appropriate special training.
The use of portable cables laid directly on the ground, causes a high degree of probability of mechanical violation of the integrity of the protective conductor, which can lead to a real threat to the lives of people who have touched the open conductive part of the equipment fed by the damaged cable.
In accordance with the requirement of the standard (GOST R 50571.23-2000) on construction sites should be installed in each switchboard to protect circuits of RCD outlets with a response current of up to 30 mA.
Industrial facilities.
The quality of service of electrical installations of industrial enterprises is higher, since it assumes the existence of continuous monitoring carried out by qualified personnel and scheduled periodic tests of protective electrical safety measures.
However, the scope of the RCD is wide. In the premises of industrial enterprises, UZOs with a setpoint of not more than 30 mA are used to protect the chains of receptacles to which a hand power tool is connected.
RCDs should be used to protect stationary equipment installed in high-risk and highly hazardous rooms (PUE, 7th ed.). In all input-distribution switchboards for fire protection, an RCD with a rated tripping differential current not exceeding 0.5 A must be installed (GOST R 50571.17-2000).
Mobile buildings.
Electrical equipment in mobile structures (workshops, repair and residential premises, medical and measurement laboratories) should be equipped with its own protection of open conductive parts, independent of the design and state of protection of the power network. This task is assigned to the RCD.
In GOST R 50669-94, as applied to buildings made of metal or with a metal frame, the value of the RCD setting is set no higher than 30 mA.
Agricultural objects.
The risk of accidents caused by electric current at agricultural facilities is extremely high.
The reason for this is the harsh operating conditions of electrical equipment (humidity, aggressive environment, etc.) and unqualified maintenance, violation of electrical safety rules. For all group circuits supplying sockets, there must be additional protection against direct contact with a RCD with a rated tripping differential current not exceeding 30 mA.
In livestock buildings in which there are no conditions that require equalization of potentials, protection should be performed with a RCD with a nominal tripping differential current of at least 100 mA installed on the input panel (ПУЭ, 7th ed.)
GLAVGOSENERGONADZOR LETTER FROM APRIL 29, 1997 No. 42-6-9-ET
On the introduction of the "Temporary guidelines on the use of RCD in electrical installations of residential buildings."
ANALYSIS OF THE CAUSES OF UZO OPERATION
On the introduction of the "Temporary guidelines on the use of RCD in electrical installations of residential buildings."
RCD analysis of causes and fault finding algorithm.

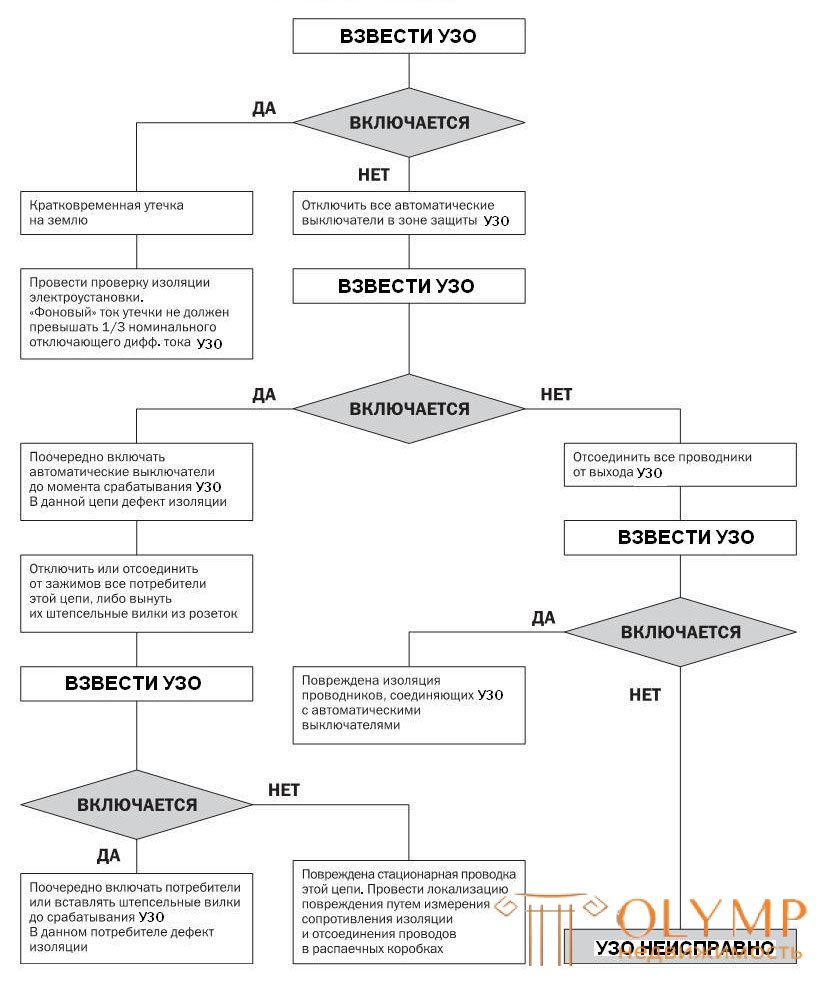
When triggered RCD, you must determine the type of fault in the mains. The procedure for the electrician is as follows:
1. Coil the RCD.
If the RCD is charged, it means that there was a leakage of current in the electrical installation caused by an unstable or short-term insulation failure. In this case, it is necessary to conduct a general control of the insulation condition. Check the operation of the RCD by pressing the TEST button.
2. If the RCD is energized and instantly triggered, this means that either the electrical installation has a defect in the insulation of any electrical receiver, wiring, electrical wiring of the electrical panel, or the RCD is faulty. In this case, you must perform the following steps:
- Disconnect all circuit breakers of the group circuits protected by the RCD.
- If the circuit breakers are single-pole or three-pole and do not open the neutral operating conductors, taking into account that current leakage is also possible from the neutral operating conductor, it may be necessary to disconnect all the neutral operating conductors from the busbar to detect a defective circuit.
3. Cock the RCD.
If the RCD is armed, test the operation of the RCD by pressing the TEST button. Instant shutdown of the RCD means that it is operational, but there is a leakage current in the protected circuit. If the RCD is not energized, it means that there is a malfunction in the insulation of the electrical installation board or a fault in the RCD.
4. Switch on the circuit breakers in sequence.
If the RCD triggers when a certain circuit breaker is turned on, this means that there is a fault in the circuit of the circuit breaker.
5. Disconnect or disconnect all electrical receivers in the circuit of the switch, when turned on, the RCD operated.
6. Cock the RCD.
If the RCD is charged, it means that there is a fault in the insulation in one of the electrical receivers. If the RCD is not charged at all disconnected electrical receivers of this circuit, this means that the insulation of the electrical wiring is defective.
7. Consistently turn on each electric receiver of this circuit.
- RCD triggers when a specific electrical receiver is turned on.
- Disable the defective power receiver.
8. Connect all electrical receivers (except the defective one), charge the RCD, make sure that the RCD does not work. Check the operation of the RCD by pressing the TEST button.
Errors during installation, connection of the RCD.
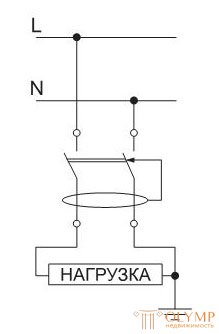
The most common error during installation is the connection to the RCD of the load, in the circuit of which there is a connection of the neutral working conductor N with the exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation or a connection with the zero protective conductor PE. In this case, the probability of a “false” actuation of the RCD is quite high. 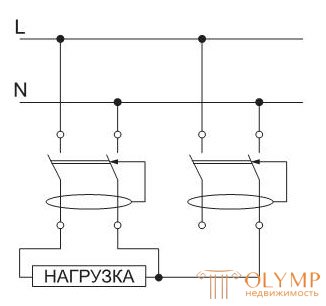
When installing or upgrading switchboards using RCDs, the following error is possible: the combination of the neutral working conductors of N different devices in the zone of their protection (the load current is differential for both RCDs and one of them or both work). 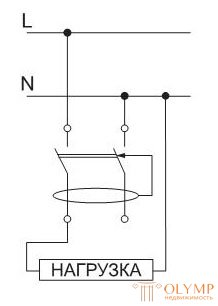
If the load is erroneously connected to the zero operating conductor N to the RCD (in this case, the load current will be differential for the RCD, and it will work). 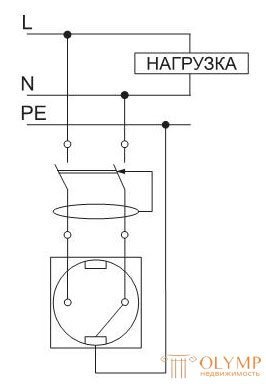
When mounting sockets or terminal boxes of electrical installations in the protection zone of the RCD, accidental connection of the neutral working conductor N with the protective conductor PE triggers the RCD operation:
- when connecting the load to the outlet (the case is similar to paragraph 1);
- if any load is connected outside the protection zone of the RCD (differential current flows through the jumper). 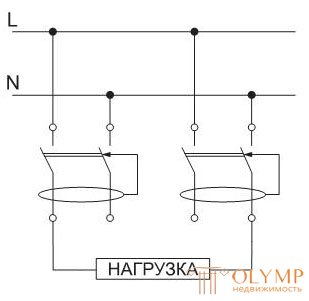
When upgrading the panel, it is possible that the load is erroneously connected to the zero working conductor N of another RCD (the load current is differential for both RCDs and one of them or both of them work). 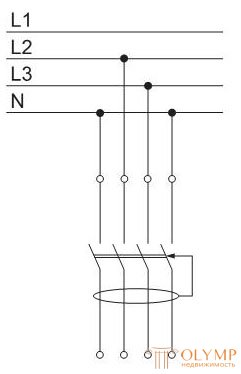
When connecting four-pole RCDs, it may be erroneously connected to its terminals of the same-named phases (this does not affect the operation of single-phase consumers). In this case, the test of the operation of the RCD using the "TEST" button is unreliable, since the failure of the RCD does not mean that it is inoperative.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)