In modern practice, furniture is divided into household appliances for home (urban and rural) and furniture for public buildings. For household furniture adopted a classification system based on the appointment of furniture products - for the equipment of residential and utility rooms. Furniture for public buildings is called special, thus emphasizing the dependence of its decision on the purpose of a particular type of building. Proposals for the classification of special furniture proceed from the functional characteristics, i.e., determine the types and types of furniture products for the equipment of the main functional areas and rooms that are included in public buildings. Classification of products according to premises and zones, and not generally in a building is most correct, since in modern practice, along with the development of special-purpose buildings, one of the main trends is to unite public buildings in various combinations and variations of similar public spaces. So, office and administrative premises are included in almost all types of public buildings; the same applies to catering facilities, warehouses, etc. The classification of furniture for basic public premises is consistent with the classification of household furniture.
Furniture products for equipment of premises in public buildings belong to the following main groups: tables - 250 types; easels, music stands - 3 types; counters - 10 types; rack barriers - 19 types; cash cabins - 6 types; tribunes - 1 type; furniture for sitting - 90 types; furniture for storage and exposure - 320 types; furniture for transportation of baggage - 12 types; furniture for lying - 29 types. Products included in each group are divided according to functional characteristics, i.e., according to the purpose of the subject. For example, dining tables, workers, magazine, student, etc.
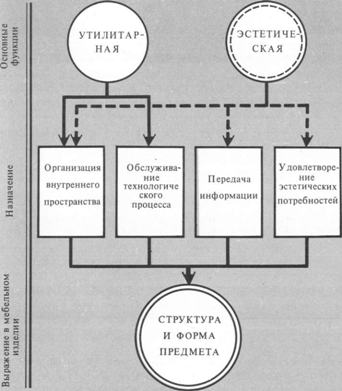
Despite the significant variety of modern furniture, it is possible to distinguish two main functions: utilitarian and aesthetic (Fig. 30).
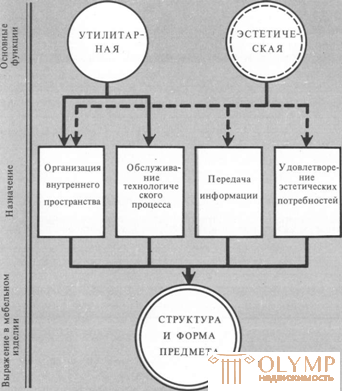
Fig. 1. The main functions of furniture
By virtue of the utilitarian function, furniture is designed primarily to serve a particular life process (sleep, eating, rest, etc.) or a labor operation (work, training sessions, etc.), taking into account their optimal organization. The most important condition for the utilitarian use of modern furniture is the organization of the internal space of the premises. Indeed, with the equipment of almost all types of modern residential and public buildings, firstly, there is a strong tendency to use built-in, stationary equipment: cabinets for various purposes in residential, educational, administrative buildings, hospitals. Secondly, in modern architecture, various open-plan techniques and functional room zoning are becoming increasingly common, in which furniture is the main means of organizing zones of various purposes. Thus, in a modern building, furniture is increasingly becoming the element that helps to solve the internal structure of not only the room, but also the building as a whole.
By virtue of the aesthetic function, furniture serves the spiritual needs of a person, so it must correspond to the idea of a particular group of people about beauty, harmony, good taste, etc. The aesthetic function is associated with the concept of information. Furniture, like other consumer goods, can act as a thing and as a sign, symbol (or both at the same time), which is a carrier of information.
The functions of an object determine its structure and shape. Since they are for the most part manifested not in isolation, but in combination with each other, they say "about the structure of functions, i.e., about their definite connection and mutual subordination, and one or some of them dominate." The functional structure of furniture products is a special system in which the change or disappearance of one of the main functions causes a change in the structure as a whole. Strengthening one function can lead to a weakening of other functions included in the system, and weakening one of the functions can lead to an increase in the intensity of some other function, i.e., a change in the structure as a whole. Therefore, in order to correctly determine the overall artistic and constructive solution of a furniture product, it is necessary to clearly identify the qualitative and quantitative attributes of its functions. This requirement is closely related to the first feature of modern furniture - its conditionality by the purpose of the building and the rooms in it.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)