During the construction of the piers of bridges and other structures located under water, underwater concreting is used (laying the concrete mix under water without producing drainage) performed in one of two ways - vertically moving pipe (VPT) and ascending solution (BP). Common to both methods is a device around the perimeter of the concreted sheet piling design, which limits the flow of water to the work site, and the erected structure is protected from leaching of cement and sand. The following methods are also used: the laying of the concrete mix with bunkers and the method of tamping the concrete mix.
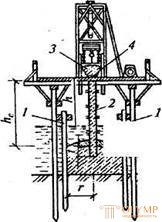
The method of vertically movable pipe (VPT) is used when concreting structures at a depth of 1.5 to 50 m, protected from running water, when high strength and solidity of the underwater structure is required (Fig. 9.2.).
Sheet walls, specially made formwork in the form of spatial blocks (boxes) made of wood, reinforced concrete, metal, or construction (slab shells, drop wells, etc.) are used as a fence. The fence design must be impermeable to cement mortar. For the production of work on the fence arrange a working platform on which set the traverse.
|
| Fig. 9.2. Underwater concreting by the VPT method: 1-boot raven; 2 - pipes; 3- formwork (sheet piling); 4-funnel funnel; 5-additional formwork fastening; 6-working flooring; 7- fencing; 8-beta-novod; 9-floating crane; 10-suspension pipe cast |
To the traverse hang steel betonovod, assembled from separate seamless pipes with a length of 1 ... 1.2 m and a diameter of 200 ... 300 mm for easily detachable waterproof connections. The pipe is lowered to the bottom of the structure, in the upper part of the pipeline, located above the surface of the water, has a funnel with a gate or a hopper for receiving the concrete mix.
Concrete pipe suspended from the traverse, can be raised and lowered with a winch. Initially, a wad of burlap is inserted into the neck of the pipe, which protects the first portion of the concrete mix, which is immersed in the pipe, from erosion by water. After filling up the funnel, the shutter is opened, and the concrete mixture after the wad drops down. After the concrete mixture fills the entire concrete pipe and the funnel itself, with the continuous continuous supply of the concrete mixture to the funnel, the pipe is lifted off the ground and slowly begins to be lifted. It is necessary to control that the pipe is permanently recessed into the concrete mix for at least 0.8 m at depths up to 10 m and 1.2 m - at great depths. Then, without stopping the supply of the concrete mix, the pipe is lifted so that its lower end is always located not less than 0.8 ... 1.2 m below the concrete surface.
At the end of the lifting of the pipe to the height of the link, the concreting is suspended, the upper link of the pipe is dismantled, the funnel is repositioned, after which the concrete mix is resumed. The block is concreted to a level exceeding the design mark by; equal to 2% of its height.










 In this concreting, only the top layer of concrete is in contact with water, which, after performing the work, lifting the pipe and erecting the whole structure above the surface of the water, is removed, but not less than 10 cm. Only plastic concrete with a draft of 16 ... 20 cm is used; - only vertical. The spreading radius of the concrete mix from the bottom hole of the pipe should not exceed 6 m, therefore large structures are divided into blocks with mandatory overlapping of concreting zones, continuous supply of concrete mix, simultaneous and uniform lifting of the pipes. Accepted concreting intensity of more than 0.3 m3 per 1 m / h.
In this concreting, only the top layer of concrete is in contact with water, which, after performing the work, lifting the pipe and erecting the whole structure above the surface of the water, is removed, but not less than 10 cm. Only plastic concrete with a draft of 16 ... 20 cm is used; - only vertical. The spreading radius of the concrete mix from the bottom hole of the pipe should not exceed 6 m, therefore large structures are divided into blocks with mandatory overlapping of concreting zones, continuous supply of concrete mix, simultaneous and uniform lifting of the pipes. Accepted concreting intensity of more than 0.3 m3 per 1 m / h.
When underwater concreting (including under the clay solution) it is necessary to ensure:
• isolation of a concrete mix from water in the process of its transportation under water and laying into a concrete structure;
• density of formwork or other accepted fencing;
• continuity of concreting within the concreting unit, working area, grapple;
• monitoring the state of the formwork (fence) in the process of laying concrete mix and the entire period of concrete gain strength;
• protection from erosion and mechanical damage to the surface of the laid concrete mix during setting and hardening.
Recommended production technology works :
1 . Before laying the concrete mix:
• check the formwork and its compliance with the project;
• clean the formwork cavity from debris and flows of soil and silt;
• install a lifting tower and a concrete pipe.
2. The sequence of processes when laying concrete mix:
• lower the concrete pipe to the bottom of the structure with preliminary drawing on it with indelible paint marking every 10 cm in length to control the lifting of the pipe;
• a bunker-funnel is attached to the top of the concrete pipe, in the throat of which a plug is secured, which protects the first portion of the supplied concrete mix from contact with water;
• the first portion of the concrete mix is fed into the funnel bunker, the volume of the bunker must be equal to the volume of the concrete casting pipe;
• open the valve at the bottom of the funnel, the wad, and behind it the concrete mix rushes down, the next portions of the concrete mix are continuously fed into the bunker. After filling the entire pipe and bunker with concrete mix while continuing to supply concrete mix, raise the end of the tube by 30 ... 50 cm and the concrete mix flows into the cavity of the formwork. The concrete mix must always be above the bottom of the pipe at least 0.8 m;
• when the concrete mixture reaches a height of 4 m in the cavity of the formwork, several pipes are forced into the concrete to stop the concrete mixture from flowing out of it into the formwork, suspend the concrete pipe by the second knee, disconnect the funnel, then the first link, again connect the funnel to the second link and continue to feed the mixture into the cavity of the pipe;
• the concrete mix used must, by its characteristics, not less than 10% exceed the specified characteristics of the project, the concrete mix must be fed into the funnel from a height of no more than 1 m.
Upon reaching concrete strength of 2 ... 2.5 MPa, the upper weak layer of concrete, continuously in contact with water, is removed during work.
In the method of VPT, concrete of a class not lower than B25 is used, the concrete mix stacked with vibration, mobility of 6 ... 10 cm and laid without vibration with mobility of 16 ... 20 cm. Prepare a mixture on gravel or a mixture of gravel with 20 ... 30% crushed stone, necessarily introducing plasticizing additives.
The method of the ascending solution (BP) is non-pressure and pressure. Concreting using the VR method with pouring a rough stone slate with a cement-sand mortar should be used when laying concrete under water at depths of up to 20 m to obtain concrete strength corresponding to the strength of rubble masonry; the same, from crushed stone at the same depths for the erection of concrete structures up to B25 and with concreting depths of 20 to 50 m and when reinforcing structures, it is recommended to use crushed stone aggregate without sand.
With the free-flow method (Fig. 9.3), shafts with lattice walls are installed in the concreted block, pipes with a diameter of 37 ... 100 mm, assembled from links up to 1 m in length with waterproof, easily removable connections, are inserted into the shafts. The cavity of the block is filled with crushed stone, gravel, stone bedding with a size of 150 ... 400 mm, and cement mortar from 1: 1 to 1: 2 is fed through the tube through the pipe. The mines are necessary for lowering and lifting the pipes over the entire height of the block to be concreted. The spreading of the solution is carried out due to the pressure of its column in the mine. Rising, the cement mortar should flow freely, filling all the voids in the stone draft. Therefore, to prepare the solution, fine sands with a grain size of not more than 2.5 mm and with a content of not less than 50% of particles not more than 0.6 mm are used. The mobility of the solution should be 12 ... 15 cm. The radius of action of each pipe is 2 ... 3 m. The pipes should be sunk into the solution to be installed to a depth of at least 0.8 m.
|
1- pipe; 2- mine; 3- formwork (sheet piling); 4 stone crushed stone dumping; 5- solution; 6- fencing; 7-us-til; 8- winch; 9- yes; 10-supply hose; 11-solution pump |
As the level of the laid solution increases, the pipes are lifted, dismantling their upper links. The level of the solution is adjusted to 100 ... 200 mm above the design mark.
In this method, the cement consumption is two times greater than with the method of a vertically moving pipe.
Pressure concreting is also carried out , when the filling pipes are installed without mines directly into the coarse aggregate layer and cement mortar (dough) is injected (pressurized) through it. The pressure of the solution in the pipe is created using a mortar pump. Sand is accepted in sizes up to 2.5 mm. The radius of action of pipes is not more than 3 m when casting stone and 2 m of crushed stone aggregate. The BP method is used when laying concrete mix at a depth of 20 m.
Fig. 9.4. Underwater concreting by tamping: 1-enclosing wall; 2- tamping; 3-wet concrete mix; 4-layered layer | In both cases, the pipe should be sunk into the solution by at least 0.8 m, the top layer of the solution 10 ... 20 cm high, in contact with water and located above the design mark, is cut off. In the bunkering method, the concrete mix is placed under water on the base (or previously laid layer) of the concreted element in the drop-down boxes, buckets or grabs and unloaded through the open hole. Closed on top of the hopper have a seal on the closing contour, which prevents |
leakage of cement paste and the penetration of water into the bunker. The concrete mix is released with a minimum separation of the bottom of the bunker from the surface of the laid concrete, thereby excluding the possibility of free dropping of the concrete mix through the water column. The method is technologically simple, does not require the installation of scaffolding and allows the laying of the concrete mix on an uneven base with large recesses and elevations. However, concrete masonry is characterized by layering. The method is applied at a depth of up to 20 m and if the class of the laid concrete is not higher than B20.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)