Depending on the soil conditions, the bored piles are arranged in one of the following ways - by the dry method (without fixing the walls of the wells), using mud (to prevent the collapse of the walls of the well) and with fixing the well with the casing.
a )
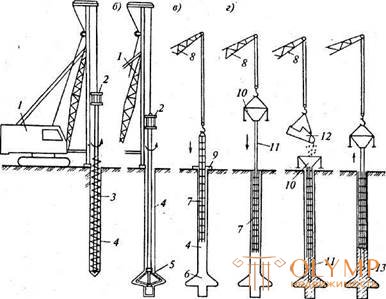
Fig. 5.1. Technological scheme of the device bored piles dry method: a - well drilling; b - drilling of the broadened cavity; in - installation of the reinforcement cage; G - installation of a concrete pipe with a vibro-bunker; d - well concreting using the vertically mixed pipe (VPT) method; e - lifting concrete pipe; 1 - drilling rig; 2- drive; 3 - screw working body; 4 - well; 5 - expander; 6-widened cavity; 7 - reinforcement cage; 8- jib crane; 9 - conductor nipple; 10-vibro bunker; 11- concrete pipe; 12 - tub with a concrete mixture; 13 - wide heel pile |
Concrete-cast pipes used in construction, as a rule, consist of separate sections and have joints, which allow to connect pipes quickly and reliably. Sections of concrete pipes 2, 4 ... 6 m long in the joints are bolted or locking connections, at the first section a receiving bunker is fastened through which the concrete mix is fed into the pipe. A concrete pipe is lowered into the well to the very bottom; |
The use of mud. The installation of bored piles in weak, water-saturated soils requires increased labor costs, which is due to the necessity of fixing the walls of the well to prevent them from collapsing (Fig. 5.2).
Fig. 5.2. Technological scheme of the device bored piles under mud: a - well drilling; b - device of the expanded cavity; in - installation of the reinforcement cage; G-installation of a vibro-hopper with a concrete-cast pipe; d - concreting of the well by the VPT method; 1 - well, 2 - drilling rig; 3 - pump; 4, - clay mixer; 5 - pit for mud; 6 - expander; 7 - bar; 8 - jib crane; 9 - reinforcement cage; 10 - concrete pipe; 11- vibration hopper | In such unstable soils, to prevent the collapse of the walls of wells, a saturated clay solution of bentonite clays with a density of 1.15 ... 1.3 g / cm3 is used, which exerts hydrostatic pressure on the walls, well temporarily holds together certain soils, especially watered and unstable, this keeps well walls from collapsing. This also contributes to the formation of a mudcake on the borehole walls due to the penetration of the solution into the soil.
|
The clay solution, which is under pressure in the well, cements the soil of the walls, thereby preventing water penetration, which eliminates the use of casing. After completion of the well penetration, if necessary, a reinforcement cage is installed, the concrete mix from the vibrating hopper goes through the concrete tube to the bottom of the well, rising up, the concrete mix
displaces the mud. As far as filling the concrete well
mix make rise of the betonovod.
Fastening wells with casing. The device of piles by this method is possible in any hydrogeological conditions; casing, pipes can be left in the well or extracted from it during the manufacture of piles (Fig. 6.15). Casing pipes are interconnected by means of locks of a special design (if they are inventory pipes) or by welding. Drill wells in a rotational or percussion manner. The casing is immersed in the soil in the process of drilling a well with hydraulic jacks.
After stripping the face and installing the reinforcement cage, the well is concreted using the vertically movable pipe method. As the well is filled with concrete mix, the casing can also be extracted. A special system of jacks mounted on the installation informs the pipe of reciprocating movement, due to which the concrete mix is additionally compacted.
but)
Fig. 5.3. Technological scheme of bored piles using casing: and - installation of the conductor and drilling of a well; b - casing immersion; в - well penetration; g - capacity of the next link of the casing; d - sweep bottom hole; e-installation of the reinforcement cage; W — filling the well with a concrete mix and removing the casing; 1 - working body for drilling; 2 well; 3 - conductor; 4 - drilling rig; 5 - casing; 6 - reinforcement cage; 7 - concrete pipe; 8 - vibrating hopper | Upon completion of concreting, the wells carry out the formation of the pile head. They use the installation for the production of ramming piles using casing with the extraction of soil from the pipe by a vibrator grab (Fig. 5.3). Currently, a special polymer concentrate based on polyacrylamide is undergoing successful testing, which in the process of hydration forms a colloidal drilling fluid that creates a protective film on the borehole walls, which, in combination with excessive hydrostatic | ||
Fig. 5.4. Technological scheme for the production of printed piles with excavation under the protection of casing: a - immersion casing vibration installation; 6 - removing the soil from the casing vibrating grab; in - concreting piles; d - extraction of the casing by a vibration unit; 1 — casing pipe; 2 — vibration installation; 3 - vibration grab; 4 - reinforcement cage; 5 - Concrete Mix Tub | tical pressure prevents shedding. Drilling in difficult geological conditions without the use of casing showed the integrity of the bored pile all the way down after pumping concrete into it and the absence of any concrete inflows or cavities on the lateral surface of the pile. The use of colloidal solution can significantly increase the productivity of drilling operations, reduce their cost and labor intensity, drastically reduce the need for casing without reducing the quality of work. Bored piles with wide heel. The diameter of such piles is 0.6 ... 2.0 m, length 14 ... 50 m. There are three ways of arranging piles broadening. The first method is soil spreading by reinforced tamping of the concrete mix in the lower part of the well, when it is impossible to assess the quality of work, the shape (which was the heel of broadening), how much concrete was mixed with the ground and what its bearing capacity was. In the second method, a well is drilled with a machine that has a special device in the form of a drop-down knife on the drillstring to form a well widening up to 3 m in diameter (Fig. 5.5). The knife opens | ||
a ) b)
Fig. 5.5. Drilling a cavity in the ground with a spreader: a is the position of the expander during the well drilling; b - the same, in the process of drilling the cavity; 1 - primer collection; 2 - cutting knives; 3 well; 4 - bar; 5 - widened cavity | hydraulic mechanism controlled from the ground. When the bar is rotated, the knives cut off the ground that enters the bucket located above the expander. After several operations of cutting the ground with knives and extracting it to the surface, an expanded cavity is formed in the ground. The well is supplied with mud from bentonite clays, which continuously circulates and ensures the stability of the walls of the well. When expanding, the cavity is drilled simultaneously with the flow of fresh mud into the well until the complete replacement of the solution contaminated with soil. After completion of drilling the well, the drill string with an expander is extracted to the design depth, and a reinforcement cage is installed in the well. | ||
a - lowering the explosive charge and filling the well with a concrete mix; b - the rise of the concrete pipe and the formation of a broad heel by an explosion; in - ready stuffed pile with camouflage broadening; / - explosive charge; 2-wire to the blasting machine; 3 - casing; 4 - receiving funnel; 5 - concrete mix; 6 - tub with a concrete mixture; 7-widened heel; 8 - reinforcement cage | washed out. The concrete mix squeezes the mud up through the pipe and through the gap between the pipe and the well. The lower end of the concrete pipe must be constantly buried in the concrete mix to a depth of about 2 m; concreting is carried out continuously, so that there is no layer of clay in the concrete. The explosive method of device broadening (Fig. 5.6). A casing is installed in the drilled well. At the bottom of the well lower the explosive charge of the calculated mass and remove the wires from the detonator to an explosive machine located on the surface. The well is filled with concrete mix for 1.5 ... 2.0 m, lift casing by 0.5 m and produce an explosion. The explosion energy compacts the soil and creates a spherical cavity, which is filled with a concrete mix from the casing. After this, the casing is filled with the concrete mixture to the top with portions and with the necessary compaction. Bored pile with a boot. The peculiarity of the method is that the casing is lowered into the drilled well, which at the end has a freely supported cast-iron shoe left in the ground after |
casing immersion to the required depth. Portionally loading concrete mix, regularly compacting it and gradually removing the pipe from the well, receive a ready-made concrete pile.
Concrete piles. The principal difference of the method is that the casing with a length of up to 40 ... 50 m has a rigid 









 fortified shoe. After reaching the bottom of the well, the pipe remains there, is not removed, but is filled with concrete.
fortified shoe. After reaching the bottom of the well, the pipe remains there, is not removed, but is filled with concrete.
Underwater concreting is used to protect the concrete mixture from erosion at a high level of sedentary groundwater. The concrete mixture is fed into the casing not in the tray, but under pressure through a pipeline immersed to the very bottom of the well. Due to the pressure, the mixture is squeezed out of the pipe, fills the space of the well from the bottom and begins to rise, displacing the water in the well. In the process of filling the well with the concrete mix, it is necessary to ensure that the concrete pipe rises at one speed with the casing, the bottom of the pipe is constantly below the top of the laid concrete mix by 30 ... 40 cm. After the well is completely filled, the top layer of concrete mix 10 ... 20 cm, which was in contact with water, cut off.
Ramming piles of any type should be concreted without interruption. If the piles are located one from the other less than 1.5 m, they are made through one in order not to damage just the concrete ones. The skipped wells are concreted during the second penetration of the concrete-casting installation, after having previously concreted piles of sufficient strength and bearing capacity. Such a sequence of work provides for the protection of both finished wells and freshly concrete piles from damage.
Bored piles have a number of disadvantages that inhibit their wider use. These disadvantages include a small specific bearing capacity, high labor intensity of drilling operations, the need to fix wells in unstable soils, the difficulty of concreting piles in water-saturated soils and the difficulty of quality control of the work performed.
The device piles in the pitted wells quite effectively in dry soils. When constructing such piles in the ground, a compacted zone is created, the strength of the soil increases, and its deformability is reduced. The device of stuffed piles in compacted wells is produced by pushing without removing the soil to the surface.
This technology works based on the formation of a well by repeatedly dropping a cast-iron cone from a height, as a result of which a well is punched. Then the well is portion-wise filled with concrete, gravel or sand and compacted to form an enlarged portion at the base of the pile. In the upper part when laying the concrete mix, it is compacted by vibration. Developed many modifications of this method. The formation of wells and cavities in the soil without excavation is carried out: punching cores and casing pipes with hammers, punching vibrators and vibratory hammers, punching shells and ramming, punching pneumatic punching, expansion hydraulic seals, punching with screw devices.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)