
The basis of hydrological surveys is the science that studies the water regime of rivers and reservoirs, called land hydrology.
Land hydrology is closely related to climatology, meteorology, soil science, hydrogeology, hydraulics, geodesy, mathematics and other sciences. At present, there is not a single branch of the national economy that, to one degree or another, was not related to hydrology. Without the necessary information from hydrology, it is impossible to design engineering structures. Calculation of water resources for the supply of cities and industrial facilities, for irrigation of agricultural land, identifying the mode of temporary and permanent watercourses for building bridges, dams and hydropower plants - all this requires special long-term observations of water levels, flow rates, water flow, direction of jets and slope flow, sediment accounting, water chemistry and much more. To obtain these data, special water measuring stations and hydrometric stations are arranged.
In the system of the Hydrometeorological Service of Ukraine, which conducts regular observations on rivers and lakes, there are several hundred water measuring stations and hydrometric stations, which are more or less evenly located on the territory of our country. In addition, individual departments arrange a network of their temporary departmental posts, designed to solve the problems of designing and building engineering structures.
Thus, we can conclude that the hydrometeorological service is engaged in a general comprehensive study of hydrological processes and their patterns throughout the country in order to meet the diverse needs of various sectors of the economy. Departmental stations and posts solve narrower and specific tasks associated with the construction of certain types of structures.
Hydrological surveys are necessary in the construction of many structures, and especially in the design of bridges, hydraulic structures. Moving water usually moves a certain amount of soil particles - sediment. Accounting for sediment is important in the designation of design slopes of irrigation and water channels, which during operation must ensure indelible and non-friable canals, as well as in determining the so-called dead volume of reservoirs.
The river system is understood as the main river and the network of tributaries 1, II, III, etc. orders. The area from which water flows into a given river is called a catchment area, or simply a catchment area, and is expressed in square kilometers, fig. 4.1. The part of the surface from which water enters the river is called a pool. Pool size and configuration important characteristic of the river system, as they affect the size and nature of the flow.
River flow is the total amount of water entering the river from different sources.
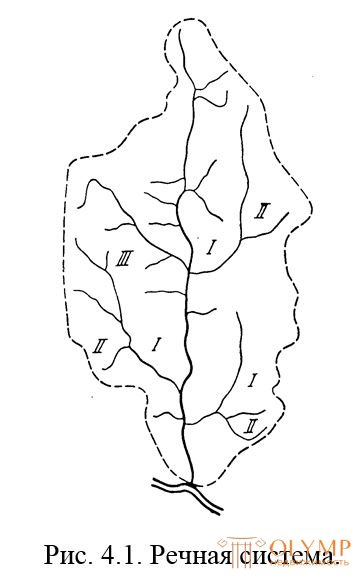
Fig. 4.1. River system.
I, II, III, inflows respectively 1, 2 and 3 orders.
The configuration or shape of the basin is determined by its length, width, asymmetry, and the nature of the increase in the basin area.
For the length of the pool take the distance from the source to its most distant point.
The nature of the increase in the basin area is usually represented in the form of a graph, which shows a gradual increase in the basin area at the expense of areas immediately adjacent to the main river and an increase in area due to the areas of the tributary basins.
The areas of the basin and its parts are usually determined by maps using a planimeter. The accuracy of this definition depends on the scale of the map, the size and shape of the area to be covered; usually it is ??? area values. To obtain a basin area with higher accuracy, it is necessary to carry out a set of field geodetic works. Such work, in particular, has to be performed when determining the areas of small watercourse basins, for designing artificial structures (bridges, pipes) on roads. Regarding the characteristics of the river itself, it is necessary, first of all, to highlight its main parts: the source, headwater, middle current, lower reaches. The source of the river can be a spring, a lake, a swamp, snow melting in the mountains and glaciers.
The delimitation of the river into three sections (upper, middle, lower) is somewhat arbitrary and makes sense only for rivers of considerable length.
The place where the river flows into the sea, lake or another river is called the mouth. When flowing into the sea, rivers form various mouths, for example, deltas, estuaries, lips, fjords.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)