Thermal insulation of various enclosing structures is designed to provide the specified thermal conditions of buildings, structures, installations, pipelines. Thermal regimes can have different purposes:
• to reduce heat losses by building envelopes
building structures;
• to ensure the normal process inside
refrigerators, special warehouses, etc.
There are two ways to perform insulation:
1) in the factory (heat-insulating layer in wall panels, coating plates, sandwich-type panels);
2) directly at the construction site. For the first type of insulation characteristic are stiffness, strength and relatively high (up to 1200 kg / m3) density. For insulation performed in a building site, its main qualities should be flexibility, plasticity and relatively low density — up to 600 kg / m3.
The tightening of requirements for building heat engineering, for improving the heat-shielding properties of buildings under construction and already constructed buildings require drastic decisions to drastically increase the resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures. It is possible to warm external walls, increase their heat-insulating properties in several ways: insulate them outside, lay thermal insulation in the thickness of the wall, place thermal insulation on the inner side of the structure, or construct enclosing structures of heat-insulating construction materials such as foam concrete or aerated concrete. The advantage of wall insulation by introducing into the design of the insulating layer is convenient in the manufacture of enclosing structures in the factory. The disadvantage of this solution may be condensate on the internal surfaces of the structures, the need for a vapor barrier.
The system of insulation outside and at the same time is the technology of erecting monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures that has appeared in recent years with the help of permanent formwork made from expanded polystyrene. With this system, reinforcement is installed in the formwork of polystyrene foam panels and concrete is laid, then protective or finishing coatings are applied to the inner and outer surfaces, and the structure can be lined with bricks on the outside.
When we insulate the existing walls outside, the heat and humidity regimes are improved, reducing the temperature loads reduces the likelihood of cracks in the walls of the building, retains their strength and carrying capacity. During the work is not required eviction of tenants. The disadvantages of outdoor insulation can be attributed to the need for continuous wall insulation, including the slopes and the seasonality of these works. According to one of the schemes, thermal insulation is a multi-layer construction, attached to the wall and consisting of a heat-insulation layer (mineral wool, expanded polystyrene, etc.), on which a plaster-decorative coating is applied. According to another scheme, the thermal insulation is also attached to the wall with dowels, and then, at some distance from it, light alloy guide rails are attached to the brackets, on which ceramic tiles or other finishing materials are fixed. The dignity of such false walls - the absence of condensation, the reflection and mitigation of thermal shocks, improved sound insulation. In the case of mechanical or other damage to the coating is not required to disassemble the entire structure, it is enough to replace the damaged fragments.
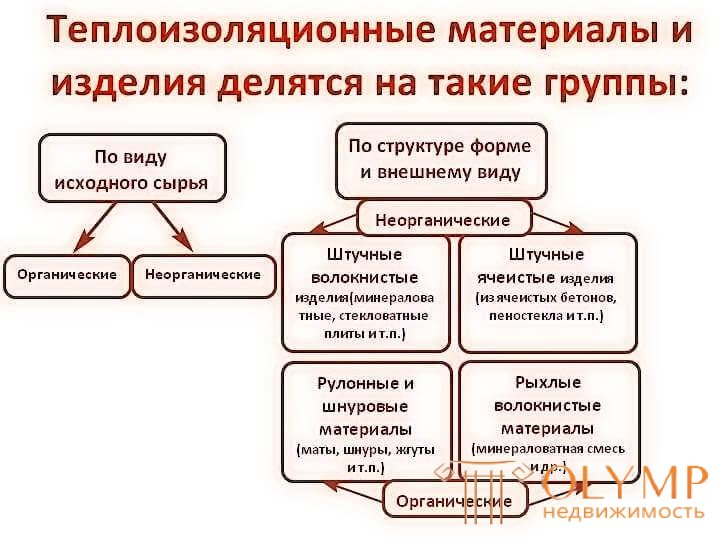
Thermal insulation, made in construction conditions, usually consists of the main insulation layer, the outer protective layer and fasteners. Depending on the location of the device, the purpose, the design features, the required heat technical qualities, thermal insulation is divided into several types.
Thermal insulation is made of mineral (asbestos and products based on it; artificial porous materials and products based on them, foam and gas concrete, etc.), organic (peat and materials based on it, reeds, fiberboard, wood concrete, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam etc.) and combined materials (mineral wool boards based on bitumen and synthetic binders, polymer concrete on porous aggregates, etc.).
Recently, the materials produced by the foaming method have been widely used: latex, polyurethane foam, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene foam, etc. The insulating materials of the new generation alveolite and arviolene are promising, which are based on polyolefin foam and combine the properties of heat, hydro, sound insulation, high, strength and thermal characteristics. In addition, the properties of these materials allow them to be subjected to cutting, stamping, vacuum forming and pressing, joining with other materials. Alveolitis and alveolen have high resistance to adverse weathering.







 favorable weather conditions, ultraviolet radiation, chemical effects. The materials are made without harmful additives, they are environmentally friendly, odorless, do not emit harmful substances when heated and burned: materials undergo little aging and decay, their properties do not change with time. The materials have an aesthetic appearance, they have a wide color gamut. Working temperature is from -80 to +130 ° C. To ensure the same resistance to heat transfer, the required thickness of materials is: mineral wool plates — 77 mm, gas-foam concrete — 348 mm, polystyrene foam — 46 mm, masonry from ceramic bricks in 2.5 bricks — 672 mm, and alveolite and alveolen — 3 mm.
favorable weather conditions, ultraviolet radiation, chemical effects. The materials are made without harmful additives, they are environmentally friendly, odorless, do not emit harmful substances when heated and burned: materials undergo little aging and decay, their properties do not change with time. The materials have an aesthetic appearance, they have a wide color gamut. Working temperature is from -80 to +130 ° C. To ensure the same resistance to heat transfer, the required thickness of materials is: mineral wool plates — 77 mm, gas-foam concrete — 348 mm, polystyrene foam — 46 mm, masonry from ceramic bricks in 2.5 bricks — 672 mm, and alveolite and alveolen — 3 mm.
Alveolite and alveolen are widely used as insulation, it is possible to significantly reduce the thickness of structures, so 1 mm of these materials replaces 26 mm of mineral wool insulation and 16 mm of foam plastic.
Depending on the position of the insulated surfaces in space, building insulation is horizontal, inclined and vertical, and according to the methods of the device - backfill, mastic, cast, coating, combined and prefabricated block.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)