
Monolithic strip foundations. Strip foundations for walls suit mainly monolithic or prefabricated blocks. Monolithic reinforced concrete strip foundations are made in the form of lower reinforced tape and non-reinforced or slightly reinforced foundation wall, above which the walls of the building are arranged.
The process of building foundations and walls of monolithic reinforced concrete includes a breakdown of the axes of the foundations, the formwork device, the assembly and installation of reinforcement and concreting. The choice of technology for the construction of foundations depends on the design solutions of the foundations and the buildings themselves, as well as on the existing technological equipment and mechanisms.








 The choice of the type of formwork affects the type of concreted structures and their repeatability. Choose a formwork based on technical and economic calculations for the possible options. Determining indicators - the cost of materials and labor, the cost of one turnover of formwork.
The choice of the type of formwork affects the type of concreted structures and their repeatability. Choose a formwork based on technical and economic calculations for the possible options. Determining indicators - the cost of materials and labor, the cost of one turnover of formwork.
With a large repeatability of the foundations of small volume and simple form, inventory metal block forms are used, which are installed in place by a crane. Block forms can be made permanent, detachable, and transformable; the latter change their size and shape by extending and then fixing the elements with special devices. In some cases, steel inventory formwork from spatial blocks or large shields, fixed formwork from flat or spatial reinforced concrete elements, small and large-panel formwork with a deck of waterproof plywood can be used.
Installation of reinforcement perform enlarged elements in the form of grids and spatial frames. The lower reinforcement grid of the foundation is installed prior to the installation of the formwork. To create a protective layer of concrete, clamps are installed in a staggered manner with a step of 1 m. Next, reinforcement cages are installed and secured with clamps. Temporary attachments are removed from the frames after they are welded to the grid of the base of the foundation. Separate rods of grids and frameworks on the site of their installation must be joined in welding. Upon completion of the formwork work on the grapple proceed to install the formwork.
Formwork strip foundations of constant cross section are collected depending on the height of the foundation. With a height of 2 ... 2.5 m, the boards are installed in series vertically, connecting them to each other on locks, temporarily unfastening them with inventory, with struts. Attach them to the fray, and then formwork planes connected with ties. The shields of the second tier are fixed to the lower ones after leveling the installed formwork and position them horizontally. With the height of the strip foundation of more than 2.5 m, a constructive solution of the formwork should be proposed in the flow chart.
Panel formwork for strip foundations of variable cross-section can first be assembled as a slab for the lower part of the foundation; the upper part of the formwork can be installed before and after concreting the lower part of the foundation.
Before laying the concrete mixture, it is necessary to carefully prepare the soil foundation. Loose, organic and similar soils should be removed, digging sites should be filled with compacted sand or rubble,
To achieve solidity of reinforced concrete foundations, concreting must be carried out continuously, preventing the formation of seams. The concrete mixture is laid in layers with a thickness of 20 ... 30 cm, each subsequent layer is placed after compaction of the previous one and, as a rule, before its setting.
Belt foundations concreted, depending on the design features in one, two and three stages (Fig. 4.1).
Single-stage layering concreting is used when arranging strip foundations of rectangular cross section in thrust or variable cross section with a cross-sectional area of less than 3 m2. Strip foundations with steps with a cross-sectional area of more than 3 m are concreted in two stages: first, steps, then the wall. In three stages, tape foundations with sub-columns, used in frame buildings, are concreted.
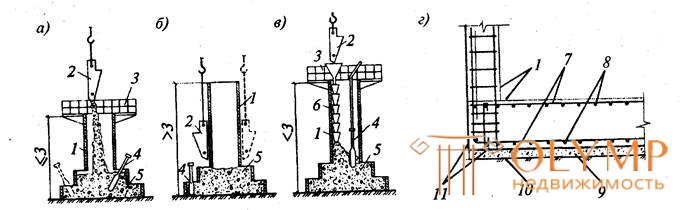
Fig. 4.1. Concreting strip foundations:
a - columnar with continuous supply of concrete mix; b - the same, concreted in steps, in - step concreted with the use of vibro-bob; g - a constructive solution to the foundation; 1- foundation formwork; 2 - a tub with a concrete mix; 3 - working platform; 4 - vibrator; 5-concrete; 6 - link trunk; 7 - longitudinal reinforcement; 8 - transverse reinforcement, 9-concrete preparation; 10 - compacted soil; 11- waterproofing waterproofing
Features of concreting the walls of the underground part of the building depend on the thickness and height of the walls, as well as on the type of formwork. Collapsible-adjustable panel formwork is installed in two steps: first, from one side to the entire height of the wall, and after installing the reinforcement, from the other. With a high height and wall thickness, the formwork of the second side is installed in the process of concreting. If the formwork is installed on the entire height of the wall, then in the formwork provide holes for the concrete mix. The formwork of walls with a thickness of more than 0.5 m can be erected to the entire height of the wall with the supply of concrete mix from above with the help of trunks.
Concreting technology of walls depends on the formwork design. It can be provided for layered laying of the concrete mix to a height of 400 ... 600 mm with the height of the tier of stackable formwork in the same 









 the limits. When concreting walls in collapsible-adjustable formwork, the height of sections performed without interruption should not exceed 3 m. With a higher height of sections of walls concreted without working joints, it is necessary to establish breaks in concreting for 40 ... 120 minutes for precipitating the concrete mix and warning formation of sedimentary cracks.
the limits. When concreting walls in collapsible-adjustable formwork, the height of sections performed without interruption should not exceed 3 m. With a higher height of sections of walls concreted without working joints, it is necessary to establish breaks in concreting for 40 ... 120 minutes for precipitating the concrete mix and warning formation of sedimentary cracks.
With a wall length of more than 20 m, it is divided into sections of 7 ... 10 m and a dividing wall is installed on the border of the sections.
The leading process in the construction of foundations is concreting, therefore the number of workers in each stream (installation of formwork, rebar placement, concreting, disassembly of formwork) is determined by the leading flow. It is necessary that the work in all the streams go in the same rhythm. For the organization of in-line work, the foundations and walls are divided into hooks, which may include a span, part of a span or foundations on the same axis.
Prefabricated strip foundations consist of prefabricated foundation pillows, reinforced by calculation, above which install wall blocks. Reinforced concrete base plates-pillows and concrete wall blocks are unified, the nomenclature provides for their division into four groups, each of which differs in perceived load. To increase the rigidity of the structure, to level the sediment during construction on weak soils and as anti-seismic measures, precast foundations are reinforced with reinforced seams or reinforced concrete belts arranged on top of the foundation cushions or the last row of wall foundation blocks along the entire perimeter of the building at the same level.
For sandy soils, the foundation blocks are laid directly on the leveled base, for other soils - on a 10 cm thick sand cushion. Under the base of the foundations you cannot leave loose or loose soil, it must be removed and sand or crushed stone should be covered in its place. Depths in the soil base with a height of more than 10 cm are filled with monolithic concrete. The width and length of the sandy base is made 20 ... 30 cm larger than the size of the foundation, so that the blocks do not hang down from the sandy pillow.
The foundation blocks are laid according to the layout scheme in accordance with the design (Fig. 4.2) in order to provide breaks for laying water supply, sewage and other inputs.
Installation begins with the installation of the lighthouse blocks in the corners and at the intersection of the walls. The foundation block is supplied by the crane to the place of installation, it is guided and lowered onto the base, minor deviations from the design position are eliminated by moving the block with a mounting crowbar with tensioned lines. At the same time the surface of the base should not be broken. Lanyards are removed after the unit takes the correct position in the plan and in height. The gaps between the blocks of the strip foundation and the lateral sinuses in the process of installation are filled with sand or sandy soil and compacted.
Fig. 4.2. Installation of prefabricated tape foundations: 1 - foundation cushion; 2 - wall block; 3 — sand preparation; 4 - reinforcing belt; 5 - bed from the solution; 6 - sealing of the joint by monolithic concrete; 7 - block slinging | When installing foundations for columns, carefully control the position of the installed blocks relative to the main axes. With the help of levels they control the position of the blocks in height, check the bottom of the glass for blocks of glass type, and check the bottom of the block for others. Installation of basement walls (wall blocks) begin after checking the position of the laid foundation blocks (pillows) and waterproofing devices. If there are no special instructions in the project, then, as an insulation, spread a layer of mortar 2 ... 3 cm thick on the cleaned surface of the foundations; the solution also serves as a leveling layer. |
In accordance with the wiring diagram on the foundations mark the position of the wall blocks of the first (bottom row), noting the place of the vertical joints. Installation begins with the installation of the lighthouse blocks in the corners and at the intersection of the walls at a distance of 20 ... 30 m from each other. After installing the lighthouse blocks at the level of their top, they tighten the cord - the quay along which the row blocks are installed.
Subsequent rows of blocks are mounted in the same sequence, marking the layout of blocks on the underlying row. The first two rows of blocks are installed from the laid foundation blocks, the subsequent ones - from inventory scaffolding. The brand of the solution on which the blocks are to be mounted is indicated in the draft.
The erection crane can be placed on the side of the excavation, then, within the grab, first all the foundation blocks are mounted, and then the basement wall blocks. If the crane is in the pit, the foundations and basement walls are installed in separate sections, the source 








 For the fact that the erection crane will not be able to re-enter the zone where the blocks are already laid above ground level.
For the fact that the erection crane will not be able to re-enter the zone where the blocks are already laid above ground level.
Fig. 4.3. The scheme of the device base plate: 1 - the height of the base plate, 2 - longitudinal reinforcement; 3 - the same, transverse; 4 - pasted waterproofing; 5 - concrete preparation; b - compacted soil | Solid foundations (monolithic slab) are made of monolithic reinforced concrete, by constructive solution they can be made in the form of a smooth plate (with prefabricated glasses for columns), a smooth plate with monolithic glasses (fig. 4.3), a ribbed plate and a box section . Base plates, tank bottoms, tunnels, etc. have large areas and are characterized by saturated reinforcement. The thickness of such plates ranges from 0.2 |
up to 2 m. The methods of their concreting are selected taking into account the size in terms of, thickness, reinforcement degree, available mechanization of work, actual delivery volumes of the concrete mix.
Base plates are reinforced with welded meshes in two layers or more. The reinforcement cages can be formed in different ways: stack horizontal grids and install supporting frameworks or pre-merge flat horizontal grids and supporting frameworks into a self-supporting spatial arblock. Armoblocks are installed with gaps that overlap with one or two rows of flat horizontal grids resting on armored blocks.
Massive foundation slabs are concreted with the use of permanent reinforced concrete formwork, disassembled-adjustable of unified elements. Large-area formwork panels, as well as reinforcing frame blocks, are mounted using mounting cranes. The fixing of the formwork and frames must be reliable and withstand the technological loads from the concrete mix, mechanisms, machines, working and inventory devices. The formwork prepared for production should be commissioned.
With a large area of the plates they are divided into blocks of concreting or maps. Along the edges of the maps, wooden or mesh formwork is installed without cutting the reinforcement at the borders of the maps. As an external and internal formwork, it is most advisable to use a steel mesh made of wire 0.7 mm in diameter with a cell of 5x5 cm. Such a mesh is fixed to the reinforcement of the slab with knitting wire or clips.
The width of the blocks take into account the conditions of continuity of concreting and the rate of supply of the concrete mix. In each block of concreting it is necessary to provide work areas: acceptance and pre-leveling and compaction. The required speed of concreting is determined from the condition that the previously laid portion of the concrete mix is overlapped with the subsequent vibration compaction before the concrete begins to set in both zones. Accepted speed of concreting should be ensured by the presence in a sufficient number of means of compaction of the concrete mix.
If the slab thickness is less than 0.5 m, the slab breakdown into maps and concreting is carried out in the same way as concrete preparation for floors, i.e., it is concrete in maps with a width of 3 ... 4 m. With a greater thickness, the slabs are divided into parallel maps with a width 5 ... 10 m, while between them leave dividing strips with a width of 1 ... 1.5 m.
The concreting front within the map should be minimal. Maps are concreted in a row, i.e. one by one; To reduce the total shrinkage, the concrete into the separation strips is placed into the strut with the hardened concrete ready-made cards after removing the formwork at their borders.
Бетонную смесь с осадкой конуса 2...6 см подают на карты бетононасосами, с помощью бетоноукладчиков, эстакад, а также в бадьях с помощью кранов. В отдельных случаях бетонирование может осуществляться пневмотранспортом, с помощью виброхоботов, ленточными конвейерами и непосредственно из транспортных средств. Подавать смесь необходимо в направлении к ранее уложенному бетону, как бы прижимая новые порции бетона к ранее уложенным. При сосредоточенных объемах работ в массиве и темпе бетонирования 50..100 м3/смену могут быть использованы стационарные бетононасосы Плиты даже предельной толщины бетонируют в один слой. При этом несколько затрудняется виброуплотнение, поскольку внутренние вибраторы требуется погружать в смесь на глубину, в 1,5...2 раза превышающую длину рабочей части. Для виброуплотнения таких конструкций целесообразно применять навесные вибраторы и вибропакеты.







 Concreting must be organized in such a way as to avoid making joints within one concreting card.
Concreting must be organized in such a way as to avoid making joints within one concreting card.
Align the concrete slabs at the beacons, smooth the surface with trowels. At the junction of the walls, bearing columns and pillars, the surface of the concrete is left rough.
It is advisable to carry out work on the installation of monolithic base plates by streamline organization of work broken down into three leading streams: reinforcement of foundations, installation of formwork, including mesh at the border of concreting zones, and direct concreting. Works must be performed in the same rhythm. The leading stream is concreting, therefore the number of workers in each stream is calculated based on the continuous work of concrete workers.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)