
Reinforcement - steel rods, rolled sections and wire, located in concrete for joint work with it.
Combined-monolithic and monolithic non-strained structures are reinforced by enlarged mounting elements in the form of welded meshes, flat and spatial frames, which are manufactured outside the erected structure and then installed with mounting cranes. Sometimes complex structures are reinforced directly in the design position from individual rods with their connection to the finished reinforcement cage by welding or knitting.
The reinforcement is subdivided according to its purpose in the construction into working, distribution and assembly (Fig. 8.1).
Working reinforcement perceives tensile forces arising in reinforced concrete structures from its own weight and external loads.
Distribution valves serve:
• for even distribution of loads between working rods;
• to ensure their joint work;
• to connect the working rods among themselves, preventing the working reinforcement from displacing during concreting.
Assembly fittings usually do not take the effort, and provides the exact position in the formwork working rods and flat reinforcing mesh and elements.
The main in modern construction is a periodic profile reinforcement with reliable anchoring and increased adhesion to concrete. When using rods from smooth reinforcement for their better fixing in concrete, the ends of the rods working in tension are bent in the form of hooks.
In civil engineering, reinforcing bars with a diameter of 12 ... 30 mm are usually used; in industrial construction, reinforcement bars with a diameter of up to 
 40 mm, in hydrotechnical - rods with a diameter of 90 ... 120 mm. As the reinforcement is sometimes used profile hire.
40 mm, in hydrotechnical - rods with a diameter of 90 ... 120 mm. As the reinforcement is sometimes used profile hire.
The reinforcing products include individual rods (rod reinforcement), reinforcing mesh, flat and spatial reinforcement cages, reinforcement products for prestressed structures, embedded parts, mounting hinges and clamps.
Rod reinforcement produce a smooth profile (due to the low efficiency of its release is reduced) and periodic with the location of the projections on a helix or herringbone. Depending on the manufacturing technology, the armature is subdivided into hot rolled (divided into 5 classes from A-1 to A-VI according to the old designation — the new designation A-240 (A-1), A300 (A-III), A400 (A-IV ), А800 (АV), А1000 (АV1)) and hot-rolled with the subsequent hardening with an extract in a cold state, it has 2 classes - А-Пв and А-Шв.
Welded reinforcing mesh consist of mutually intersecting rods connected at the intersection of welding. They are produced with longitudinal, transverse and mutually perpendicular working reinforcement. In general, the grid combines the working and distribution armature and consists of separate wires with a diameter of 3 to 9 mm inclusive and rods of reinforcing steel with a diameter of 10 mm, is located
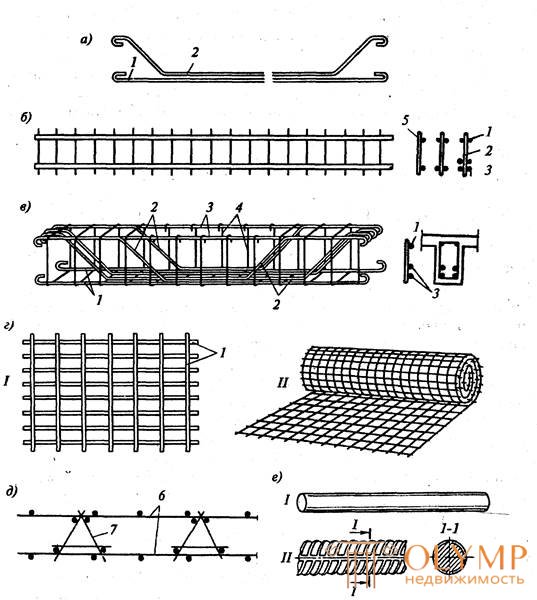
Fig. 8.1. Types of fittings:
|
|
and - reinforcing bars; b —flat frame; in - spatial framework; d — armature grids: 1 — flat; II - roll; d - reinforcement block; e - hot rolled reinforcing steel: / —smooth; // - periodic profile; W - skeleton of a column of rod reinforcement; h — the same, from rigid reinforcement; 1 - straight working rods; 2 - the same, bent; 3 - mounting rods; 4 - clamps; 5 - distribution rods; 6 - grids; 7 — spatial framework; 8 - reinforcing release; 9 — corner; 10 - bracing
in two mutually perpendicular directions and connected at the intersection by resistance spot welding. These nets are used if necessary to provide the structure with a minimum non-design reinforcement. The distance between the individual rods - ranging from 50 to 250 mm, formed between the rods and wires of the cell usually have a size from 50x100 to 150x250 mm. The total width of the grids along the axes of the outermost rods is set from 900 to 3500 mm (the grid must be placed between the longitudinal sides of the truck during transportation).
| |
Fig. 18.2. Armature for prestressed structures:
a seven-wire strand; b is the same, 19-wire; c, d - ordinary wire ropes (strands of 7 and 19 wires); d- the same, three-strand; e, w - beam; h, and - multi-strand ropes; I- working wire; 2, 9 - knitting wire; :spiral; 4- shorty; 5- axial rod; 6, 7- outer protective coating
Flat working grids are produced up to 2.5 m wide, up to 9.0 m long,
sometimes in accordance with the order up to 12.0 m. Longitudinal working rods
have a diameter of 12 ... 25 mm at a pitch of 200 mm, mounting fittings are usually
with a diameter from 8 to 12 mm with a maximum step up to 600 mm. If necessary, the grids in factories may be subjected to additional processing — cutting holes, welding additional rods, and bending.
The grids in the form of rolls have a wide range of steel used, the diameters of the rods, the size of the cells and the width of the grids. The length of the nets is not specified, but the weight of the individual roll should not exceed 1200 kg.
Flat steel frames usually consist of longitudinal reinforcement, forming one or two belts and connecting lattices in the form of separate transverse or continuous snake-like rods. A large number of transverse rods in frames, connected to the working rods by spot welding, creates reliable anchoring in concrete of the longitudinal rods along their entire length and makes it possible to refuse to hook the hooks even with smooth reinforcement. The working armature of the unified frameworks is accepted with a diameter of 10 to 30 mm, and distributional valves are accepted only with a diameter of 10 mm (during welding, rods of smaller diameter may be burned). Used frames for the reinforcement of linear structures - beams, girders, girders, hollow flooring.
Spatial reinforcing cages consist of two or four flat cages connected together by separate rods or clamps. Such frames are used for the reinforcement of columns, beams, beams and foundations.
Sometimes they use reinforcing supporting frames, which, together with the formwork, are called reinforcing-shuttering blocks. Usually, such a decision is made if necessary to build a single structure with a span of up to 9 m. In this case, rolling profiles are used for reinforcement, mainly in the form of angles, strip and square steel, which allows you to dispense with special scaffolds supporting formwork unit, reduce the consumption of timber, significantly reduce labor costs and the timing of work.
The assembly loops made of reinforcement are an element of precast concrete structures and are intended for slinging during lifting and installation.
Embedded parts - metal plates attached to the reinforcement cage of the structure in welding, are necessary to connect the prefabricated elements among themselves during the erection of buildings and structures; the docking of elements is carried out by welding of embedded parts embedded in the structure during their manufacture.
Clamps are used to connect individual work and mounting rods into a finished spatial frame.
For the reinforcement of pre-stressed structures, wire reinforcement is most often used (Fig. 8.2).
Wire armature is divided into several types:
• low-carbon reinforcing wire of class B-1 and high-strength carbonaceous material class В-П;
• wire strands of three-, seven- and multiwire strands on the right side of the twist, and when cutting the strands of their wire does not unwind;
• high-strength wire ropes.
In recent years, non-metallic reinforcement in the form of fiberglass and asbestos has been widely used.
Fiberglass mixed with cement mortar forms glass cement with high strength, but low water and gas permeability. The strength of cement stone increases when using chopped fiberglass with a chaotic distribution of it in the structure. Also, the high strength characteristics will have a monolithic design with a chaotic distribution in it of scraps of reinforcing rods and wire.
With the use of asbestos fibers produce asbestos cement, products from which have high strength and impermeability.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)