Special types of reconstruction include changing the volume of buildings, their shifting, lifting and demolishing. They are used as town-planning measures, when they want to change the density of the housing stock and buildings or the position of a house on the ground, to free up a platform for punching a highway, building a new building or planting greenery on a territory.
The volume of buildings is changed by adding them or erecting a number of extensions and buildings.
The superstructure is an increase in the number of floors of a house or its parts. The use of the third dimension of development is an effective measure, since it allows to increase the effective area of buildings without compacting the area of development, and this intensifies the use of urban land. Such an event is possible even in densely built-up areas, which is important in the reconstruction of the central areas of cities, where land is valued not only in terms of prestige, but also the cost of rent.
The decision to increase the height of the building, as a rule, take into account urban constraints imposed by the concept of development of the territory. First of all, the limit on the number of floors and population density.
Superstructures are of particular importance as a means of creating unified ensembles. Floors of buildings can be leveled by a superstructure of some of them, partial and complete. Or vice versa, they emphasize one of the volumes, for example, a corner house at the intersection of streets. If at the same time the gaps between the buildings are filled, the building takes on a finished look.
The superstructure is simplified when the floors in adjacent buildings are located at the same level. However, joint solutions are also possible in buildings with floors in different levels. In these cases, the vertical displacement of window openings has to be masked by horizontal divisions of the facades, decorative spots or other architectural techniques.
There are three types of use of the third dimension of a building — its height:
1) the attic device, that is, the location of housing in the under-roof space, on the site of the rebuilt attic;
2) the superstructure itself;
3) placing on a functionally operated roof recreational space, allowing you to create places for leisure in the fresh air. It as if expands the near-house plots, which is important in densely built-up areas.
The layout of the terrace - open space on the roof at the apartments of the upper floor is diverse. Usually they break lawns, playgrounds for recreation and games, set up pergolas or gazebos.
An example of such a solution is Fig. 6.8. Here the apartments are equipped with a roof terrace of only 20 m 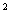 . However, in the practice of urban planning, there are samples of operated roofs with landscape landscaping of considerable size.
. However, in the practice of urban planning, there are samples of operated roofs with landscape landscaping of considerable size.
but - the first tier; b - the second tier.
Fig. 6.8. - Recreational sites on the flat, operated roof of a pre-revolutionary building, the upper floor of which, together with the under-roof space, is turned into a solution by bunk apartments
They create not only summer, but also winter gardens and greenhouses. In town planning, the principle of multi-level landscape organization is gradually being established in densely built urban centers. Human-created “above-ground territories” are used. In relation to this, the term “artificial gardening” has been formed in landscape architecture. Green plantings that cannot develop naturally, are supported by engineering and biological means, by creating artificial bases, favorable conditions: insolation, aeration, and temperature-humidity.
In the case of terraced construction, additional loads appear, so reinforcement of the supporting structures is required. At the same time, a promising increase in green mass and root system is envisaged, which occurs as the stands grow.
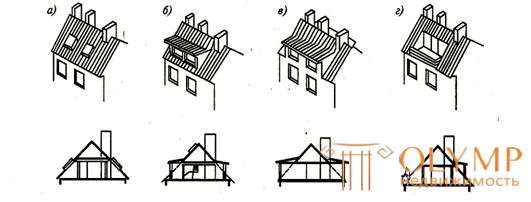
Attic device.
Mansards are satisfied using four methods. The easiest way is to place them in buildings whose upper floor is technical. Then its height is used as part of the height of the dwelling (Fig. 6.9 a). According to the second method, the last floor of the house is converted into the lower floor of a two-story apartment, which allows placing the sleeping area of this apartment under a new roof (Fig. 6.9 b ).
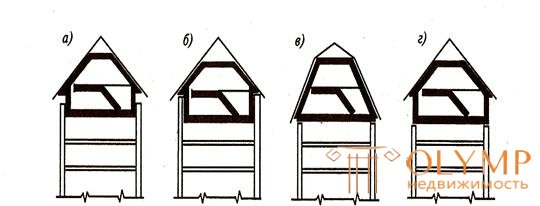
a - above the building with a technical upper floor; b - with a device of two
Fig. 6.9. - Attic device options
floor apartments transforming the existing upper floor into a zone of daytime residence and placing a sleeping area in the under-roof space; in - with the placement of two-storey apartments under a high roof; d - a solution combining the attic with a superstructure of one floor.
The reconstruction according to the third method provides for one- or two-tier flats entirely located under the roof with broken slopes (Fig. 6.9c ), but in the presence of inclined external walls. According to the fourth method, the attic is combined with the superstructure of one floor (Fig. 6.9 g).
In all the variants in Fig. 6.9. Shows solution schemes with two-story (two-tier) apartments. When designing apartments in the same level, the principle of placement of under-roof housing is preserved. The choice of this or that decision depends not only on the social order of users, but also on the possibility of installing an elevator, since according to current standards, the floor level of entrances to the upper floor apartments and the staircase vestibule should not differ by more than 13.5 m .
The windows in the attic rooms are easiest to lay on the slope of the roof (Fig. 6.10 a). However, the methods of their vertical installation are used more often (Fig. 6.10 b-d). In one case, the window jumper is pulled out, as shown in Fig. 6.10 b, in the other - it is installed in the plane, increasing along the height of the wall of the facade (Fig. 6.10 c). Often, the lintel of the vertical window opening with the door is left in the plane of the roof slope. Then a part of the outer fence - the walls are pushed inside the building, and in front of the window they arrange the balcony shown in Fig. 6.10 g, and sometimes increased drainage - the roof over this balcony, the width of which can reach 1.5 m .
a - in the plane of the roof slope; b - vertically with the window box extending from the roof plane; in the same way, with building up the outer wall of the building; d - the same, with a latch of window blocks into the interior of the room and arrangement of balconies
Fig. 6.10. - Placement of window openings in the roofs of buildings
with attic
In the rooms with sloping outer walls, “dead zones” appear in the place of junction with the floors, which are not accessible for people to approach. In this case, the lower part of the wall is made vertical, and its height is assumed to be 0.9-1.4 m.
In practice, they use not only solutions where the second tier of apartments does not exceed the dimensions of the first, but also with a mismatched external outline, it is characteristic to combine in the sub-roof superstructure of apartments in one and two levels. The planning feature of two-level apartments is the location at the bottom of only the hallway with an internal staircase and
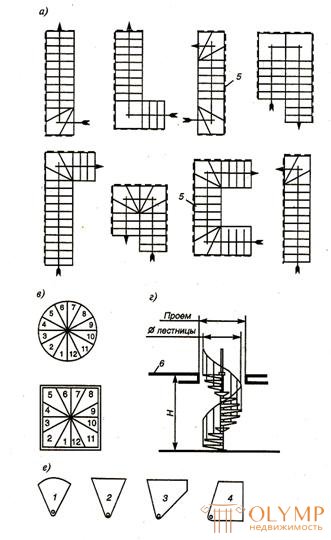
a - marching (plans); B - e - screw (B - various configurations in the plan; d - vertical breakdown scheme; e - transaxle steps); 1,2,3 - configuration in terms of steps for spiral staircases; 4 - the same, marching zabezhnyh; 5 - walls; 6 - overlap.
Fig. 6.11. - Apartment stairs
Bearing structures of mansards as under-roof space are usually carried out in wood. Apply frame truss system with struts, and not naslonnuyu. In Fig. 6.12. The solution to such a one-story frame is shown, but it can be made two floors high. Then the interfloor beams will serve as puffs reducing the free length of the uprights.
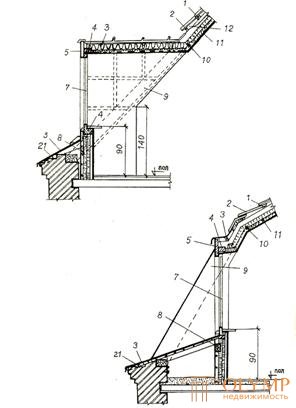
1 - crate; 2 - tiles; 3 - steel roof; 4 - black box; 5 - frontal board with facing; 6 - sealing gasket; 7 - window unit; 8 - support bar; 9 - truss foot; 10 - insulation; 11 - plates of the finishing layer; 12 - holes for ventilation of the under-roof space; 13 - stand; 14 - walls of an existing building; 15 - beam overlap, at the same time being the tightening of the frame; 16 - struts - rafters; 17 - frame struts; 18 - diagonal boards; 19 - coating form; 20 - run; 21 - filly.
Fig. 6.12. - The frame supporting structure of a penthouse with a span of 6-12 m.
External enclosing structures of attic rooms are performed as shown in Fig. 6.13. Window and doorways are filled, constructively resolved in accordance with this pattern.
When constructing an attic, window openings are best performed using the Velux system. In combination with the beautiful Andulin coating, Velux skylights give the building a great view. In the attic you can arrange terraces by trimming the roof and indenting a new wall from the line of the old wall. The construction of roof elements of the attic are performed in any version: wood, reinforced concrete, metal.
The roof window is part of the roof. Due to its inclined position, this window illuminates more space than usual.
When calculating the size and location of dormer windows, it is important to know two things. Firstly, the size of the window depends on the degree of slope of the roof: the smaller the slope, the longer the window should be. Secondly, the window should be located at a distance of 90-110 cm from the floor, and in no way higher than the slopes of the dormer windows should in no case be parallel to each other - this will severely damage the lighting of your attic. The bottom slope should be strictly vertical, and the top should go horizontally across the floor, forming a much larger right angle with the glass. The battery located directly under the window is not a tribute to traditional thinking, but an engineering necessity. A properly installed battery will prevent condensation, ensuring that the glass is washed with a stream of warm air.
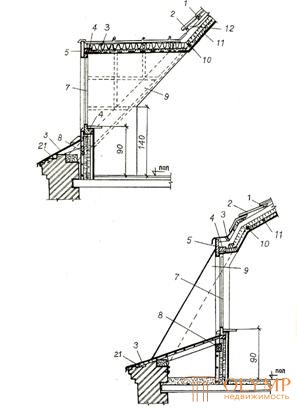
1 - crate; 2 - tiles; 3 - steel roof; 4 - black box; 5 - frontal board with facing; 6 - sealing gasket; 7 - window unit; 8 - support bar; 9 - truss foot; 10 - insulation; 11 - plates of the finishing layer; 12 - holes for ventilation of the under-roof space; 13 - stand; 14 - walls of an existing building; 15 - beam overlap, at the same time being the tightening of the frame; 16 - struts - rafters; 17 - frame struts; 18 - diagonal boards; 19 - coating form; 20 - run; 21 - filly.
Fig. 6. 13. - Structural scheme of the frame for the attic device and its protecting structure
Mansard superstructure is currently happening everywhere, even without reconstruction and change of the building plan. In some cases, the construction of the attic took place even without the resettlement of the tenants or the cessation of the administrative building.
In residential buildings, the attic area can be given for new apartments or the space of apartments on the last floor joins it, creating magnificent two-level apartments for large families.
Quite often in the attic houses workshops of architects, artists and designers, less often - scientists, composers and writers are located. In public buildings with mansard add-ons, additional space is added for offices and other services.
If the building had a rather high pitched roof, then it can be easily replaced by a two-level attic, but the area of the upper level is very small and, as a rule, it houses a bedroom.
The construction of two-level apartments is easy, as there are any types of spiral and zabezhnye stairs, both wooden and metal, on sale. The most difficult option is - an attic superstructure with an additional floor. This is a serious load on the old walls of houses, and the appearance of the building varies greatly. Such a decision is rarely approved by the inspection for the protection of monuments of architecture. However, in a town-planning situation, there are cases when it is necessary to align the silhouette of a building, raising the number of floors to 5-6 floors. If in the old building there are weak walls and foundations, and their reinforcement does not have any effect on the structure of the superstructure, then in this case they resort to a solution on the construction of additional foundations. They are constructed with great care and without dynamic loads, on which columns are installed inside the volume, if the image of the house cannot be changed. On high pillars they are building a new building, but with the organization of the entrance through the old building. As a rule, in this case, arrange a new monolithic overlap and build a new ladder, taking into account fire regulations. In some cases, when raising the height of more than a height from the mark in the vestibule (13.5 m), it is necessary to arrange an elevator, and this is additional difficulties. But in the practice of reconstruction of buildings there are no easy options.
In the practice of building superstructures with flat roofs, there are options when small rooms for clubs, auxiliary buffets, mini-cafes, and, consequently, recreation areas with landscaping and fountains are built on them. These activities make it necessary to strengthen the overlap over the last floor and create conditions for the operation of the roof, green spaces are set in tubs, and lawns are made of rolled carpets. Pools with fountains are made of floor type, of course, not deep, but rather decorative, but they require special reinforcement of structures, even the introduction of additional beams, and, of course, enhanced waterproofing of the bath. Therefore, they are made of metal with a polyethylene coating. The superstructure is clearly performed on the bearing walls. If they are not designed for the perception of a new load, they are strengthened with an additional pilasters device.
The basic principle of designing an attic is the principle of the unity of the internal and external. The possibilities of interior design of the attic is very closely connected with architectural and engineering solutions. In order not to regret about missed opportunities, remember: the design and design of such unusual spaces as the attic should be strictly interconnected. Even at the stage of project approval, you can ask the architect to increase the slope of the roof. For the general form of the house, this factor is not so significant, but for the internal structure of the attic it is fundamental. The higher the ridge of your roof, the more spacious the attic rooms will be and the more opportunities you will have to “play” with height.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)