Load.

The loads acting on the structure and the strength characteristics of the materials from which the structure is made have variability and may differ from average values. Therefore, in order to ensure that during normal operation none of the limit states occur, a system of calculated coefficients is introduced, taking into account possible deviations in the unfavorable direction of various factors affecting the reliable operation of structures.
one.  load safety factor
load safety factor  f, takes into account the variability of the load;
f, takes into account the variability of the load;
2. safety factors for concrete  b and fixture
b and fixture 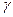 s, take into account the variability of their strength properties.
s, take into account the variability of their strength properties.
3. reliability coefficient according to the design purpose 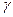 n, takes into account the degree of responsibility and capital of buildings.
n, takes into account the degree of responsibility and capital of buildings.
4. ratios of working conditions 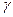 bi
bi 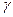 si, allowing to evaluate some features of materials and structures that can not be reflected in the calculations in a direct way.
si, allowing to evaluate some features of materials and structures that can not be reflected in the calculations in a direct way.
The basic idea of the method of calculation for limiting states is to ensure that even in those rare cases when the structure is subject to the maximum possible loads, the strength of concrete and reinforcement is minimal, and the operating conditions are most unfavorable, the structure does not collapse and will not receive unacceptable sags and cracks.
Load classification.
The loads acting on the building can be permanent and temporary.
Temporary , depending on the duration of the action, are divided into:
1. Durable;
2. Short-term;
3. Special.
Permanent loads include: own weight of structures, soil pressure
Temporary long-term loads include: the mass of stationary equipment (machines, devices), the load on the floors in warehouses, libraries, refrigerators.
Short-term loads include: loads from the masses of people, snow loads, wind, crane loads, loads arising during installation or repair of structures.
Special loads occur during seismic, explosive or accidental impacts.
In the calculations using the normative and calculated values of loads. Established by the norms of the greatest values of loads that can act on the structure during its normal operation, called regulatory.
The actual load, due to various circumstances, may differ from the standard in a greater or lesser direction. This deviation is taken into account by the load safety factor.
q = qn 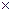
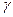 f - uniformly distributed load
f - uniformly distributed load
N = Nn 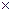
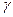 f - concentrated load.
f - concentrated load.
The calculation for group I is made for the design load
For constant loads 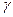 f = 1.1 - 1.3; for temporary
f = 1.1 - 1.3; for temporary 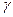 f = 1.2 - 1.6.
f = 1.2 - 1.6.
For snow load 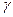 f = 1.4.
f = 1.4.
The design of the design according to group II of limit states is carried out on the design loads at 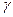 f = 1.
f = 1.
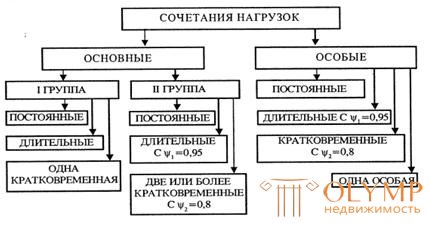
The building is subjected to the simultaneous action of various loads, so their calculation should be carried out taking into account the most unfavorable combination of design loads. Depending on the composition of the loads taken into account, the main combinations are distinguished, consisting of constant, long-term and short-term loads. Special combinations consist of permanent, long-term, possible short-term and one of the special loads.
The values of the design loads must also be multiplied by the reliability factor for the intended purpose of the structure. 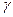 p, taking into account the degree of responsibility and capital of buildings. For buildings of the 1st class (objects of particular economic importance)
p, taking into account the degree of responsibility and capital of buildings. For buildings of the 1st class (objects of particular economic importance) 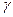 n = 1; for buildings of the 2nd class (having important economic significance)
n = 1; for buildings of the 2nd class (having important economic significance) 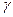 n = 0.95; for buildings of the 3rd class (having limited value)
n = 0.95; for buildings of the 3rd class (having limited value) 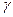 n = 0.9; for temporary structures with a service life of up to 5 years
n = 0.9; for temporary structures with a service life of up to 5 years 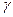 n = 0.8
n = 0.8
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)