Concrete is a man-made stone. Mixing of four components - cement, fillers (crushed stone, building sand) and water. Concrete is a composite material - the result of molding and hardening. The main component is cement of a certain brand, thanks to the cement, the mixture after hardening acquires properties that are not inferior to natural stone.
The brand and (or) class of concrete is the most important indicator characterizing the strength of concrete.
Axial compressive strength - the ability of a concrete mixture to resist destruction from external loads.
Depending on the axial compressive strength index, concretes are subdivided into classes. The class is designated by the letter "B" and numbers indicating the withstand pressure in megapascals (MPa).
Along with the classes, the strength of concrete is also set by the marks designated by the letter "M" and the numbers 50-1000, showing the ultimate compressive strength in kgf / cm2, and the higher this figure, the heavier the concrete.
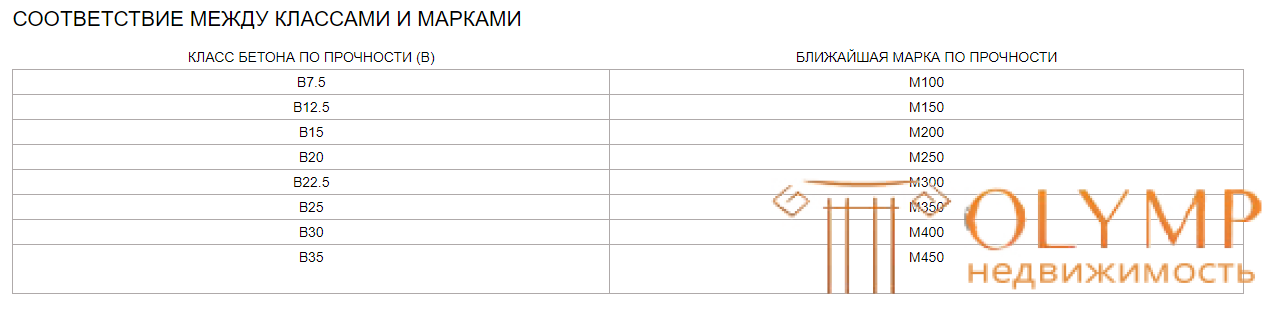
| CONCRETE STRENGTH CLASS (B) | NEAREST STRENGTH BRAND |
|---|---|
| B7.5 | M100 |
| B12.5 | M150 |
| B15 | M200 |
| B20 | M250 |
| B22.5 | M300 |
| B25 | M350 |
| B30 | M400 |
| B35 | M450 |
М100 B7.5 is the worst concrete grade. Main application: preparatory concrete work, laying a thin layer on compacted soil or sand cushion.
In construction, concrete M100 B7.5 is used quite often, but as an unloaded layer - preparation for monolithic supporting structures, floors concreted on the ground.
When carrying out preparatory work, M100 B7.5 is cast on compacted soil or a layer of sand. The purpose of the preparation from concrete M100 B7.5 is to prevent the leakage of cement laitance from the monolithic bearing structures into the ground and, accordingly, the ingress of moisture from the outside so that the concrete of the main structure retains its strength characteristics.
Used concrete M100 B7.5 and in road construction as a preparation for the main roadbed. M100 B7.5 concrete is used as a grout for fixing curbs, installing small architectural forms and in other irresponsible structures.
Ready-mix concrete М150 B12.5 is used as a preparatory material for screed floors and concrete sidewalks, pouring strip foundations, monolithic slabs.
Concrete M150 B12.5 has sufficient strength, which makes it the main brand used for laying concrete paths and slabs.
M200 B15 concrete is used in the manufacture of concrete screeds for floors, foundations, blind areas, paths. The strength of M200 B15 is sufficient for solving most of the tasks of individual construction: foundations (tape, slab, pile-grillage), production of concrete stairs, platforms.
In road construction, concrete M200 B15 is used to create a monolithic cushion for the main road pavement.
M250 grade is used mainly for the manufacture of monolithic foundations, including strip, slab, pile-grillage, lightly loaded floor slabs, fences, stairs, retaining walls.
The most frequently ordered concrete grade (this also applies to M200 B15). The combination of technological qualities and a relatively low price of concrete of this brand makes its use universal for almost any construction needs. M300 B22.5 is suitable for a monolithic or strip foundation for almost any house, including a country cottage.
The main application of М350: production of load-bearing walls, floor slabs, beams, columns, reinforced concrete structures and products, casting of monolithic foundations.
The main application of the M400 is: pouring pool bowls, cross beams, hydraulic structures, retaining walls, bridge structures, basements of monolithic buildings.
М450 is used for bridge structures, hydraulic structures, bank vaults, in the metro construction.
Cement mortar - does not contain coarse filler, it has three components - water, cement and sand. The cement slurry is greatly influenced by additives and plasticizers, which are introduced into the mixture during mixing. The additives increase the quality characteristics of the solidified solution - water resistance, frost resistance, additional strength, etc.
In accordance with GOST 28013-98, cement slurries differ in compression strength grades.
Table of applications depending on the strength grade of the cement mortar
|
Solution grades compressive strength |
Areas of use |
The proportions of the components parts of cement М400 |
|
| M40 (4MPa) |
reinforcing compound for gluing to expanded polystyrene or mineral wool |
||
| M50 |
Sealing gaps indoors |
7.4 parts of sand | |
| M75 | Internal masonry work | 5.4 parts of sand | |
| M100 |
Exterior laying of bricks and blocks, floor screed device |
4.3 parts of sand | |
| M150 |
Grouting heavy concrete structures, making screed, when equipping hydraulic facilities |
3.25 parts of sand | |
| M200 |
Due to its high water resistance, the product is used as waterproofing layer; in the manufacture of material for structures, who will contact during operation with aggressive media, sulfate-resistant cement is used |
2.5 parts of sand |
Mixed on the basis of one binder ( cement , gypsum, lime, water glass, clay).
Made with the addition of mixed powder materials. Mixtures can be lime-gypsum, cement-lime, cement-clay.
By composition, cement mortars are divided into the following types:
Difference between grout and concrete.
The main difference between concrete and cement mortar is that concrete contains a large aggregate - gravel or crushed stone. But the cement mortar contains only building sand as a filler.
Another difference follows from this - the use of building mixtures. Parts of supporting structures are made of concrete, and cement mortar is used to fill joints, plaster and to treat other surfaces.
Concrete has a wider scope of application in construction work, because it is stronger than cement mortars. But it cannot be used as a decorative coating for finishing individual elements of the structure. Cement mortars, in comparison with concrete mix, age quickly, become covered with cracks, and then crumble.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)