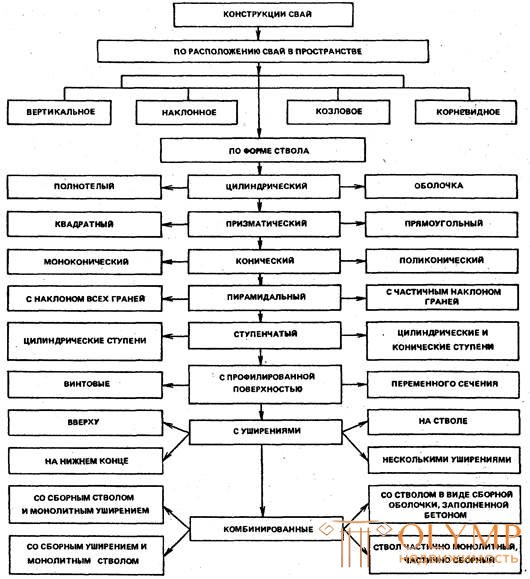
Piles are divided by a number of signs into several groups (Fig. 4.4):
on material - wooden, metal, concrete and reinforced concrete, combined, soil;
by construction - square, tubular, rectangular and polygonal, with and without broadening, integral and composite, prismatic and conical, continuous section and hollow, screw and pile-columns;
by the method of the device - driven, manufactured at the plant or on the site itself and immersed in the ground, and stuffed, arranged directly in the ground (in a pre-drilled well);
by the nature of the work (by the method of transferring the load to the base) - piles-pillars that transfer the load from the building to the rocky or practically incompressible soil at their ends, and hanging piles that transfer the load due to the friction of the soil along the side surface of the pile;
by the type of perceived load - central, vertically acting load, load with eccentricity, and pulling effort;
by type of reinforcement of reinforced concrete piles - with prestressed and non-stressed longitudinal reinforcement, with and without transverse reinforcement.
Pile bush - several adjacent piles, jointly perceiving the total load; the grillage is a construction that unites the top of the pile for their joint work.
Wooden piles are made of pine, spruce, larch, cedar, fir, oak. The pile length is 4 ... 12 m, the diameter at the thin end is 18 ... 34 cm. At the lower end, the pile is pointed at 3 ... 4 faces, the point should coincide with the axis of the pile, the tip deviated from the axis can lead the pile away from project position. When driving into dense soils and protecting the tip from destruction, a metal shoe is put on the tip, and the upper part is an iron ring-yoke protecting the pile head from being destroyed (shredded) during driving.

Fig. 4.4. Pile classification by design







 When long piles (> 12 m) are required, they are pulled together from several logs - in the butt, in the half of the tree or on the lining. To protect the piles from rotting, they are impregnated with antiseptics or immersed in such a way that the entire pile is located below the lowest water table.
When long piles (> 12 m) are required, they are pulled together from several logs - in the butt, in the half of the tree or on the lining. To protect the piles from rotting, they are impregnated with antiseptics or immersed in such a way that the entire pile is located below the lowest water table.
Wooden tongues are made of uneven bars, a comb is arranged on one face, and a groove, preferably of a rectangular cross section, on the other. Before driving, the grooves are joined by 2 ... 3 pcs. in the package, make a common bevel on the tip and put on a common bow. Typically, the thickness of the groove is 5..14 cm, but can reach up to 26 cm.
Metal piles are used in the port, bridge, energy and industrial construction, in the construction of high-rise structures (radio masts, television towers). Use steel pipes with a diameter of 25 ... 100 cm, rails, I-beams, screw piles with a special tip, screwed into the ground.
Shell piles - metal tubular piles with a diameter of 1.2 ... 2 m and more, up to 14 m long, if necessary, they are expanded and joined in welding. Piles with an open bottom end as the depth is filled with soil, which, compacted, increases the carrying capacity of the pile. Piles-shells with a closed lower end in the form of a removable tip are driven into the ground. The metal tip always remains in the ground, the pile itself can be left and filled with concrete mixture to increase the carrying capacity or removed. In the process of extracting the pile shell, its cavity is filled with concrete mixture.
Steel sheet piling used for the device waterproof walls of the pits, retaining walls, piers, embankments. For the tongue, special profiles are produced - flat, trough-shaped, z-shaped, up to 30 m long, in some cases using ordinary steel bars.
Reinforced concrete piles produce a cross section of 20 x. 20 to 60x60 cm and a length of 3 to 16 m with conventional and prestressed reinforcement. Pre-stress reduces the consumption of concrete by 15 ... 20%, metal up to 50 ... 60% compared with conventional reinforcement. Reinforcement is necessary for transporting and driving piles; for normal compression work, indirect reinforcement is sufficient. Preloading during driving prevents the occurrence of deformations, cracks, tightens the existing cracks.
Hollow piles of square and tubular section with a length of 2 ... 6 m are used in dense soils and low loads from the construction under construction, the outer diameter can be up to 80 cm.
The construction of pile foundations is a complex process, including the example of the method of driving:
■ preparation of the territory for conducting works;
■ geodetic breakdown with the removal in nature of the position of each pile;
■ delivery to the construction site, installation, commissioning and testing equipment for piling;
■ transportation of finished piles from the place of their manufacture to the place of their immersion;
■ pile driving;
■ cutting of finished piles at a given mark;
■ removal of cut residues from the construction site;
■ device monolithic or precast grillage;
■ dismantling equipment.
Analysis of soils, their carrying capacity shows that for most of the territory of Russia, dense soils lie at a relatively shallow depth, which allows the use of piles with a length of 3 ... 7 m.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)