On the basis of the decisions made at the choice of the type of heating system, the installation sites for heating devices are planned. The devices should be installed under each window, in the corner rooms there should be a device near the outer wall, even if there is no window in it. Heating devices on the staircases are, as a rule, only on the ground floor; in high-rise buildings, the appliances can be additionally installed on staircases up to the 3rd – 4th floor.
The next stage of construction - placement of risers. Mandatory installation of risers in the corners of rooms formed by external walls. In residential buildings, open laying of risers is recommended. For heating the staircase provides a separate riser (or two risers - ascending and descending with the lower wiring of highways). The main riser (with the upper wiring) is installed on the staircase or in the common corridor.
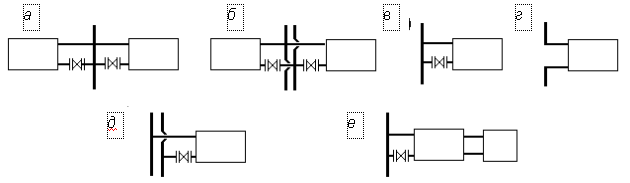
The number of risers depends on how the heaters are attached to them (Fig. 2.4).
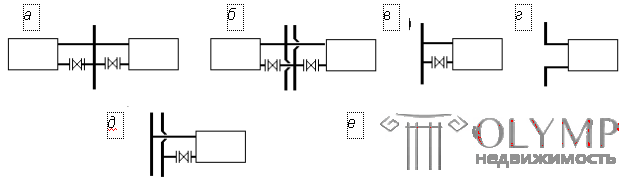 | With one-sided attachment of devices, it becomes possible to use standardized units of factory production, which speeds up and reduces the cost of installation, with double-sided, the number of risers decreases. The flow connection is mandatory for instruments on the staircase and in other rooms where there is a risk of freezing, on the coupling, attachment of instruments is allowed only in auxiliary rooms (storerooms, etc.). | |
Fig. 2.4. Options for connecting heaters to the risers: a - two-way in a single-pipe heating system; b - the same in the two-pipe system; in , d - one-sided; g - according to flow diagram; e - connection of the device on the hitch |
According to the location of the supply lines, there are systems with upper and lower wiring. If there is an attic in the building, either the top or bottom piping can be accepted, in the absence of the attic - only the bottom one. The upper wiring is more favorable for the operation of the system, since air is more simply removed from it and the natural circulation pressure generated by the cooling of water in heating devices is somewhat higher in it. The lower wiring avoids flooding the apartments in case of accidents and is easier to maintain.
| With the upper wiring, all risers are downward, one or two devices are attached to them on each floor. In case of lower wiring, the risers have ascending and descending parts. Devices can be attached to both parts or, as is often practiced in Khabarovsk, only to the descending part. The arrangement of highways in the attic and in the basement is shown in fig. 2.5. In the course project, the student must independently make the choice of the heating system design and justify the decisions. Examples of various schemes and designs of water heating systems are given in [4-6]. After placing the risers on the floor plan, their locations are transferred to the basement and attic plan (with the upper wiring), the supply and return lines are traced along the walls of the building, the heat transfer points are assigned to the basement of the building and the substation is placed. Then an axonometric diagram of the heating system is constructed showing all heating devices, risers, highways, heat point, air collectors, stop and control valves, as well as devices for air intake and water drainage. | |
| Fig. 2.5. The location of the heating system: a - with the lower wiring; b - with the upper wiring |
For heating networks, both traditional non-galvanized steel (black) pipes and plastic (metal-polymer) pipes can be used.
Steel water and gas pipes with outer diameters up to 60 mm (GOST 3262–75 *) can be used with water as well as with heat exchangers. These pipes have thick walls and the possibility of cutting at their ends of the thread. To connect the water and gas pipes used are attached to the thread fittings (couplings, tees, etc.) or welding.
The metal-polymer pipe is a five-layer construction (Fig. 2.6) consisting of a thin-walled aluminum pipe with a thickness of 0.2–0.5 mm (protects the system from oxygen diffusion), on which an adhesive base is applied on the inside and outside, and then layers of polyethylene.
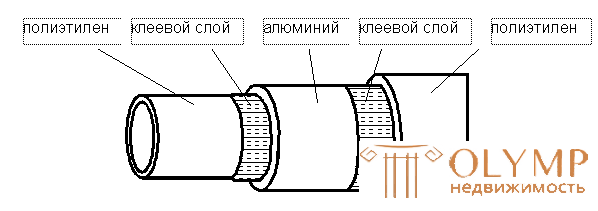 | Metal pipe combines the following advantages of metal and plastic pipes: 100% oxygen tightness; corrosion resistance; lack of mineral deposits on the pipe walls; durability not less than 25 years; frost resistance; reliability of work in conditions of high seismicity; increased noise absorption capacity; ease of transportation; manufacturability of the installation - the pipes are easily bent, they allow to bend around the elements of the premises, no precise adjustment of the linear dimensions is required. The installation of such pipes is carried out directly (without welding, threading) with equipment and devices made of steel, brass, plastics using fittings. | |
Fig. 2.6. The structure of the metal pipe |
Shut-off valves (valves, valves, cork taps) are installed on the input to the building (on the supply and return pipelines), branching highways and risers in the places of their connection to highways. To regulate the heat transfer of devices, three-way valves, double-adjustment valves or modern thermostats are provided [4, Fig. 7.12]. For the release of water from the system as a whole and individual risers, tees with plugs are placed at the lower points of the risers and at the inlet into the building (on the supply and circulation pipelines). To release air at the lower wiring on the devices of the upper floors, install Mayevsky cranes [4, Fig. 7.2], with the upper wiring in the upper points of the hot water pipelines (usually at the ends of the branches) air vent valves are provided.
In closed systems of water heating to compensate for changes in the volume of coolant in the system with fluctuations in water temperature set the expansion tank, it is in systems with natural circulation is used to remove air. In modern heating systems of individual buildings, automatic expansion systems that perform the same functions as a conventional expansion vessel, but are located directly in a heating unit, have proven themselves well. An example of the design of the heating system is given in Appendix. 13.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)