Ancient Greece occupied the southern part of the Balkan Peninsula and numerous islands of the Aegean Sea.
The climate is Mediterranean, rather hot and arid. The mountain slopes were completely covered with forests, cut down at a later time. Several species of oak (including evergreens), pines (seaside and Italian), cypress, cedar, elm, poplar, fig, pomegranate, olive, laurel and myrtle grew here.
In the cultural heritage of ancient civilizations, Greek-Roman or ancient culture holds a special place.
In the history of culture of ancient Greece, there are several periods or epochs: Kritomikenskaya (XX – XIII centuries. BC), Homer (XII – VIII centuries BC.), Archaic (VIII – VI centuries. BC .), Classical (V – IV centuries BC) and Hellenistic (III – I centuries BC.).
Greece The archaic period was a series of policies (city-states), of which the largest was Athens. K VI century. BC e. Greek settlements on the Black Sea also belong to Olbia, Chersonesos, Theodosius, Phanagoria. Stone architecture develops. The architecture is developing a clear order system. An order (order) is a specific set of architectural elements, an integral artistic system of combinations of constructive and decorative parts with a certain ratio of their dimensions in the structure. He formed the basis of the structures of architectural structures, their harmonic structure and ideological solutions. During this period, Doric and Ionic orders are formed.
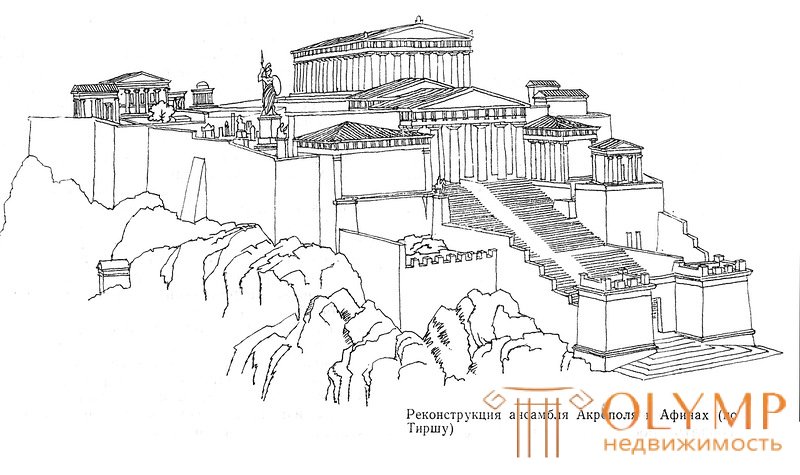
The classical era began with the Greco-Persian Wars, culminating in the creation of the Athenian maritime state. The political system - the slave-owning republic. In 460 BC Pericles came to power, one of the brightest and most talented figures of the era of slave-owning democracy. His rule is called the golden age of Greece. In this short period of time, the culture reached its highest peak. Cities were rebuilt and rebuilt according to a regular plan. Created architectural complexes, temples were built. Doric and Ionic orders reached perfection and were supplemented with new - Corinthian. A high level of development reached the arts and crafts. On the Acropolis, a mountain towering over Athens, Pericles built the Parthenon in honor of the goddess Athena. The remarkable creation became a sacred place, the national center of the Greek state, its culture.
The Hellenistic era is characterized by the formation of large Greek-eastern monarchies. In the IV. BC. The king of Macedonia, Alexander the Great (Macedonian) conquered Persia, Egypt, and the Mediterranean countries. After his death, the empire fell into a series of states. In the Hellenistic period, the construction of public buildings, stadiums, theaters. Formed type residential house peristilnogo type. Improvement and greening of cities is developing.
For landscape art of ancient Greece, the following types of green areas are typical:
Sacred groves - heroons. They were dedicated to the heroes and wore a memorial character. These are forest tracts with sources, sculptures and architectural structures. Later, heroes began to organize memorable sports competitions, and later, equipped with lanes, playgrounds, hippodromes, they turned into sports parks.
Roads and grounds were surrounded by rows of plane trees, poplars, etc.
Philosophical gardens were intended for scholarly conversations and studies.
The green decoration of the agora (urban squares, streets) was made up of ordinary landings along the roads and at the buildings.
Private gardens were purely utilitarian in nature. They widely used flower plants
In general, the landscaped territories of Greece carried a certain function, the placement of plantings in them was subordinated to this function, and from the utility and quality of the device itself there was an idea of its beauty.
For the further development of landscape architecture, not only the considered types of green areas in Greece are important, but also the theoretical positions of the composition and the spatial solution of the architectural ensembles of antiquity.
In ancient Greece, a system of proportions was developed - the principles of the golden section and module as the ratio of parts and the whole, as well as the principles of balance, rhythm and symmetry. These provisions are reflected not only in the buildings themselves, but also in their placement - the planning decision of the ensembles.
A classic example is the ensemble of the Athenian Acropolis (Appendix, Fig. A1, 6), located on a rocky hill and is a complex of temples. The various sizes of temples and other architectural forms, their free placement determined the picturesque beginning in a spatial composition. In this arrangement lies a certain sequence of perception of architectural volumes, their angle and plastic, focused on the line of movement of the solemn procession. The ensemble is dominated by the point of perception from the corner, and the entire Acropolis is perceived gradually, as the disclosure of paintings, each of which includes only one dominant structure. The whole ensemble is consistent with the landscape by subordinating the axes of the temples to the relief or the coast.
The use of all these principles has not lost its importance in modern landscape art.
In 146 BC. e. Greece became a Roman province. However, Greek culture was towering over Athens, - Pericles built the Parthenon in honor of the goddess Athena. The remarkable creation became a sacred place, the national center of the Greek state, its culture.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)