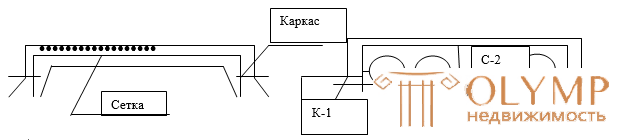
Bending elements include beams and slabs. Beams are linear elements for which the length is significantly greater than the height and width of the section ( h ≤ l ≥ in ). The plates are flat elements, the thickness of which means less than the length and width ( in ≥ h ≤ l ) (where in is the width of the plate, h is its thickness). Plates (solid, ribbed, hollow) are reinforced with nets, in which the reinforcement in one direction is working, and the other is assembly.

The working reinforcement perceives tensile forces from the bending moments M , the mounting serves to distribute the concentrated loads, to restrain the temperature and shrinkage deformations. Working rods with a diameter of d = 3-10mm are placed with a pitch of 100-200 mm, and transverse rods with a pitch of 250-300 mm.

 Beams can have the most various cross section.
Beams can have the most various cross section.
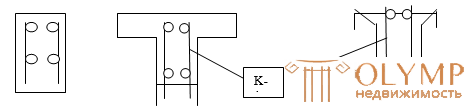
In them, the working reinforcement serves to perceive the tensile forces arising from the action of the bending moment "M", and the transverse rods - for perception, together with concrete, of the transverse force Q. Use the installation reinforcement - to fix the transverse reinforcement and create a spatial framework. Frameworks are most often welded, but sometimes knitted. In narrow beams (<150 mm) they put one welded frame, in wider ones - several; in the latter case, flat frames are combined into a spatial one, by installing connecting rods. Longitudinal rods are placed in the working zone in one or two rows.

With a beam h section height h> 700 mm, longitudinal rods d = 10 ÷ 12 mm should be installed every 400 mm along the section height at the side faces. The area of the longitudinal reinforcement is determined with the calculation and d. Be
not < 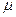 min = 0.05% of the area of concrete.
min = 0.05% of the area of concrete.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)