Water intake facilities (also known as a water intake facility - VZU, or capturing) are facilities for drawing water from a source, consisting of a number of basic engineering objects:
- a water intake with a first-lift station (usually submersible pumps);
- water metering unit from water meters - flow meters;
- water treatment to bring the water quality to the standards of drinking water;
- clean water reservoir (RF);
- fire reserve tanks (fire tank);
- second lift pumping station to maintain pressure and supply water to the consumer in the required volume;
- water tower (alternative pumping station second lift);
- fire extinguishing station (fire pumps);
- drainage system discharges water in case of emergency overflow of reservoirs, flooding of water intake structures.
- instrumentation and automation (abbr. I & C or I & C) monitor equipment operability, control water consumption, keep logs of changes in characteristics: levels, water consumption, emergency situations, etc., perform automatic equipment maintenance, for example, automatic station washing water treatment. The full list of actions performed automatically depends on the specific requirements of the Customer’s technical specification for the water intake facility;
Large (pumping over 10,000 m³ / day) water intake facilities can have their own infrastructure: an electrical substation, a gas distribution substation (PIU), a boiler room, a control room with the ability to keep a watch, a laboratory to monitor water quality and so on.
The location for the water intake facility, the so-called land acquisition, must be coordinated with the state body of sanitary and epidemiological supervision and meet the sanitary and epidemiological (SanPiN) and construction standards (SNiPs), etc.
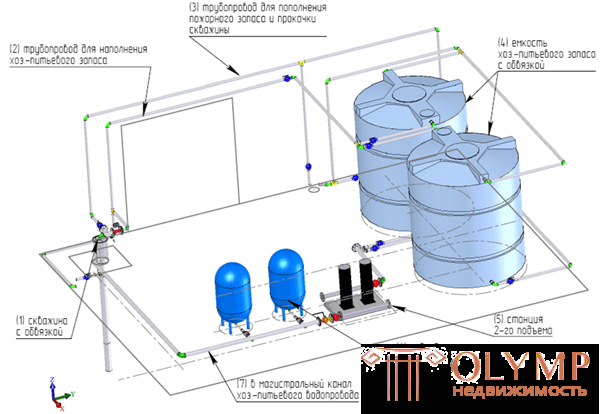
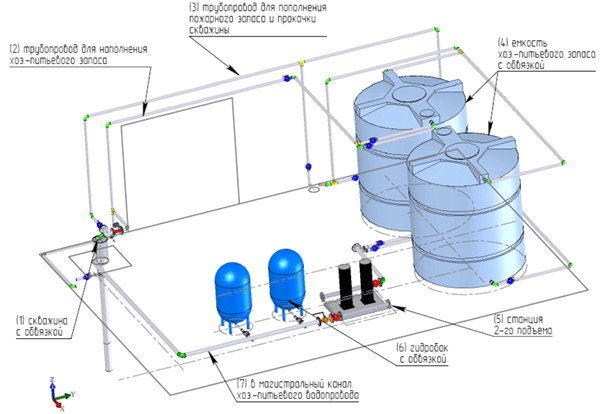
Diagram of a water intake node, arrangement of a water intake node, water supply from an artesian well
Content
- 1 Classification of water intake facilities
- 1.1Underground water sources
- 1.2Surface water sources
- 2 Sanitary protection zone (SOA) of the water source
- 3Legal-technical documents, standards
- 4Notes
- 5SM. also
- 6Bibliography
Classification of water intake facilities
According to the characteristics of the source, water intakes are divided into underground and surface. Underground sources of water supply, as a rule, are distinguished by more stable characteristics of water quality and relative protection from surface contamination. Surface sources of water supply are distinguished by high productivity, but require constant supervision over the observance of the sanitary condition of the territory of the surface source: lakes, rivers.
Underground water sources

Under construction. Underground water intake structure (two wells in the caissons - round barrels), next to the wells there is a building with pumping units, a metering station, a reservoir of clean water.
Groundwater according to clause 5.3. SNiP 2.04.02-84 * “Water supply. External networks and facilities ", water intake facilities (most commonly used: underground source of water supply) are divided into:
- Water wells (more commonly we use the term: artesian well) for the extraction of artesian water;
- Mine wells for the extraction of mostly groundwater;
- Horizontal water intakes, which in turn are divided into:
- trench structures are used for relatively low water consumption with a shallow depth of groundwater;
- gallery (proper galleries and galleries), which are used for constant water supply to relatively large water consumers, built with a considerable depth of aquifers;
- Karyaz - primitively arranged water intake structures used for agricultural water supply and irrigation of small land plots in semi-desert areas with unseasoned occurrence of aquifers;
- Combined intakes;
- Beam water intakes are used to more fully capture underground water - a combination of a shaft well with horizontal boreholes embedded in different sides of an aquifer;
- Captures of springs;
Surface water sources

Surface water intake facilities (two round towers) on the banks of the Volga in Kstovo
Surface sources for water supply are divided into:
- River - water intake from the river;
- Reservoirs - water intake from the reservoir;
- Lakes - water intake from the lake;
- Marine - water intake from the sea.
For surface sources, the following types of water intake structures are distinguished [1]:
- Coastal water intake facilities are used at relatively steep banks of the river, it is a concrete or reinforced concrete well of large diameter, carried out by the front wall into the river. Water enters it through the holes protected by gratings, and then passes through the grids, carrying out a rough mechanical purification of water.
- Channel intake structures are usually used at a gentle coast, have a tip, handed down into the river bed. The designs of the tips are very diverse. From the top of the water is supplied by gravity pipes to the shore well; the latter is often combined with the pump station of the first lift.
- Floating intake structures are a pontoon or barge on which pumps are installed that take water directly from the river. Water is supplied to the shore through pipes (with movable joints) laid on the connecting bridge.
- Bucket intake facilities . Water comes first from the river to the ladle located on the shore (artificial gulf), at the end of which the river proper is located. The bucket is used to sediment sediment, as well as to combat ice disturbances - sludge and deep ice.
Sanitary Security Zone (SOA) of the water supply source
Main article: Sanitary Security Area
The sanitary protection zone (SOA) of water sources is regulated by SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02 “2.1.4. DRINKING WATER AND WATER SUPPLY OF POPULATIONS. Zones of sanitary protection of water sources and drinking water pipelines ”. The SOA consists of 3 belts:
- the first zone - the zone of strict regime is surrounded by a deaf fence, signs of protection are installed.
- the second belt is a zone of bacteriological contamination.
- the third belt is a zone of chemical pollution.
The sanitary protection zone of the 2nd and 3rd zones is determined by calculation.
Regulatory and technical documents, standards
- GOST 26966-86 (ST SEV 4467-84) Water intake, catchment and gates. Terms and Definitions. Water intake and outlet works and gates. Terms and definitions.
- SP 31.13330.2012 Water supply. External networks and facilities. Updated version of SNiP 2.04.02-84 (with Amendments N 1, 2).
- GOST 2761-84: Sources of centralized drinking water supply. Hygienic, technical requirements and selection rules. Sources of centralized economic-drinking water supply. Sanitary and technical requirements
(the list is not complete)



Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)