The origin of the "warm floor" system and its relationship with traditional heating systems.
Systems "warm floor" are known almost as much as there is heating in general. One of the first mentions relates to warm floors in ancient Roman baths, where heated air passed through special channels in the stone floor. There were warm floors of a similar design in the Turkish baths, and there they were a mandatory attribute.
Thus, mankind has more than two thousand years (and according to other data, five) appreciates the remarkable comfort that the “warm floor” systems carry. However, before the beginning of the twentieth century. the heat carrier was exclusively heated air, which, under the action of natural thrust, passed through channels in the floor, gradually giving away its heat to the granite slabs. At the beginning of the twentieth century. with the advent of pumps, heated floors appeared with the use of heated water. And finally, from the middle of the century, with the advent of relatively cheap and affordable electricity, systems began to spread using heating cables. Especially widely they began to spread in the last 10-15 years. It is necessary to specify the zones of the greatest distribution of warm floors. Today these are the countries of Northern Europe - Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, where a significant proportion of the heating systems of buildings fall on the systems of "warm floor". According to various sources, this proportion ranges from 15 to 50%. Interestingly, these systems spread very quickly in countries with a fairly warm climate - Spain, France, the countries of Latin America, and the Near and Middle East. This is due to the fact that the heating period in these latitudes is very short, and the lowest temperatures often do not fall below +3 - + 5 ° C. Since the capital costs of floor heating are very low and they do not take up much space, these systems are spreading wider and wider. It was noted that the rule applies: what is the share in the country's energy sector of electricity produced by renewable sources (nuclear and hydroelectric power plants), so is the share of electric heating.
Our country, of course, is an exception to the rule. Just 15 years ago, the “warm floor” system as a household product was completely unknown. Today, an apartment can not be considered not only elite, but even average, if it does not have a warm floor in the bathroom or kitchen, or even in all rooms.

 .
.
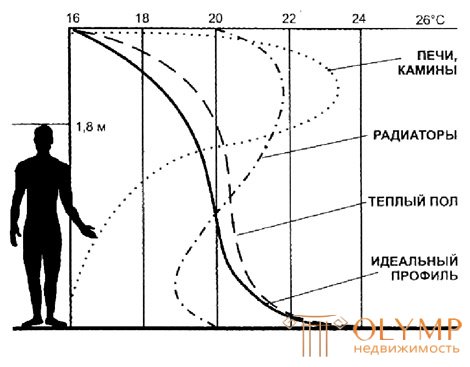
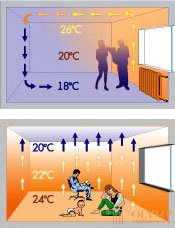
The figure and graph shows the difference in air temperature distribution in a conventional heating system and in a “warm floor” system.
The basis of the action of warm floors laid several physical and physiological phenomena. First, according to Newton's law, the amount of heat given off from the surface, overheated by the temperature Dt relative to the surrounding air, is equal to
Q = ax S x D
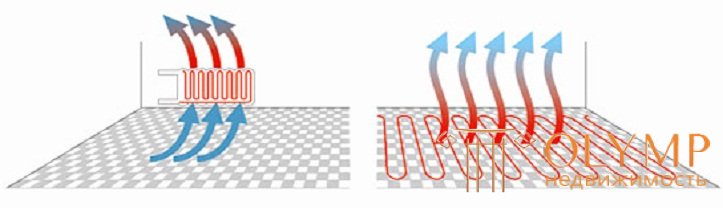
For a horizontal floor, the heat transfer coefficient is 11–13 W / m 2 ° C, while for the ceiling it is 8–9, and for walls 10–11 W / m 2 ° C. In addition, the floor area in the room ranges from units to tens of square meters, while the heat-transfer surface area of other heating devices (radiators, convectors, etc.) is, at best, close to a square meter. Due to this, warm floors operate at a very low temperature differential Dt, ranging from a few degrees in a room with a steady thermal condition to ten to fifteen degrees in the mode of forced heating. As a structural element of a heating device called “warm floor”, a part of the floor structure is used, which is very effective from the point of view of saving materials, and most importantly - space in the interior.
The next physical principle of the work of warm floors is that the warmest air is at the bottom, and the coldest one is at the top. The temperature distribution of altitude inherent in the systems “warm floor” is shown in the right figure. This is where physiology comes into play. The fact is that the only part of the body that constantly gives off heat by heat transfer is the surface of the feet, therefore touching the feet to a physiologically comfortable temperature of 25-28 ° C (high temperatures are undesirable for a number of reasons) immediately causes a physiological feeling of comfort, and relatively cool air at head level - feeling fresh. Virtually no common heat appliances today create a level of comfort comparable to floor heating systems. The choice of a heating cable can achieve very high floor temperatures (up to 40-50 ° C or even 90-100 ° C), however, SNiP prohibits heating the floor surface above 26 ° C. To one of the advantages, closely related to the physical device of warm floors, is the simplicity and low cost of thermal control, or, more simply, to maintain the same temperature in the room. The flexibility of regulation allows you to easily adjust the mode of operation of the sexes to the mode of life of the owners, and not vice versa. Suffice it to say that today the floors are heard not only by turning the knob of the device, but also by orders given by telephone and the Internet.
In many rooms, due to the considerable humidity, the floor must be tiled, for example, in a bathroom or a shower room. Often this flooring is laid in the hallway and kitchen. Ceramic tiles have a rather cold surface and a long stay in such a room is not very comfortable.
In order to feel the pleasant sensations in any room of the house, you can equip them with a warm floor. This will be a good addition to the usual room heating.
Installing a heated floor under a tile seems at first glance technically very difficult, but today it can be done with your own hands, without resorting to the services of specialists.
Content:
Arrangement of it provides uniform distribution of heat in the room. Spreading from below, it creates additional comfort. In addition, finding a warm zone at the bottom of the feet and cooler air at the top of the head is medically beneficial.
While the use of radiators and converters increases the movement of air in the house, underfloor heating, on the contrary, helps to reduce the number of drafts, with less dust rising, which also has a beneficial effect on the health of residents.
Ceramic tile has good thermal conductivity, is resistant to temperature changes, is able to withstand significant mechanical loads and therefore will be perfectly combined with a warm floor. In addition to a long service life, this floor has other remarkable qualities.
To date, there are several types of it. Since ceramic tile has a high thermal conductivity, any kind of heating can be laid under it.
Including:
 In order to choose a warm floor under the tile, you must first decide the answers to several questions:
In order to choose a warm floor under the tile, you must first decide the answers to several questions:
Only by answering all these questions, you can make the best choice.
This design is by far the most common for corridors, kitchens and bathrooms. It is a system of water pipes that fit directly into the screed.
The resulting floor cake consists of:
Metal pipes are placed on the reinforcing mesh with a small gap between them (from 10 to 30 cm) and fixed with plastic clamps. In those places where the deformation seam will pass, you should wear a corrugation on them. The pipe in the system should not have joints, its input and output should be located in the manifold.
Before pouring around the perimeter of the room install the damper tape. It is necessary to compensate for the expansion of the screed, which will occur as a result of temperature changes.
After conducting a hydraulic test of the system, you can begin to fill the sub floor. Its thickness must be at least 30 mm. The water floor under the tile is a fairly efficient heating system, which allows saving almost 10% of thermal resources per month.
Gone are the days when this system was a luxury and an attribute of the home of only wealthy people. Especially since its use has become less energy-intensive. Having equipped it with a thermostat, we can achieve energy savings of up to 35%.
For example, a heating mat laid in a bathroom with an area of 0.65 m2 consumes like a single light bulb. The heated area of 1.5 m2 uses energy like three bulbs, 3 m2 like a computer, and 6 m2 like a refrigerator.
It should be noted that the power consumption depends only on the cooling rate of the surface. In other words - on the quality of insulation.
The price of such a floor depends on the quality, reliability, power and number of conductive wires in the heating cable. It can be single-core and two-core. In the latter form, due to its design, two conductive elements compensate each other's electromagnetic fields. Single-core cable due to increased emission of electromagnetic waves is mainly used only in non-residential premises.
To date, several types of them are produced. Depending on what is used as a heating element, the electrical appearance is divided into:
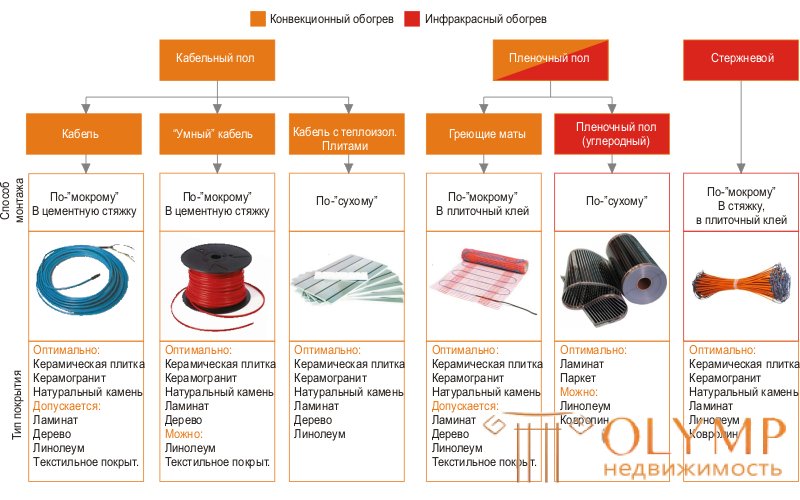
Each of these types is a safe system, the main qualities of which are stability and reliability, because the warranty provided by manufacturers for their products reaches 20 years. The system can function as an additional or primary type of heating and, unlike other means, which heat the floor, but the air in the room, is more energy efficient.
Installation of a warm floor under the tile using this element was used not so long ago. His popularity is constantly growing. Heated floor on the basis of the heating mat is a cable system used in the reconstruction or arrangement of new floors.

It is produced using a special technology with the use of two-core shielded cable, 2.5 mm thick. The installation of the system is quite simple: the heating element is filled with a mortar-free cement-free mortar.
Such a warm floor is a heating system, with a special electric cable that fits the snake on the surface with a certain step, fixing it with the petals of the mounting tape. The laid element and corrugated tube with a thermal sensor are poured with a concrete screed with a thickness of 3 to 5 cm.
This floor can be mounted on a variety of surfaces - walls and even the ceiling. The heating element is a material made in a special way. The film is covered with a floor covering and in the future a special cement screed is not required. This can significantly reduce installation time. They can be closed by any type of coatings that are used in construction today.
Which one is better
As mentioned above, the choice depends on many factors. And each of the considered systems has many positive qualities. So pipes of a water heat-insulated floor can be connected both to an autonomous system of heating, and to central. One of the obvious advantages of this design is its low cost.
Installation of water heated floor and its maintenance is also not very expensive. But not everywhere such a system can be applied. For example, in old houses, floor slabs are not designed for heavy loads and the installation of a water-heated floor in such buildings is simply impossible.
The undoubted advantages of electric models include the simplicity of their device, energy efficiency and rapid heating of the floor covering.
The basis of the design of warm floors, of course, is the heating cable (NC) (Fig.13.1.). Outwardly, it resembles radio frequency cables for transmitting television signals, but its purpose is not to transmit electrical signals or power at a distance, but to convert the electric current flowing through it into heat. Usually a small part of electricity is converted into heat in any cable or wire, but it is a very small amount - 1-3%, and a whole set of measures is taken to reduce it. For heating cables, the opposite is true - all 100% of the power must be converted to heat, and the allocation of this power per unit length of cable (specific heat release) is the most important technical parameter of heating cables.
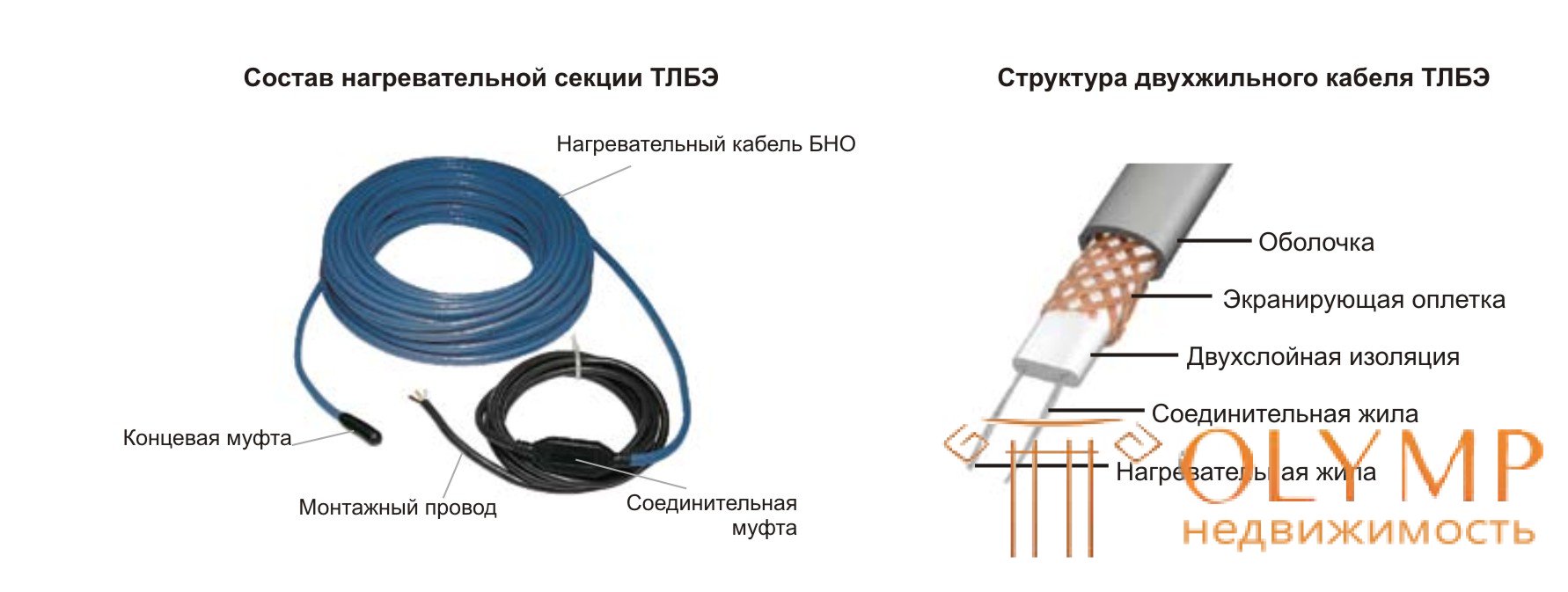
Fig. 13.1. - Heating cable BNO
In this sense, a heating cable is not a cable, but a heating element made according to cable technology. Heating cables for “warm floor” systems of various manufacturers are characterized by specific heat emission from 17 to 21 W / m, and an increase in this parameter is undesirable and does not at all indicate any special advantages. Firstly, when laying the cable into the floor, an air cavity can form near the surface, thus overheating of the cable material occurs and the risk of its failure increases. Secondly, with an increase in the power density of the cable, its length per a certain area is reduced. In this case, such an increase in the distance between the individual threads is possible, which will make the heating unevenness noticeable. For all manufacturers, the allowable distance between adjacent threads can vary from 5-6 to 10-12 cm. Reducing the linear power below the specified values leads to cable waste and the risk of unacceptable convergence of adjacent cable threads.
During warm floor operation, the cable heats up to 60-70 ° C, and the insulation and sheath materials withstand temperatures above 100 ° C. This is one of the secrets of high reliability of warm floors.
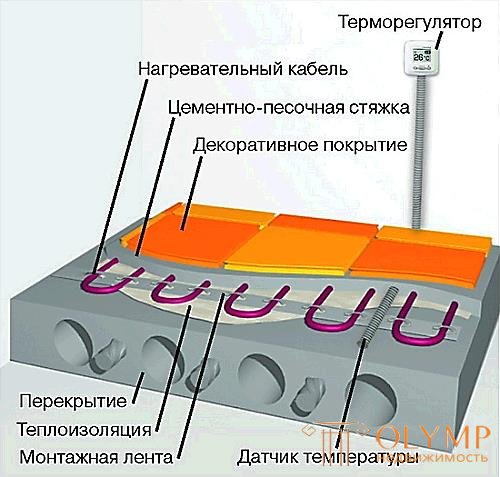
The floor heating system includes:
- heating section;
- control equipment (thermostat with temperature sensor);
- accessories to facilitate and accelerate installation (mounting tape, corrugated plastic tube, etc.);
- heat insulation.
Typical floor heating design is shown in Fig. 13.2.
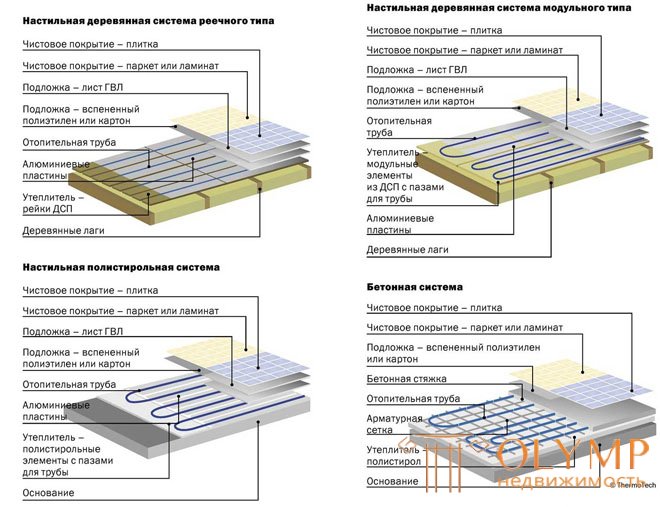
Fig. 13.2. - Variants of warm floor designs
Thermal insulation is laid on the leveled and cleaned subfloor, then the mounting tape is fixed, with which the heating section is fixed. "Cold ends" lead to the wall to connect to the thermostat. Determine the place of installation of the thermostat, and placed near the place of installation of the thermostat between the two threads of the heating cable corrugated tube to install a temperature sensor. At this point, it does not hurt to make a small sketch of the installation, on which to show the places of installation of the couplings and the thermal sensor. If ever the system is damaged (for example, during the subsequent repair of the premises), this sketch will serve the owner in good stead. The section is checked for integrity by an ordinary tester. After that, the cement-sand screed is cast. The thickness of the screed can not be less than 3 cm, primarily based on its strength and the requirements of the SNiP. The complete curing time of the screed (again, as required by SNiP) is at least 28 days. Only then can the installed system be turned on. It is unacceptable to accelerate the hardening of the screed, including the warm floor. Before switching on (and even better on day 3-5 after pouring), it is necessary to check the integrity of the heating section with a tester. Due to the fact that there is some moisture inside, it is advisable to warm the coupler for at least a day when it is first turned on. After that, the system is ready for operation. When installing warm floors in large areas, it may be necessary to pass the heating section through the expansion joint. The passage scheme is shown in Fig. 13.3.
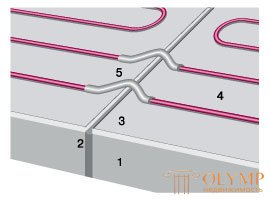
1 - draft floor (overlap)
2 - expansion joint
3 - heat insulation
4 - heating section
5 - curved steel tubes filled with sand.
Fig. 13. 3. - Diagram of the passage of the heating cable through the expansion joint
Often the thickness of the screed can be 5-7 cm, and if it is unevenly hardened, cracks may appear. To eliminate this and make the coupler more durable, several ways are possible:
- cable laying on metal grids that simultaneously reinforce the coupler;
- the use of fiberglass to harden the surface of the screed;
- the use of special mixtures;
- The use of "floating" screed.
It is important to pay attention to the choice and device of thermal insulation. Использование теплоизоляции позволяет сэкономить до 30-40% эксплуатационных расходов и безусловно необходимо в случае использования системы «теплый пол» как основной и единственной системы отопления. В этом случае наиболее целесообразно использовать пенополистирольные плиты из твердого ППС с твердостью не ниже 100 и толщиной 5-10 см (если позволяет структура пола). Поверх плит укладывается плотная бумага и устраивается «плавающая» стяжка. Использование такой теплоизоляции в теплоаккумулирующих системах также обязательно.
When installing underfloor heating in existing premises, it is usually impossible to install thick layers of insulation. In this case, foiled heat-insulating materials with thicknesses of 3, 4, 5, 8 and 10 mm are used. Their use allows you to save 12-20% of electricity. It is necessary to use only materials duplicated over the foil by lavsan. Otherwise, the foil layer after filling the screed collapses within 3-5 weeks due to the presence of an alkaline medium. Both imported (Isoflex) and manufactured in Russia - Penofol, folgoizolon and others are widespread on the market. Sheet and foil sheets are also used as thermal insulation for underfloor heating. In terms of efficiency, they correspond to foiled materials, but much more expensive.
When choosing a system, you must answer a few questions:
- - whether it is the main heating system or comfortable heating;
- - What is the nature and characteristics of the room where it is planned to install a warm floor;
- - whether there is sufficient electrical power;
- - how much a “smart” thermostat is needed;
- - What kind of insulation can be placed in the room, based on the thickness of the existing floor, its cover and door thresholds;
- - what kind of heating cable is available at a price.
Consider first of all the choice of system power, since the remaining issues are covered in the relevant sections. Each of the systems in the assortment of any manufacturers is designed to be installed on a specific area, for example, 2-4 square meters. These capacities are chosen from the condition that the specific power of the system should correspond to the heat losses to the surrounding space from this room, and the length of the section allows the layout on this area with permissible steps (from 5 to 15 cm). The method of accurate calculation of heat loss is set out in SNiP II-3-79, however, for simplicity, it is necessary to calculate for the conditions of the middle zone of Russia and the average construction conditions, based on the values of 120-140 W / sq.m. It should also be noted that the heating section, as a rule, is placed at some (10-20 cm) distance from the walls, and with comfortable heating - only on the area free from furniture. Thus, when constructing a main heating in a room of 3 x 5 m, you need to select a system with a minimum power of 140 x 3 x 5 x 1.2 = 2.5 kW, while with a comfortable heating device it will be sufficient to install the system on an area free of furniture of 9 square meters. m 120 x 9 x 1.2 = 1.3 kW At the same time, the safety factor 1.2 is taken. Obviously, the power has almost doubled from this or that answer to the question about the purpose of the system. The above calculation is very simple, but usually you need to take into account the characteristics of the room, which include:
- - first and last floors of buildings;
- - rooms with large glazing - winter gardens, bay windows, balconies;
- - rooms with insufficient heat insulating enclosing structures (thin walls, balconies, etc.);
- - flooring with special materials with a large thickness or high heat capacity (thick slabs of marble or granite, etc.);
In all these cases, it is necessary to increase the power of the system, as well as to conduct a thermal calculation. Particular attention should be paid to rooms with wooden floors or parquet. Due to the low thermal conductivity of wood with a standard power density of a warm floor, the temperature on the surface of such a floor will be noticeably lower than desired. At the same time, under the wooden coating in the space between the lags, due to poor heat transfer, the temperature on the cable surface will increase. Thus, the cable power will be primarily spent on heating the wood, which is highly undesirable from the point of view of maintaining its humidity. Some companies offer sections of heating cable with a specific power of 10 W / m for premises with wooden floors. Of course, the cable will not heat up too much, but the heating in such systems is almost imperceptible. On the use of warm floors as the main heating system in such areas can not speak. In order to avoid misunderstandings, and also taking into account the increased fire risk, we do not recommend using heated floors in their classic design in rooms with wooden floors.
When installing underfloor heating during repair or renovation, it is often not possible to increase the floor thickness even by 3 cm (the minimum thickness of the screed for cable installation). In this case, ultrafine systems come to the rescue. A mesh of plastic threads, into which a thin heating cable is woven. Thickness - 3-5 mm. Designed for laying directly into a slightly thickened layer of tile adhesive. Comes in rolls, ready to eat.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)