3. The device floor of wood
Such floors include: wooden boards, parquet, parquet, shield parquet, mosaic parquet flooring, which are laid in residential and civil buildings. High-strength wood made of pine, spruce, larch, fir, cedar, oak, beech, birch and alder is used for coatings.
Before the start of work on the laying of the coating on the object should be performed:

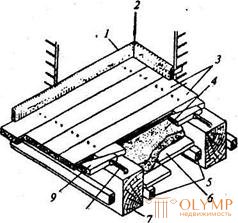
Fig. 25.4. Single deck flooring:
/ - plinth; 2 - plastered wall surface; 3 - floorboards; 4 - backfilling; 5 - cranial bars; 6 - reel (black floor); 7 — beam; 8 - bracket; 9 - wedge
eight |
· All general construction, sanitary and electrical works with the exception of the installation of sanitary appliances and electrical fittings;
• plastering and all painting and painting operations, except for the last one;
• pasting walls with paper;
• laying of ceramic tiles.
All the processes on the construction of the floor of wood can be divided into three cycles: - preparation under the floor or "black floor", the device clean floor and bring the coating to the presentation.
Board floors consist of a covering, a layer and the basis. The coating or the top construction element is the main part of the floor, which works by abrasion during operation. Distinguish between single (Fig. 25.5) and double flooring of tongue-and-groove boards. The interlayer is an intermediate layer designed to fasten the coating to the base, often it serves as a sound insulation pad. The base under the plank floor transfers the load to the ground or interfloor overlap and may include:
when installed on the ground - brick or concrete columns, above - waterproofing and logs;
on interfloor overlappings - an insulating layer and logs;
in the case of two-layer plank flooring - continuous flooring of the lower layer of unedged boards 25 mm thick, antiseptic on both sides and sewn on nails. The surface of such a black floor is covered with construction paper.
Lags are unpainted boards with a thickness of 40 and a width of 80 ... 100 mm, usually from coniferous wood. When the device is laid on a reinforced concrete base, the step lag is 0.7 ... 0.8 m, while the device is laid on brick columns - 0.4 ... 0.6 m. Lags are laid across the direction of light, in corridors - across the passage; Thus, the boards are laid perpendicular to the window and in the direction of movement of people. The first lighthouse lag is placed over the overlap at a distance of 2 ... 3 cm from the wall of the room, the following - in 1.5 ... 2 m. ... 0.8 m
There is a specificity when laying a log on brick columns. Initially check their level and align marks on this level. On top of the columns lay wooden pads on two layers of waterproofing. Next, on these pads install, align with the level and temporarily embroidered lags. The joints of the lag should be in the plane of the brick columns.
Increasing the hydro and sound insulation of the floor is ensured by laying waterproofing pads 100 ... 150 mm wide made of roofing material, ruberoid or asphalt and soundproofing backfilling (in floors on a reinforced concrete base to the space between lags) under sanding slag, slag, expanded clay and others. porous materials. Backfilling is performed over the entire area of the base with a layer of at least 20 mm without compaction.
Planed boards having ridges and grooves on the side edges are used for the board coverings. The width of the boards is within 74 ... 124 mm, the thickness of the boards is 29 mm for housing. All planes of the boards, with the exception of the upper, working antiseptic. The humidity of the boards during installation should not be more than 12%.
When laying the grooved boards, the first one is laid with a groove against the wall, each subsequent groove is put on the crest with a hammer blow through the gasket and nailed to each lag. Nails 60 ... 70 mm long are nailed to the board at an angle with the hats being inserted with a doboynik. The maximum hanging of boards for lags is allowed not more than 100 mm, otherwise you need to stack additional lags. The finished floor is cut off from above, the thickness of the guard is no more than 1.5 ... 2 mm.
Fiberboard floors are arranged in residential and office buildings. The coating of super hard CT plates is silent when walking, easy to clean, resistant to abrasion, has a good appearance.
When arranging the floor on the compacted and leveled ground, the following layers are laid successively: waterproofing, concrete preparation, heat insulation layer and cement screed. After drying and a set of required strength, the screed is cleaned of dirt, dedusted and covered with a bitumen primer. After two days, hot bitumen mastic is applied to the screed and a layer of solid wood-fiber plates is laid on which super-hard wood-fiber plates are then glued as a floor covering.
It is enough to pour a layer of sand 50 ... 60 mm thick as sound insulation on the floor panels, to make a cement-sand screed on top, on which to lay two layers of wood-fiber boards. If in residential buildings panels of a size of a room are used, then it is enough to glue a layer of soft fibreboard 12 mm thick on them, on top of a layer of solid and as a coating a layer of superhard plates on hot bitumen mastic.
For low-rise construction, floors of superhard CT plates are arranged on a wooden base. On brick or concrete pillars, logs are laid, on them - a solid base of unedged boards of equal thickness, on top of which is a coating of CT plates. The slabs in the room are pre-sized. To obtain a tight connection of adjacent plates they are laid with an overlap of 5 ... 10 mm and jointly cut along an electric saw blade along the junction line. After fitting all the plates in the room they are glued to the base on adhesive mastic KN-2 and KN-3.
Glue or mastic is applied to the base under the slabs of ST coating with a notched trowel, after which the slab pre-fitted in place is laid and loaded. After drying, the entire floor is covered with waterproof paints or enamels, and on top with light varnish. Paint the floor for 2 ... 3 times, drying each previously applied layer.
The floors of parquet boards are usually arranged in residential premises where, during operation, there is no intense wear on the flooring. Constructive solution of the floor and the technology of its device is similar to the floor with a plank floor.
Parquet boards consist of a rack base and a front covering of the slats. Boards are manufactured with a length of 1200 ... 3000 mm with a gradation of 600 mm, a width of 137 ... 200 mm, a thickness of 15 ... 18 and 23 ... 27 mm with slats-slats with a thickness of 4; 6 and 8 mm. The front side of the slats in the manufacture of polished and varnished for 2 ... 3 times. A parquet board is a base on which parquet strips are pasted in the form of various patterns with a specific pattern .
To connect the boards with each other, there are special grooves and ridges on their edges and ends. To avoid warping in the boards make cuts.
When arranging the parquet floor on the ground, two layers of roofing are put on brick or concrete columns for waterproofing, then wooden antiseptic gaskets, on them logs with a pitch of 400 ... 500 mm, along which parquet boards will be laid.
Floors on interfloor overlappings are laid on logs, sunk into a 20-mm-thick layer of sand or on a solid sound insulation sheet. If necessary, the logs align, compacting the layer of sand under sound insulation strips. To avoid bias
lag before parquet planks; adjusted lags are fastened with nails or boards laid across the log.
Parquet boards are laid perpendicular to the lags in the direction of light, and in the corridors - in the direction of movement of people. The boards on the logs are joined together in the groove and the ridge initially with the help of clips, finally the floorboard is nailed to each lag with nails 50 ... 60 mm long. Nails slaughtered obliquely in the area of the groove parquet boards, hats vtaplivayut doboynikom. The joints of the ends of the boards should be only on the logs with a mandatory attachment to these lags.
Laying parquet boards on lags start from the wall opposite the doorway, and carry out a consistent laying of boards towards this opening. Considering that the walls are not always arranged parallel, the first row of parquet boards are laid on a pre-tensioned cord at a distance of 10 .. L5 mm from this wall. Each subsequent board is placed on the previously laid with a hammer on the strip of trimming bar. The use of clips contributes to a better unification of the boards and an improvement in the quality and integrity of the coating. In the places of transition from room to room or into the corridor, whole parquet boards are laid, connecting them together in a sheet pile or comb. Be sure to lay a wide lag in the doorway, eliminating the fluctuation of the base and the floor in the aisle.
When laying parquet boards on a solid soundproofing layer of fibreboard, the base is cleaned of debris and dust, then lay the plates dry at intervals of 5 ... 8 mm and cut them to the protruding parts of the room. Then each slab is raised, a layer of bitumen mastic is poured under it, lowered and pressed to the base. The surface of the glued plates is cleaned and primed. Parquet boards are laid on wood-fiber boards also on bitumen mastic, and they are laid in straight rows parallel to one of the longitudinal walls of the room. The gap with this wall should not exceed 10 mm. Before laying the boards must be selected according to the rocks, color and pattern.
The flooring of parquet boards should be smooth, dense and not unsteady. The evenness of the floor is checked with a rail attached to the floor in any direction, and the gap between the rail and the floor should not exceed 2 mm. Gaps between parquet boards are allowed up to 0.3 mm, between the floorboard and the wall - up to 10 mm. Parquet boards come to the construction site with varnished, in the scraping of floors is not necessary.
Advantages of the floor of the floorboard: cost, due to the small thickness of the valuable wood layer; undemanding to the basis of gender; large dimensions of the board, which means ease of installation; factory varnishing, the possibility of repair and replacement of damaged strips, if necessary, scraping.
According to the constructive solution distinguish floors from piece parquet, parquet boards and inlaid mosaic parquet.
The floors of the piece parquet are made of separate rivets (slats), having a groove or a crest on the side and end edges. Parquet rivets are made 15 mm thick from hardwood (oak and beech) and 18 mm thick - from coniferous wood. The width of the staves is 30 ... 90 mm with a gradation of 5 mm. The moisture content of rivets before laying should not exceed 6 ... 10%.
Parquet floors will be laid after all general construction, special and finishing works associated with possible moistening and contamination of the coatings.
Parquet floors are arranged according to logs laid on brick or concrete columns (usually on the ground floor), on interfloor reinforced concrete and wooden floors.
The base under the parquet floor can be a solid plank floor when fastening rivets on nails, cement-sand or asphalt screed and accordingly fastening to the base on mastic or rubber-bitumen emulsion.
On a full planked flooring from above, it is necessary to lay building paperboard, fibreboard or chipboard to eliminate possible squeaking in parquet staves when walking. With such a base parquet strips are laid on a layer of mastic or fastened with nails.
For cement-sand screeds apply a solution of not less than grade 150. The thickness of the screed depends on the base on which this screed is arranged. When laying on sand and slag backfill, the thickness of the screed must be 40 mm, if the screed is a leveling layer over concrete preparation, then it is made with a thickness of at least 20 mm. The coupler is laid with stripes of 2 ... 2.5 m. The base can be made of prefabricated prefabricated slabs with dimensions of 500x500x35 mm; under the piece parquet the base is often made of fibreboard.
When laying the floor on mastic great attention is paid to the evenness of the base. Irregularities can be leveled with a plaster cement solution with drying of the corrected places. The base is primed with bitumen mastic, which is allowed to dry to a lack of stickiness. Parquet is laid on the primed base after 5 ... 8 hours and is carried out on cold or hot mastics. On mastic, parquet floors are laid on cement-sand screeds, on reinforced concrete floors.
Laying the floor of the piece parquet on cold or hot mastic produced in the following technological sequence:
• cleaning and leveling the base;
• base primer;
• marking of center axes;
• application and leveling of the mastic with a notched trowel to a thickness of 1 mm;
• laying parquet rivets on mastic;
• fitting and trimming of the wall rows;
• final finishing of the floor surface, including cleaning the premises, grinding and scraping the floor after setting and drying the mastic, installing baseboards and rubbing the floor.
Floors from parquet can have a different pattern, which depends on the order of laying the planks, their size, color, texture, etc. In each room it is necessary to lay parquet of the same wood species, pattern and size of staves.
Piece parquet is laid in a straight row, in a Christmas tree, with and without a frieze. Parquet in a straight row is usually laid only in small rooms and narrow corridors. Most often, parquet is laid in the Christmas tree, when parquet planks are interconnected at an angle of 90 °, with the end of one plank resting on the edge of the common edge of the adjacent riveting. The Christmas tree is laid along the line of the room in the direction from the window to the door. With this set of coating looks good, visible natural wood texture. It is first necessary to make a breakdown of the rows in order to rationally lay parquet and reduce the cost of cutting.
For the proper laying of the parquet in the middle of the room along the longitudinal axis, tension the cord. When flooring with friezes, the rows are divided in such a way that between the friezes and the width of the room there is an integer number of slats. You can arrange the slats so that the ends of the slats cut off on one side fill the missing slats on the other side of the room, thereby eliminating waste. In some cases, you can change the width of the frieze so that the parquet strips are placed without waste, in other cases - to change the length of the strips.
Piece parquet on cold mastic laid on the tree without a frieze. On hot mastic, parquet can be laid in the Christmas tree with and without a frieze.
Cold mastic is delivered to the construction site in a closed container, transferred to the work site in smaller containers in the form of tanks or buckets with a spout or in watering cans, of which a thin stream is poured into the place of laying parquet staves. Works begin from the wall opposite to the entrance in order to prevent workers from moving on freshly laid parquet with unstressed mastic. First, the first two rows, which are called the beacon, are laid over the entire length of the wall. Additionally, parquet rivets can be fixed by placing wedges between them and the adjacent wall. Subsequent rows to the lighthouse is recommended to attach order.
Mastic is poured into a thin stream and leveled with a layer thickness of 1 mm. Slats of parquet should be laid immediately, the lower part of slats should be completely covered with mastic. Then hammer together the planks, eliminating possible gaps between them. Surplus mastic from the slats removed with a knife or rag.
The parquet flooring should be fixed throughout the entire room with wooden liners (wedges), hammered around the room between the parquet and the wall with a step of 0.5 ... 0.6 m. Wedges are necessary to protect the coating from swelling when the humidity conditions change indoors. Cold mastic hardens slowly, until its complete hardening (within 3 ... 4 days) to walk on the floor and to engage in its final finishing is not allowed. The laid parquet is covered with a layer of paper or glassine.
For piece parquet, hot mastic is delivered in auto-sprinklers and stored in thermoses. In the work area, hot mastic is served in electric locomotives or insulated tanks. Mastic is poured in small portions, simultaneously under 3 ... S slats, so that the parketchik can put the rivets on this hot mastic, level them, slightly pressing them and pressing them to the previously laid ones. Excess mastic is removed by riveting.
Frieze spread only after the completion of flooring parquet in the herringbone. They mark the border of the frieze, stretch the cord along this border, outline the cutting line of the previously laid ordinary planks of the Christmas tree, along which they carry out the exact cut. Lay the stripe strips on themselves from the corner of the room, controlling that the comb would fit into the groove of the previous plank. Laying horizontal check level and rail.
Laying piece parquet on a wooden base includes the following workflows:
• cleaning, leveling and checking the horizontal position of the base;
• laying or laying of cardboard;
• marking of floor space;
• laying the lighthouse rows of the Christmas tree;
• laying and mounting parquet throughout the area of the room;
• scraping and grinding coating;
• installation of ventilation grilles and installation of baseboards.
Наиболее часто паркетные полы по деревянному основанию укладывают в елочку. По оси помещения закрепляют шнур; маячный ряд располагают под углом 45° к этому шнуру. В начале елки укладывают на гвоздях — 3...4 ряда справа и слева от оси шнурка, укладку последующих клепок осуществляют введением новой в паз двух ранее уложенных и закрепленных к основанию. В торцевой паз настланной клепки забивают один гвоздь, в продольный паз — 2...3 гвоздя в зависимости от длины паркетной планки.
При настилке пола с фризом по периметру чаще укладывают рядовую клепку, выложенную елочкой, далее после набора полом достаточной прочности вдоль стены на расстоянии, равном длине фризовых клепок, отрезают кромку ранее уложенного паркета и далее на мастике настилают фриз с прокладкой или без нее.
Отделка паркетного пола включает циклевку, шлифование и полирование. Сплошную острожку стремятся не делать, заменяя циклевкой отдельных мест. Покрытия шлифуют паркетно-шлифовальными машинами, в труднодоступных местах — шкурками с разной зернистостью посыпки. Очищенный пол покрывают пергамином или бумагой, завершают все оставшиеся строительные работы. Перед сдачей объекта покрытия снимают, полы покрывают лаком за два раза.
Паркетные щиты (щитовой паркет) предназначены для устройства покрытия в жилых и общественных зданиях. Паркетный щит может состоять из паркетных планок, квадратов шпона или фанерной облицовочной плиты, которые с определенным рисунком наклеены на основание. Основание под паркетные щиты может быть рамочным, реечным однослойным и двухслойным (рейки склеены во взаимно перпендикулярном направлении), из древесностружечной или цементно-стружечной плиты.
Основание-щит обычно изготовляют из отходов лесопиления и деревообработки. Щиты можно изготовлять толщиной 22...40 мм, размерами щитов: 400х400; 500х500; 600 х600; 800х 00. В качестве покрытия используют паркетные планки толщиной 4; 6 и 8 мм шириной 20...50 мм при длине 100...400 мм. Все элементы щитов склеивают в заводских условиях водостойкими клеями.
Паркетные щиты могут иметь различные рисунки. Лицевое покрытие может быть изготовлено из древесины дуба, бука, клена, вяза, каштана, березы, сосны, лиственницы. Щитовой паркет можно укладывать из планок разного размера, получая различные декоративные покрытия. Квадраты бывают развернутые и прямые. При наборе прямых квадратов планки располагают параллельно граничным элементам, а развернутых — под углом 45°. В зависимости от размеров помещения подбирают размер планок, чтобы уложить соответствующее число квадратов по ширине и длине помещения.
Для реек и брусков обвязки применяют древесину хвойных пород, березы, осины и ольхи.
Shield parquet flooring on concrete and cement-sand screed on mastic, logs or wooden cells laid on the level of a layer of dry sand 60 mm thick. The distance between the lags in the axes is equal to the size of the shields. First, stack lighthouse rows along two adjacent  walls, then privates, and complete the laying of the shields at the door. Shields are fastened to the logs with nails in an inclined position, and the insertion of caps is carried out by doboyniki. A more durable connection of the shields is achieved when, after the first shield has been laid and secured, laths are laid in its slots on the lags, on which the next shields are placed. The joints of the shields should be along the axis of the lag, fastening to the lags - on nails, by analogy with the parquet boards.
walls, then privates, and complete the laying of the shields at the door. Shields are fastened to the logs with nails in an inclined position, and the insertion of caps is carried out by doboyniki. A more durable connection of the shields is achieved when, after the first shield has been laid and secured, laths are laid in its slots on the lags, on which the next shields are placed. The joints of the shields should be along the axis of the lag, fastening to the lags - on nails, by analogy with the parquet boards.
Inlaid mosaic parquet consists of individual factory-made floor mats, which are glued to the base on a layer of mastic about 1 mm thick. 8 and 12 mm parquet strips are stuck in the factory in heavy paper, which can be easily removed if necessary. Sizes of rugs 400x400, 480x480, 600x600; 800x800 mm.
Shield parquet laid on logs or solid base. To improve sound insulation under them lay strip pads of soft wood-fiber boards. Lags are placed parallel to the long wall of the room. When laying boards on logs, the distance between the axes of the log should be equal to the width of the shield. Parquet boards, having a size of 800x800 mm, are laid along logs with a pitch of 400 mm, and with a thickness of 22 and 25 mm - only along a solid base.
Pre-shields are sorted by color, rock and pattern, and then by size into full-size and complementary, which will fit into the outer rows adjacent to the walls. Shields are selected for each room, the corresponding stack is placed at the entrance to this room. Directly in the room, the axes of the rows are laid out and lags are laid over the whole area. In the far corner of the room, the first shield is laid on the base, and two cords intersecting at right angles are placed along adjacent walls. They put the shields in order to control their edges on the lag axis, and then connect the shields to each other with the slats.
The boards of the shield frame should be located across the log. With this installation, the shield is more stable under load. Horizontalness and parallelism of the shields are checked by level and rail. Only after careful adjustment of the shields they are fastened with nails. The parquet shield is fixed to each log, nails are inclined obliquely into the grooves of the groove and be sure to heat the caps.
Extreme or complementary shields are slaughtered in place. Before laying the slats and the groove of the shields grease with waterproof glue. Grease with glue should also edges of the joined shields. Spacing wedges are driven into the gap between the covering and the wall.
Parquet panels are laid with a distance of 10 mm from the walls. This gap in the future will be blocked by the plinth. Lugs between the edges of two adjacent shields are not allowed. Gaps between adjacent boards are possible up to 0.3 mm, and the clearance between the floor covering and the control rail should be between 0 ... 2 mm.
When working, they control that the mats do not move and create a clear geometric pattern. For a change between rugs it is possible to lay rack laying. The surface of the floor is rolled by a hand roller. Before putting the object into operation, the surface of the floor is moistened with water and the upper protective paper layer is removed. Sand floors (if necessary) only after all the finishing work.
Parquet flooring finishes include scrubbing the floor, sanding the surface, rubbing with mastic or varnishing. Parquet flooring is usually not planed, but cycled after the flooring and the complete hardening of the mastic. Scraping eliminates possible surface waviness, ledges between the slats, gouges, scratches, oil and other stains, etc.
When processing the surface, it is recommended to remove a layer of wood no more than 1 mm with a picker. Near the walls and in the corners, floors are treated with electric planers, manual planers, cycled with manual cycles with a short and long handle. Before this operation, the floor must be moistened with a wet rag.
After scraping, the floor surface is polished with a parquet-grinding machine (Fig. 13.17), in which the working unit — the rotating drum — is covered with a sandpaper. In the first grinding of the floor, a coarse-grained pelt is used, in the second - a fine-grained skin.
After sanding and dedusting the floor, a mastic is applied to it or varnished, as a result, the surface becomes shiny,  wood texture is clearly visible. A good coating is obtained by using a colorless varnish, which is applied to a completely dry and clean surface with a brush or spray gun. After complete drying, a second, and if necessary, third layer is applied.
wood texture is clearly visible. A good coating is obtained by using a colorless varnish, which is applied to a completely dry and clean surface with a brush or spray gun. After complete drying, a second, and if necessary, third layer is applied.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)