The result of the development of soil is an earth structure, which is an engineering structure, constructed from soil in a soil massif or erected on the soil surface. Earthworks share:
in relation to the ground surface - excavations, embankments, underground workings, backfilling;
on service life - permanent and temporary;
by functional purpose - pits, trenches, pits, wells, dumps, dams, dams, roadbeds, tunnels, planning sites, workings;
By geometric parameters and spatial form - deep, shallow, extended, concentrated, simple, complex, etc.
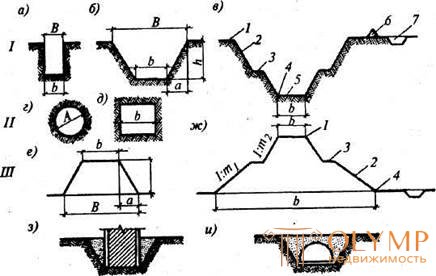
The most typical types of earthworks are presented in Fig. 2.1.
The permanent structures include structures intended for long-term operation - earth dams, canals, rail and trackless tracks, excavations and embankments erected during planning. The temporary earthen structures include excavations, torn off during the construction of the foundations of residential and industrial buildings, bridges, dams, trenches for laying water, sewer, gas and other networks, embankments for temporary roads and dams. Each earthen structure must be stable, durable and protected from water erosion.
Notches with a width of more than 3 m are called trenches, narrower notches for strip foundations or communication networks are tranches , and recesses for separate foundations or pillars are holes. These structures have a bottom and side surfaces, sloping slopes or vertical walls. Excavations developed for mining for the construction of the soil, called reserves; embankments into which dumping of excess soil is carried out - by cavaliers or dumps .
|
Fig. 2.1. Types of earthworks:
1 - transverse profile of the grooves: a - a trench of a rectangular profile; 6 - trapezoidal pit (trench); in - the profile of the permanent excavation; 1 - slope curb; 2-nd; 3 - berm 4 - base of the slope; 5 - the bottom of the slope; 6 - banquet; 7 - upland ditch; II - sections of underground workings: d - round; d - rectangular; III - embankment profiles: e-temporary embankment; W-permanent; IV - backfilling: s - the sinuses of the pit; and - trenches
Places for dumping construction and other debris are called landfills, and places where they develop sand, rubble and other building materials are called quarries . Excavations, closed from the surface of the earth and arranged for the laying of transport and communication tunnels are called underground workings .
The notches have a bottom and sloping slopes.
After the installation of the underground structures (or the underground part of the structures), the sinuses are returned to the ground - filling the space between the structure and the slopes of the excavation with soil.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)