The video surveillance system is a software and hardware complex (video cameras, lenses, monitors, recorders, video servers, and other equipment) designed to organize video monitoring on both local and geographically-distributed objects. Consider their main characteristics, types, features, settings and installation, and work in them. The functions of video surveillance include not only protection against criminals, but also the observation of employees, visitors in the office, in a warehouse or in a store, control of activity in any room.
Thus, the video surveillance system provides:
visual monitoring of the situation at the protected object - providing information on the observation post in real time;
recording video information on a digital video recorder that allows you to document events occurring at the facility;
performing the functions of burglar alarm through motion detectors of video cameras or external security sensors and the awareness of the system operator about the occurrence of an alarm in the controlled area.
Analog CCTV cameras are used to monitor a limited number of protected objects. Since the technical indicators of this type of camera are at a relatively low level, the image quality obtained through analog surveillance cameras is rather low. In this case, the positive quality of analog surveillance cameras is the simplicity of their use, recording from a surveillance camera goes to a VCR, and information is stored on the tape.
The main negative aspects of analog surveillance cameras are quite frequent cassette changes, and not the quality of recording information. In addition, the price of analog CCTV cameras is slightly different from the cost of digital cameras.
The equipment does not stand still, so today, new analog CCTV cameras have been designed, which are equipped with built-in special blocks for converting an analog signal into a digital signal of a CCTV camera. This unit allows you to connect an analog camera to digital video surveillance systems.
In addition, there are DVRs capable of digitizing the incoming analog stream, multiplexing and recording video and audio to disk, as well as transmitting the video signal to a local network and the Internet.
In this case, analog video cameras are always connected to the DVR using a coaxial cable. at the same time it is possible to power the camera over the same cable with the installation of additional devices.
At the same time, a coaxial cable has a limit on its maximum length, usually up to 100m or in some variants up to 500m. Also, when installing a coaxial cable, there is a maximum radius of the cable when installing, intermediate connections are very undesirable, the entire route should be made with a single cable. For a coaxial cable, special connectors are used. The quality of cable termination by such connectors can also greatly affect the quality of the recorded video signal.
Characteristics of analog cameras:
Main settings
Format - a parameter characterizing the dimensions of the camera video matrix. Unfortunately, this parameter does not reflect the physical dimensions of the video matrix and is historically associated with cathode ray tubes. The format is indicated in inches and allows you to determine the angle of view of the camera when using a lens with a particular focal length. The higher the format of the matrix, the greater its physical dimensions and the greater the viewing angle it can provide. This parameter is not strictly related to the physical dimensions and video matrices having the same format can have slightly different geometrical dimensions. Let's take, for example, the sizes of some video matrices:
- 1/3 "(width - 4.8 mm; height = 3.6 mm);
- 1/2 "(width: 6.4 mm; height = 4.8 mm);
- 2/3 "(width 8.8 mm; height = 6.6 mm);
- 1 "(width - 12.7 mm; height = 9.5 mm).
As the level of technology develops on the market, there is a steady trend towards a permanent decline in format as the price of television cameras falls. At present, the video matrices of the 1 "and 2/3" format have practically disappeared, and the most common are 1/2 ", 1/3" and 1/4 "(there were reports of the creation of 1/5" video matrices).
The resolution is measured in television pines (TVL) and describes how small details can be distinguished using a television camera. This value, as already noted, is mainly determined by the number of elements of the video matrix: the more elements, the higher the resolution (recall that we are talking about horizontal resolution, because the number of elements is strictly tied to the television standard). The absolute value of the resolution can be associated with the number of elements using the following empirical relationship:
Resolution in TVL = 3/4 of the number of elements
The exact measurement of this value is carried out with the help of special test tables with a marked system of converging alternating black and white lines (the unit of measure was named in their honor). Placing the table in front of the television camera so that it occupies the entire monitor screen, determine the point at which the differences between the black and white lines become indistinguishable and read the absolute value of the resolution on a special scale.
Of course, the electronic part of a television camera (for example, the band of frequencies transmitted by it) also influences the resolution, but it can only change in the direction of deterioration. It should be noted that the reduction in the format of the video matrix has little effect on the resolution of the camera, since the capabilities of the technology make it possible to make the elementary areas small enough. From the principle of the color matrix, it is clear that its resolution is lower than black and white.
Currently, the market offers cameras of the following resolution (the higher the resolution, the higher the price of the camera):
- B / W cameras of medium resolution (approximately from 510 to 560 elements horizontally) have a resolution from 380 to 420 TVL;
- B / W cameras of high resolution (up to 800 elements horizontally) have a resolution of up to 600 TVL;
Medium resolution color cameras have resolutions from 280 to 330 TVL;
High-resolution color cameras have resolutions up to 460 TVL (up to 560 TVL on S - VHS output).
Cheap medium-resolution cameras are suitable for monitoring the overall situation. If the definition of small parts is required (for example, reading car numbers), then cameras with higher resolution are needed.
High Definition Video Cameras
D1 (704х576) СVBS (Composite Video Baseband Signal) D1
960H (960x576)
AHD , 720p / 1080p quality on coaxial on 500 meters without delays and losses.
HDCVI , (High-Definition Composite Video Interface) high resolution 720P and 1080P, transfer of audio, video and data over a coaxial cable (transfer of three types of data over one coaxial cable), clear video without loss and attenuation at distances up to 500 m. HDCVI camera equipped with TX-chipset, HDCVI DVRs - RX-chipset. In particular, the signal in HDCVI video surveillance systems is transmitted at a frequency below 50 MHz and is much more resistant to interference than using, for example, HD-SDI technology.
HDTVI , unlike its predecessor - PAL standard, allows you to transmit video signals with resolutions up to 1920x1080 pixels. The copyright to the HD-TVI standard is owned by HIKVISION. The main difference of the new standard is the modified technology of video signal formation and transmission, the standard assumes a complete separation of the luminance signal and color-containing signals, thus avoiding the accumulation of interference to obtain a clearer image, and also in the HDTVI a proprietary algorithm of preprocessing a non-modulated video signal is implemented followed by quadrature amplitude modulation for transmission over the communication line - the usual coaxial cable with a characteristic impedance of 75 Ohms.
HD-SDI is nothing more than a High-Definition Serial Digital Interface, a high-resolution serial digital interface, and this technology has come to video surveillance systems from HDTV - high-definition television. The main difference between HD-SDI and IP video surveillance is the difference in the used infrastructure. If for IP video surveillance it is necessary to use Ethernet local networks, then HD-SDI requires laying of coaxial lines and this is perhaps the only fundamental difference between the two systems, which is not related to image quality or the ability to view the image using Internet connections. HD-SDI is also an HD camera that transmits video to a recording device (DVR) without any compression or packaging - hence the absence of delays in HDSDI surveillance as opposed to IP surveillance, in which the image delay is quite normal Noe yavlenie.Dlya such standard is characterized by high demands on the quality of the cable and connectors as well as a small distance from the cameras DVR (up to 100m. without gain)
Minimum illumination characterizes the level of illumination at which a television camera produces a “normally perceived” image. This parameter is measured in lux (photographic characteristic relating to the spectral range perceived by the human eye). The minimum illumination is one of the most "crafty" parameters, since it provides for several different measurement methods, and the camera's passport does not always indicate which of them was measured. First, there are various criteria for determining the "normally perceived" image (most often the criterion for the fall of the signal of approximately 30% of the nominal is used), and secondly, it should always be indicated where the minimum illumination is measured: on the video matrix or on the lens (in in this case its relative opening is indicated).
When measuring the minimum illumination on the lens, the light loss inside it is taken into account, which is the greater, the higher the relative aperture (less aperture ratio) of the lens. For example, with a standard F 1.4 relative aperture, the light loss is one order of magnitude (only 10% of the light passes) and therefore the minimum illuminance on the video matrix equal to 0.01 lux corresponds to the minimum illumination on the lens of 0.1 lux ,. The value of the minimum illumination is largely determined by the size of the video matrix element (the smaller the elementary area, the less light it can collect).
From the above, two conclusions follow: first, the minimum illumination of color cameras is much higher than that of black and white, and secondly, the smaller the video matrix format, the more stringent the requirements for the illumination of the object of observation. The characteristic minimum illumination on the lens F1.4 for black and white cameras lies in the range from 0.1 to 0.5 lux, and for color cameras from 1 to 3 lux.
Approximate illumination of objects. | |
| Outdoor: cloudless, sunny day | Over 100,000 lux (55 ° sun angle) |
| Sunny day, with light clouds | 70,000 lux |
| It's a nasty day | 20,000 lux |
| Early morning | 500 lux |
| Dusk | 4 suites |
| Clear night full moon | 0.2 lux |
| Clear night, incomplete moon | 0.02 lux |
| Night moon in the clouds | 0.007 lux |
| Clear, moonless night | 0.001 lux |
| Moonless night with light clouds | 0.0007 lux |
| Dark cloudy night | 0.00005 lux |
| Indoors without windows with artificial lighting | 100 - 200 lux |
| Well lit rooms, offices | 200 - 1000 lux |
All case cameras have a standard node for attaching television lenses. There are two standards: "C" and "CS" with the same connecting thread D25.4 x 0.8 and different rear section (17.5 mm and 12.5 mm, respectively). If the camera has a type C connection, then only a C lens will fit it. For a camera with a CS node, CS and C lenses with a special adapter ring are suitable.
The camera angle is a parameter that is determined by the focal length (f) of the lens. Often this parameter is indicated in degrees. A wide viewing angle corresponds to small focal lengths (2.8-5.0 mm). To observe distant objects, lenses with long focal lengths (28.0 - 75.0 mm and more) are used. Having a lens with a wide viewing angle, you can get a good panoramic view (overall picture), but you will see the distance worse, smaller, you will not be able to see some small details there. And when using long-focus lenses, the field of view is certainly narrowed, but you will see better into the distance.
Selecting the viewing angle of the camcorder
The first thing you need to consider is that video cameras are somewhat different from the human eye. Your eye, though not perfect, is a sufficiently high-quality surveillance system. You can look with equal success both into the distance, even to the horizon, and distinguish the lines on your arm. By simply turning your head, you can see what happens to your right or left. The camera is looking straight ahead (if it is not a controlled camera) at the same distance and angle as the focal length of the lens allows. That is why the choice of focal length - is one of the most important moments in the selection of equipment for video surveillance systems. If you select lenses with a fixed focal length, pay special attention to this! In addition to lenses with fixed focal length, there are lenses with variable (varifocal). Varifocal lenses allow you to adjust the visible image directly on the object, in addition, in the future you have the opportunity to change the viewing angle. But only in a pre-selected range. For a more convenient selection of the lens below is a sample table of viewing angles and distances from the camera to the object.
FOCAL LENGTH
The focal length of the lens is measured in millimeters and represents the distance from the extreme point of the lens to the video matrix on which the resulting image is focused.

The most common focal length value in video surveillance is 3.6 mm, which is approximately equal to the viewing angle of 72 ° horizontally and 90 ° diagonally, which is an approximate number to the angle of view of a normal human eye. Lenses with a focal length of 3.6 mm are an excellent solution for building a video surveillance system in small residential or office premises.
When choosing a focal length, it is also necessary to remember that the smaller the focal length, the less far-sighted your video camera will be, but at the same time it will cover a larger viewing area. Conversely, the larger the focal length of the lens, the more detailed the video image will be, but the coverage will be less. In fact, there is no concept better and worse. Simply, wide-angle lenses are suitable for a general overview (for example, a protected yard or parking area), and a longer focal length allows you to see a more detailed image that is required at cash registers in supermarkets or in banks.
REVIEW ANGLE
The value of the viewing angle indicates how large the area your lens can cover during video recording. If you hear the term “wide angle”, then usually this means lenses with focal lengths of 3.6 mm or less. Wide-angle lenses allow you to see a large area of the observed territory, but with less detail. To keep a general overview of the room with an area of 20x20 meters, a wide-angle lens will be most welcome, but in order to see and capture a person’s face or banknote well, you will need a lens with a long focal length, for example, 16 mm.
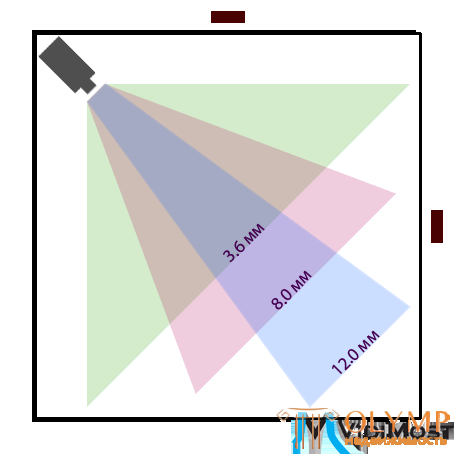
Table of viewing angles and distances from the camera to the object:
| f focal distance lens | Horizontal viewing angle for CCD 1/3 ″ | Opportunity discoveries human | Opportunity identification human | Opportunity definitions numbers the car |
| 2.8 mm | 86 ° | up to 19 m | up to 1.4 m | - |
| 2.9 mm | 83 ° | up to 20 m | to 1.45 m. | - |
| 3.6 mm | 72 ° | up to 25 m | up to 1.8 m | - |
| 4.0 mm | 67 ° | up to 28 m. | up to 2 m | up to 2.6 m |
| 6.0 mm | 48 ° | up to 42 m. | up to 3 m | up to 4 m |
| 8.0 mm | 36 ° | up to 56 m. | up to 4 m | up to 5 m. |
| 9.0 mm | 30 ° | up to 63 m | up to 4.5 m | up to 6 m. |
| 12.0 mm | 25 ° | up to 84 m. | up to 6 m. | up to 8 m. |
| 16.0 mm | 17 ° | to 112 m. | up to 8 m. | up to 10 m. |
| 25.0 mm | 12 ° | up to 175 m | up to 12.5 m | up to 16 m. |
| 50.0 mm | 6 ° | up to 350 m | up to 25 m | up to 33 m. |
| 80.0 mm | 3.3 ° | up to 560 m. | up to 40 m. | up to 53 m. |
| 100.0 mm | 2.8 ° | up to 700 m | up to 50 m. | up to 66 m. |
| 120.0 mm | 2.1 ° | up to 840 m. | up to 60 m. | up to 80 m |
For video cameras with matrix size 1/2 ″, the viewing angle will be approximately 17-18% larger, and for matrix 1/4 - less.
It is also worth noting that the viewing angle indicated by manufacturers of video cameras, as a rule, is represented not diagonally, but diagonally.
Here is a good example of using lenses with different focal lengths:
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Provided that the object of observation must be completely visible in height, the focal length of the lens of a video camera can be calculated by the following formula:
f = v * D / V, where
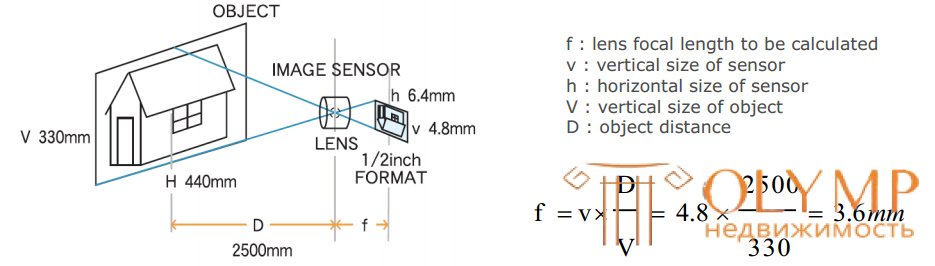
Dimensions of photosensitive matrix cameras (height * width):
Below are the detail areas for video cameras with different arrays and focal lengths of lenses.
Zones of detail (the distance from the video camera to the object of observation, under which one of the following conditions is met):

| Lens focal length, mm | Viewing angles, ° | Detail zones, m | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontally | Vertically | Observation | Recognition | Identification | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | |||
| 2.8 | 92.6 | 60.9 | ten | 15 | 21.4 | 21.9 | 26.3 | 30.1 | 34.2 | 5.02 | 7.52 | 10.7 | 10.9 | 13.1 | 15 | 17.1 | 2.51 | 3.76 | 5.35 | 5.47 | 6.56 | 7.52 | 8.55 |
| 3.6 | 78.3 | 49.2 | 12.9 | 19.3 | 27.5 | 28.1 | 33.8 | 38.7 | 44 | 6.45 | 9.67 | 13.8 | 14.1 | 16.9 | 19.3 | 22 | 3.22 | 4.84 | 6.88 | 7.03 | 8.44 | 9.67 | eleven |
| 3.8 | 75.2 | 46.9 | 13.6 | 20.4 | 29 | 29.7 | 35.6 | 40.8 | 46.4 | 6.81 | 10.2 | 14.5 | 14.8 | 17.8 | 20.4 | 23.2 | 3.4 | 5.11 | 7.26 | 7.42 | 8.91 | 10.2 | 11.6 |
| four | 72.4 | 44.8 | 14.3 | 21.5 | 30.6 | 31.3 | 37.5 | 43 | 48.8 | 7.17 | 10.7 | 15.3 | 15.6 | 18.8 | 21.5 | 24.4 | 3.58 | 5.37 | 7.64 | 7.82 | 9.38 | 10.7 | 12.2 |
| five | 60.7 | 35.6 | 17.9 | 26.9 | 38.2 | 39.1 | 46.9 | 53.7 | 61.1 | 8.96 | 13.4 | 19.1 | 19.5 | 23.4 | 26.9 | 30.5 | 4.48 | 6.72 | 9.55 | 9.77 | 11.7 | 13.4 | 15.3 |
| 6 | 52 | 30.7 | 21.5 | 32.2 | 45.9 | 46.9 | 56.3 | 64.5 | 73.3 | 10.7 | 16.1 | 22.9 | 23.4 | 28.1 | 32.2 | 36.6 | 5.37 | 8.06 | 11.5 | 11.7 | 14.1 | 16.1 | 18.3 |
| eight | 40.2 | 23.3 | 28.7 | 43 | 61.1 | 62.5 | 75 | 86 | 97.7 | 14.3 | 21.5 | 30.6 | 31.3 | 37.5 | 43 | 48.8 | 7.17 | 10.7 | 15.3 | 15.6 | 18.8 | 21.5 | 24.4 |
| ten | 32.6 | 18.7 | 35.8 | 53.7 | 76.4 | 78.2 | 93.8 | 107 | 122 | 17.9 | 26.9 | 38.2 | 39.1 | 46.9 | 53.7 | 61.1 | 8.96 | 13.4 | 19.1 | 19.5 | 23.4 | 26.9 | 30.5 |
| 12 | 27.4 | 15.6 | 43 | 64.5 | 91.7 | 93.8 | 113 | 129 | 147 | 21.5 | 32.2 | 45.9 | 46.9 | 56.3 | 64.5 | 73.3 | 10.7 | 16.1 | 22.9 | 23.4 | 28.1 | 32.2 | 36.6 |
| sixteen | 20.7 | 11.8 | 57.3 | 86 | 122 | 125 | 150 | 172 | 195 | 28.7 | 43 | 61.1 | 62.5 | 75 | 86 | 97.7 | 14.3 | 21.5 | 30.6 | 31.3 | 37.5 | 43 | 48.8 |
| 50 | 6.7 | 3.77 | 179 | 269 | 382 | 391 | 469 | 537 | 611 | 89.6 | 134 | 191 | 195 | 234 | 269 | 305 | 44.8 | 67.2 | 95.5 | 97.7 | 117 | 134 | 153 |
| 60 | 5.59 | 3.15 | 215 | 322 | 459 | 469 | 563 | 645 | 733 | 107 | 161 | 229 | 234 | 281 | 322 | 366 | 53.7 | 80.6 | 115 | 117 | 141 | 161 | 183 |
| 90 | 3.73 | 2.1 | 322 | 484 | 688 | 703 | 844 | 967 | 1100 | 161 | 242 | 344 | 352 | 422 | 484 | 550 | 80.6 | 121 | 172 | 176 | 211 | 242 | 275 |
| 100 | 3.35 | 1.89 | 358 | 537 | 764 | 782 | 938 | 1070 | 1220 | 179 | 269 | 382 | 391 | 469 | 537 | 611 | 89.6 | 134 | 191 | 195 | 234 | 269 | 305 |
| 120 | 2.8 | 1.57 | 430 | 645 | 917 | 938 | 1130 | 1290 | 1470 | 215 | 322 | 459 | 469 | 563 | 645 | 733 | 107 | 161 | 229 | 234 | 281 | 322 | 366 |
| 150 | 2.24 | 1.26 | 537 | 806 | 1150 | 1170 | 1410 | 1610 | 1830 | 269 | 403 | 573 | 586 | 703 | 806 | 916 | 134 | 202 | 287 | 593 | 352 | 403 | 458 |
| Lens focal length, mm | Viewing angles, ° | Detail zones, m | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontally | Vertically | Observation | Recognition | Identification | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | |||
| 2.8 | 90 | 58.7 | 10.5 | 15.7 | 18.3 | 22.8 | 27.4 | 31.5 | 35.7 | 5.24 | 7.86 | 9.14 | 11.4 | 13.7 | 15.7 | 17.9 | 2.62 | 3.93 | 4.57 | 5.71 | 6.85 | 7.86 | 8.93 |
| 3.6 | 75.8 | 47.3 | 13.5 | 20.2 | 23.5 | 29.4 | 35.3 | 40.4 | 45.9 | 6.74 | 10.1 | 11.8 | 14.7 | 17.6 | 20.2 | 23 | 3.37 | 5.06 | 5.88 | 7.34 | 8.81 | 10.1 | 11.5 |
| 3.8 | 72.8 | 45 | 14.2 | 21.3 | 24.8 | 31 | 37.2 | 42.7 | 48.5 | 7.12 | 10.7 | 12.4 | 15.5 | 18.6 | 21.3 | 24.2 | 3.56 | 5.34 | 6.2 | 7.75 | 9.3 | 10.7 | 12.1 |
| four | 70 | 43 | 15 | 22.5 | 26.1 | 32.6 | 39.2 | 44.9 | 51 | 7.49 | 11.2 | 13.1 | 16.3 | 19.6 | 22.5 | 25.5 | 3.75 | 5.62 | 6.53 | 8.16 | 9.79 | 11.2 | 12.8 |
| five | 58.5 | 35 | 18.7 | 28.1 | 32.6 | 40.8 | 49 | 56.2 | 63.8 | 9.36 | 14 | 16.3 | 20.4 | 24.5 | 28.1 | 31.9 | 4.68 | 7.02 | 8.16 | 10.2 | 12.2 | 14 | 15.9 |
| 6 | 50.1 | 29.4 | 22.5 | 33.7 | 39.2 | 49 | 58.8 | 67.4 | 76.5 | 11.2 | 16.9 | 19.6 | 24.5 | 29.4 | 33.7 | 38.3 | 5.62 | 8.43 | 9.79 | 12.2 | 14.7 | 16.9 | 19.1 |
| eight | 38.6 | 22.3 | thirty | 44.9 | 52.2 | 65.3 | 78.3 | 89.9 | 102 | 15 | 22.5 | 26.1 | 32.6 | 39.2 | 44.9 | 51 | 7.49 | 11.2 | 13.1 | 16.3 | 19.6 | 22.5 | 25.5 |
| ten | 31.3 | 17.9 | 37.5 | 56.2 | 65.3 | 81.6 | 97.9 | 112 | 128 | 18.7 | 28.1 | 32.6 | 40.8 | 49 | 56.2 | 63.8 | 9.36 | 14 | 16.3 | 20.4 | 24.5 | 28.1 | 31.9 |
| 12 | 26.3 | 15 | 44.9 | 67.4 | 78.3 | 97.9 | 118 | 135 | 153 | 22.5 | 33.7 | 39.2 | 49 | 58.8 | 67.4 | 76.5 | 11.2 | 16.9 | 19.6 | 24.5 | 29.4 | 33.7 | 38.3 |
| sixteen | 19.9 | 11.2 | 59.9 | 89.9 | 104 | 131 | 157 | 180 | 204 | thirty | 44.9 | 52.2 | 65.3 | 78.3 | 89.9 | 102 | 15 | 22.5 | 26.1 | 32.6 | 39.2 | 44.9 | 51 |
| 50 | 6.41 | 3.61 | 187 | 281 | 326 | 408 | 490 | 562 | 638 | 93.6 | 140 | 163 | 204 | 245 | 281 | 319 | 46.8 | 70.2 | 81.6 | 102 | 122 | 140 | 159 |
| 60 | 5.35 | 3.01 | 225 | 337 | 392 | 490 | 588 | 674 | 765 | 112 | 169 | 196 | 245 | 294 | 337 | 383 | 56.2 | 84.3 | 97.9 | 122 | 147 | 169 | 191 |
| 90 | 3.57 | 2.01 | 337 | 506 | 588 | 734 | 881 | 1010 | 1150 | 169 | 253 | 294 | 367 | 441 | 506 | 574 | 84.3 | 126 | 147 | 184 | 220 | 253 | 287 |
| 100 | 3.21 | 1.81 | 375 | 562 | 653 | 816 | 979 | 1120 | 1280 | 187 | 281 | 326 | 408 | 490 | 562 | 638 | 93.6 | 140 | 163 | 204 | 245 | 281 | 319 |
| 120 | 2.67 | 1.5 | 449 | 674 | 783 | 979 | 1180 | 1350 | 1530 | 225 | 337 | 392 | 490 | 588 | 674 | 765 | 112 | 169 | 196 | 245 | 294 | 337 | 383 |
| 150 | 2.14 | 1.2 | 562 | 843 | 979 | 1220 | 1470 | 1690 | 1910 | 281 | 421 | 490 | 612 | 734 | 843 | 956 | 140 | 211 | 245 | 306 | 367 | 421 | 478 |
| Lens focal length, mm | Viewing angles, ° | Detail zones, m | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontally | Vertically | Observation | Recognition | Identification | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | |||
| 2.8 | 86.1 | 55.4 | 11.2 | 16.9 | 19.6 | 24.5 | 29.4 | 33.7 | 38.3 | 5.62 | 8.43 | 9.79 | 12.2 | 14.7 | 16.9 | 19.1 | 2.81 | 4.21 | 4.9 | 6.12 | 7.34 | 8.43 | 9.56 |
| 3.6 | 72 | 44.4 | 14.4 | 21.7 | 25.2 | 31.5 | 37.8 | 43.3 | 49.2 | 7.22 | 10.8 | 12.6 | 15.7 | 18.9 | 21.7 | 24.6 | 3.61 | 5.42 | 6.3 | 7.87 | 9.44 | 10.8 | 12.3 |
| 3.8 | 69.1 | 42.3 | 15.2 | 22.9 | 26.6 | 33.2 | 39.9 | 45.7 | 51.9 | 7.62 | 11.4 | 13.3 | 16.6 | 19.9 | 22.9 | 26 | 3.81 | 5.72 | 6.64 | 8.31 | 9.97 | 11.4 | 13 |
| four | 66.3 | 40.4 | 16.1 | 24.1 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 48.2 | 54.6 | 8.03 | 12 | 14 | 17.5 | 21 | 24.1 | 27.3 | 4.01 | 6.02 | 6.99 | 8.74 | 10.5 | 12 | 13.7 |
| five | 55.2 | 32.8 | 20.1 | 30.1 | 35 | 43.7 | 52.5 | 60.2 | 68.3 | ten | 15 | 17.5 | 21.9 | 26.2 | 30.1 | 34.2 | 5.02 | 7.52 | 8.74 | 10.9 | 13.1 | 15 | 17.1 |
| 6 | 47.1 | 27.5 | 24.1 | 36.1 | 42 | 52.5 | 63 | 72.2 | 82 | 12 | 18.1 | 21 | 26.2 | 31.5 | 36.1 | 41 | 6.02 | 9.03 | 10.5 | 13.1 | 15.7 | 18.1 | 20.5 |
| eight | 36.2 | 20.8 | 32.1 | 48.2 | 56 | 69.9 | 83.9 | 96.3 | 109 | 16.1 | 24.1 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 48.2 | 54.6 | 8.03 | 12 | 14 | 17.5 | 21 | 24.1 | 27.3 |
| ten | 29.3 | 16.7 | 40.1 | 60.2 | 69.9 | 87.4 | 105 | 120 | 137 | 20.1 | 30.1 | 35 | 43.7 | 52.5 | 60.2 | 68.3 | ten | 15 | 17.5 | 21.9 | 26.2 | 30.1 | 34.2 |
| 12 | 24.6 | 14 | 48.2 | 72.2 | 83.9 | 105 | 126 | 144 | 164 | 24.1 | 36.1 | 42 | 52.5 | 63 | 72.2 | 82 | 12 | 18.1 | 21 | 26.2 | 31.5 | 36.1 | 41 |
| sixteen | 18.6 | 10.5 | 64.2 | 96.3 | 112 | 140 | 168 | 193 | 219 | 32.1 | 48.2 | 56 | 69.9 | 83.9 | 96.3 | 109 | 16.1 | 24.1 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 48.2 | 54.6 |
| 50 | 5.99 | 3.37 | 201 | 301 | 350 | 437 | 525 | 602 | 683 | 100 | 150 | 175 | 219 | 262 | 301 | 342 | 50.2 | 75.2 | 87.4 | 109 | 131 | 150 | 171 |
| 60 | 4.99 | 2.81 | 241 | 361 | 420 | 525 | 630 | 722 | 820 | 120 | 181 | 210 | 262 | 315 | 361 | 410 | 60.2 | 90.3 | 105 | 131 | 157 | 181 | 205 |
| 90 | 3.33 | 1.87 | 361 | 542 | 630 | 787 | 944 | 1080 | 1230 | 181 | 271 | 315 | 393 | 472 | 542 | 615 | 90.3 | 135 | 157 | 197 | 236 | 271 | 307 |
| 100 | 3 | 1.69 | 401 | 602 | 699 | 874 | 1050 | 1200 | 1370 | 201 | 301 | 350 | 437 | 525 | 602 | 683 | 100 | 150 | 175 | 219 | 262 | 301 | 342 |
| 120 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 482 | 722 | 839 | 1050 | 1260 | 1440 | 1640 | 241 | 361 | 420 | 525 | 630 | 722 | 820 | 120 | 181 | 210 | 262 | 315 | 361 | 410 |
| 150 | 2.1 | 1.12 | 602 | 903 | 1050 | 1310 | 1570 | 1810 | 2050 | 301 | 451 | 525 | 656 | 787 | 903 | 1020 | 150 | 226 | 262 | 328 | 393 | 451 | 512 |
| Lens focal length, mm | Viewing angles, ° | Detail zones, m | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontally | Vertically | Observation | Recognition | Identification | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | 1 Mp | 2 Mp | 3 Mp | 5 Mp | 6 Mp | 8 Mp | 12 Mp | |||
| 2.8 | 65.5 | 39.8 | 16.3 | 24.5 | 26.1 | 32.6 | 39.2 | 49 | 51 | 8.16 | 12.2 | 13.1 | 16.3 | 19.6 | 24.5 | 25.5 | 4.08 | 6.12 | 6.53 | 8.16 | 9.79 | 12.2 | 12.8 |
| 3.6 | 53.1 | 31.4 | 21 | 31.5 | 33.6 | 42 | 50.4 | 63 | 65.6 | 10.5 | 15.7 | 16.8 | 21 | 25.2 | 31.5 | 32.8 | 5.25 | 7.87 | 8.39 | 10.5 | 12.6 | 15.7 | 16.4 |
| 3.8 | 50.7 | 29.8 | 22.1 | 33.2 | 35.4 | 44.3 | 53.2 | 66.4 | 69.2 | 11.1 | 16.6 | 17.7 | 22.1 | 26.6 | 33.2 | 34.6 | 5.54 | 8.31 | 8.86 | 11.1 | 13.3 | 16.6 | 17.3 |
| four | 48.5 | 28.4 | 23.3 | 35 | 37.3 | 46.6 | 56 | 69.9 | 72.9 | 11.7 | 17.5 | 18.7 | 23.3 | 28 | 35 | 36.4 | 5.83 | 8.74 | 9.33 | 11.7 | 14 | 17.5 | 18.2 |
| five | 39.6 | 22.9 | 29.1 | 43.7 | 46.6 | 58.3 | 69.9 | 87.4 | 91.1 | 14.6 | 21.9 | 23.3 | 29.1 | 35 | 43.7 | 45.5 | 7.29 | 10.9 | 11.7 | 14.6 | 17.5 | 21.9 | 22.8 |
| 6 | 33.4 | 19.2 | 35 | 52.5 | 56 | 69.9 | 83.9 | 105 | 109 | 17.5 | 26.2 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 52.5 | 54.6 | 8.74 | 13.1 | 14 | 17.5 | 21 | 26.2 | 27.3 |
| eight | 25.4 | 14.4 | 46.6 | 69.9 | 74.6 | 93.3 | 112 | 140 | 146 | 23.3 | 35 | 37.3 | 46.6 | 56 | 69.9 | 72.9 | 11.7 | 17.5 | 18.7 | 23.3 | 28 | 35 | 36.4 |
| ten | 20.4 | 11.6 | 58.3 | 87.4 | 93.3 | 117 | 140 | 175 | 182 | 29.1 | 43.7 | 46.6 | 58.3 | 69.9 | 87.4 | 91.1 | 14.6 | 21.9 | 23.3 | 29.1 | 35 | 43.7 | 45.5 |
| 12 | 17.1 | 9.65 | 69.9 | 105 | 112 | 140 | 168 | 210 | 219 | 35 | 52.5 | 56 | 69.9 | 83.9 | 105 | 109 | 17.5 | 26.2 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 52.5 | 54.6 |
| sixteen | 12.8 | 7.24 | 93.3 | 140 | 149 | 187 | 224 | 280 | 291 | 46.6 | 69.9 | 74.6 | 93.3 | 112 | 140 | 146 | 23.3 | 35 | 37.3 | 46.6 | 56 | 69.9 | 72.9 |
| 50 | 4.12 | 2.32 | 291 | 437 | 466 | 583 | 699 | 874 | 911 | 146 | 219 | 233 | 291 | 350 | 437 | 455 | 72.9 | 109 | 117 | 146 | 175 | 219 | 228 |
| 60 | 3.44 | 1.93 | 350 | 525 | 560 | 699 | 839 | 1050 | 1090 | 175 | 262 | 280 | 350 | 420 | 525 | 546 | 87.4 | 131 | 140 | 175 | 210 | 262 | 273 |
| 90 | 2.29 | 1.29 | 525 | 787 | 839 | 1050 | 1260 | 1570 | 1640 | 262 | 393 | 420 | 525 | 630 | 787 | 820 | 131 | 197 | 210 | 262 | 315 | 393 | 410 |
| 100 | 2.06 | 1.16 | 583 | 874 | 933 | 1170 | 1400 | 1750 | 1820 | 291 | 437 | 466 | 583 | 699 | 874 | 911 | 146 | 219 | 233 | 291 | 350 | 437 | 455 |
| 120 | 1.72 | 0.967 | 699 | 1050 | 1120 | 1400 | 1680 | 2100 | 2190 | 350 | 525 | 560 | 699 | 839 | 1050 | 1090 | 175 | 262 | 280 | 350 | 420 | 525 | 546 |
| 150 | 1.38 | 0.773 | 874 | 1310 | 1400 | 1750 | 2100 | 2620 | 2730 | 437 | 626 | 699 | 874 | 1050 | 1310 | 1370 | 219 | 328 | 350 | 437 | 525 | 656 | 683 |

| Focal length, mm | Viewing angle by horizontals degrees | Viewing angle by vertical degrees |
| 1.3 | 110 | 93 |
| 1.4 | 105 | 90 |
| 1.47 | 101 | 85 |
| 1.6 | 95 | 80 |
| 2.0 | 83 | 68 |
| 2.1 | 81 | 65 |
| 2.3 | 77 | 60 |
| 2.5 | 71 | 57 |
| 2.8 | 65 | 52 |
| 2.9 | 63 | 50 |
| 3.0 | 62 | 48 |
| 3.5 | 55 | 42 |
| 3.6 | 53 | 41 |
| Focal length, mm | Viewing angle by horizontals degrees | Viewing angle by vertical degrees |
| 1.3 | 123 | 110 |
| 1.4 | 120 | 105 |
| 1.47 | 117 | 102 |
| 1.6 | 113 | 97 |
| 2.0 | 100 | 85 |
| 2.1 | 97 | 80 |
| 2.3 | 93 | 75 |
| 2.5 | 88 | 72 |
| 2.8 | 82 | 65 |
| 2.9 | 80 | 63 |
| 3.0 | 77 | 62 |
| 3.5 | 69 | 55 |
In accordance with the selected viewing angle, we determine the required focal length.
Lenses are divided into
monofocal (fixed focal length lenses),
variofocal (variable focus) (manually adjustable focal length lenses) and
zoom lenses (lenses with variable focal length remotely).
Lenses with manual adjustment “variofokatori”, allow you to change the focal length of about 2 times, it allows you to adjust the angle of view of the camera on the optimal image.
A variofocal lens of a video camera (Varifocal Lens) consists of a single optical system in which the components mechanically mutually move relative to each other, due to which there is a smooth change in the focal length and image scale of the image in the range of these focal lengths. In this case, when changing the focus of the lens, the sharpness of the focus on the object and the relative aperture remain unchanged.
Varifocal lenses of a video camera with a remote control "zoom lens" , give the opportunity to change the focal length from 6 times to 34 times. They are used on objects, during video surveillance of which you want to remotely change the scale of the monitored image.
Recently, most often used lenses with automatic adjustment of the aperture, variofokalnye, with variable focal length. They are easy to configure and use, the most versatile. The most common options for using lenses:
1 . Wide-angle lenses with a viewing angle of 70 ° -95 ° are used to observe:
• front door;
• in a small room (not more than 5x5 m);
• if you only need general control over the situation in a medium-sized room (10x10 m).
2. Lenses with a viewing angle of 30 ° -70 ° are used to observe:
• in rooms of medium size (not more than 10x10 m);
• for the territory adjacent to the entrance to the building.
3. Cameras with narrow-angle lenses 3 ° -30 ° are installed:
• in the corridors;
• around the perimeter of the building;
• along the fence;
• in those places where it is necessary to control long areas of the territory.
Often the desire to see as much as possible leads to the choice of wide-angle lenses. However, there is one problem - the more objects are visible in the frame, the smaller each of them, the harder it is to distinguish them. Meanwhile, for the confident identification of a familiar person, he must be about half a frame tall. For the most common cameras (with a 1/3 "matrix), this means that the focal length in millimeters should be equal to the distance to a person in meters. If you need to recognize a person at a distance of 50 meters, you need a lens with a focal length of 50 mm. Or vice versa - Using a lens with a focal length of 3 mm You can confidently identify a person at a distance of up to 3 meters. What to do if the required angle of view does not work at the chosen scale? Try to correctly choose the location of the camera and the viewing angle, or use Ariofocal lenses to accurately adjust the minimum allowable scale, thereby increasing the angle of view. You may have to install not one, but two cameras. It is pointless to strive for very wide viewing angles - lenses with an angle of view of 90 ° and more have a significant barrel distortion, and At the edges of the field of view, the image is severely deformed, so that there can be no recognition in this case. When using very long-focus lenses (focal length greater than 100 mm) problems also arise:
• 1. Greater sensitivity to focusing accuracy, especially with the aperture fully open. Depth of field is shown with full force.
• 2. Cameras with such lenses should be mounted on massive bases, in order to exclude mechanical and wind vibrations that appear in jitter
Images.
• 3. Meteorological visibility conditions (haze, precipitation) and even fluctuations of heated air layers begin to influence the image quality.
So such lenses should be used very carefully. You should also take a responsible approach to the decision to use a lens with a zoom lens (optical zoom). It should be immediately noted that using the zoom lens to solve the “Who came there?” Task (ie, first look at which car, and then read its number) is waste. It is better to immediately take two cameras - one with a wide-angle lens, the other with a long-focus lens, it will be much cheaper.
Type of photosensitive matrix video camera (applies to both analog and digital).
Basically there are two types of matrices: CCD and CMOS. The main difference between them is the cost of production. Because of the relative cheapness in CMC cameras, they are much more often used. The quality and the first and second matrix give the same in daylight, however, if there is insufficient lighting, the CMOS-matrix noticeably lose the CCD matrix.
Auxiliary parameters
Like all semiconductor devices, the video matrix has a saturation mode when all free charges in the system are used and the total charge acquired by the unit cell ceases to depend on the intensity of the light incident on it. This mode of operation is called “flare” of the video matrix and, of course, it is unacceptable. To avoid this effect, modern cameras have the ability to change the charge reading time using a special electrode built into the video matrix - the "electronic shutter".
It helps the camera to adapt to the conditions of increased equipment, reducing the time of charge accumulation (besides reducing the accumulation time, we improve the transfer of images of fast moving objects). The range of the electronic shutter is indicated in seconds (similar to the camera's shutter speed) and currently ranges from 1/50 to 1/100000 seconds.
It must be emphasized here that for outdoor applications it is advisable to use lenses with automatic adjustment of the diaphragm, since the range of illumination changes in outdoor conditions can be 10 5 - 10 6 times.
The signal-to-noise ratio is measured in decibels (dB) and characterizes the purity and stability of the image. If this parameter is more than approximately 45 dB, a clear and sharp image is observed on the monitor screen; if it is smaller, then noises appear in the form of "snow" across the screen field, and if the value is less than 30 dB, it is almost impossible to make out anything because of noise. It should be noted here that the larger the format of the video matrix, the better, ceteris paribus, the signal-to-noise ratio, since the charge accumulation area is larger.
Automatic gain control (AGC) is the property of the camera amplifier to change its gain depending on the level of the video signal. The maximum gain increase is called the depth of the AGC. Usually this value is about 10 - 20 dB. It should be remembered that no amplifier can improve the signal-to-noise ratio, because together with the signal, noise is always amplified at the same time.
If you observe an object illuminated from behind by a bright light, the camera adjusts its parameters to a large integrated illumination and the object itself will be a dark spot without a well-defined internal structure, which will markedly reduce the effectiveness of the observation. To exclude such situations in good cameras there is a special hardware function called backlight compensation. Different models can have a different algorithm for working out this situation.
In the simplest case, in the backlight compensation mode, the parameters of the camera are not to the integrated illumination across the entire field of the frame, but to the illumination in its center.
Thus, due to some deterioration in the image quality of the environment, the image of the object itself is improved. In more complex models in different parts of the frame, adaptation to light conditions occurs independently of each other.
The operating temperature range of the camera is taken into account when choosing the installation location of the camera, usually the external cameras have a special housing design, and a larger temperature range of operating temperatures compared to the internal surveillance cameras.
The maximum effect of vibrations (accelerations) is especially important for cameras installed on moving objects, for example, on vehicles or aircraft.
The range of working pressures is especially important for chambers installed in mountainous areas or when installed on aircraft.
The ability to install in corrosive environments is important when installing the camera in industrial premises.
On a design: unpackaged, case (cylindrical or square), dome. Packageless video cameras have dimensions of approximately 25x25 mm, are supplied by the manufacturer without a housing and are mounted in interior items of a room that is guarded by a video surveillance system. Body cameras - supplied with or without lens. They are mainly used for indoor video surveillance, and for outdoor use a special thermal housing. They may have infrared illumination for working in the night mode, the built-in zoom lens is a lens that allows you to receive images of various scales at a constant distance from the video surveillance object. Dome video cameras are devices installed under the ceiling for video surveillance in offices and cottages. Depending on the model, they can be used both in warm and unheated premises or on the street, waterproof. May have a special cooling fan and heater. There are special models for installation in suspended ceilings.
Design options for camcorders

Modular cctv camera
They have, as a rule, dimensions from a matchbox, are supplied by the manufacturer without a case, and can be mounted in any interior items of a room that is guarded by a video surveillance system. In principle, the basis of almost any surveillance camera is such a module. Whether it is a standard camera, dome, street, zoom lens - if you disassemble it, you will find such a module inside.
 Cylindrical (Finger) CCTV Camera
Cylindrical (Finger) CCTV Camera
Surveillance cameras Minicylinder are probably the most common of inexpensive, but at the same time high-quality video cameras. They are distinguished by their diminutiveness, reliability, quite good parameters and favorable price.

Dome CCTV Camera
Usually represent a hemisphere, installed on the ceiling in the room. As a rule, this is a plastic case with a modular (bodyless) video camera integrated inside.

Video-eye
The video camera is made in a special case for installation and imitation of a video eye. As a rule, they have a very wide viewing angle - up to 180 degrees, which makes the image very distorted, and the image on the screen is almost round. But this is the same as in the ordinary door peephole.
 For hidden installation (pin-hall) CCTV camera
For hidden installation (pin-hall) CCTV camera
Pin-Hall Cameras they are distinguished by the smallest dimensions and are used for conducting covert video surveillance. There may be different versions, the most important thing here is the lens (this is called a pin-hall). Currently, such lenses are banned for importation and free sale on the territory of the Russian Federation, but many craftsmen continue to actively use them (not quite officially).

Vandal-proof CCTV cameras
Cameras with anti-vandal enclosures are ideal for video surveillance systems that are installed in places with large crowds. As a rule, anti-vandal video cameras of street performance and therefore they are suitable for use in different climatic conditions. Most of the anti-vandal cameras are made in the form of a dome or hemisphere, since this form protects the camera as much as possible from all sides. The case of domed vandal-proof video cameras is made of the impact of durable metal, it allows the camera to be resistant to external influences. Such cameras can withstand even a hammer blow to the body. Anti-vandal cameras are recommended for use as part of a video surveillance system for residential buildings, office centers, parking lots, stadiums, museums and other public places of objects.

Outdoor security cameras
Any video camera installed in an appropriate heated enclosure, or a special video camera originally assembled as suitable for outdoor use.

Case surveillance cameras
a separate device that can be used in various conditions, both inside and when using housings with heated outdoors. For the operation of this camera requires a lens. Another name - standard video cameras. Usually sold without a lens.

PTZ video cameras or high-speed, robotic, PTZ security cameras
Pivoting cameras are for outdoor and indoor use, which adds to their versatility. The peculiarity of these camcorders is that they can be controlled. In addition to the video camera itself, you need a control, it can be a program on a computer and a special remote with a joystick. PTZ cameras are also all different, they start with simple zoom lenses - a video camera, where you can remotely control only the lens and the internal menu, the next stage is the PTZ cameras - they add the ability to make small turns of the lens or the entire camera (~ 30 degrees), then speed, swivel video cameras - They already have the ability to turn on all 360 grams. horizontally and at least 170 gr. vertically.

Dummy cctv camera
A dummy camcorder, with its relative cheapness, in some cases, can be very effectively used to reduce the loss of shops and scare away potential intruders. As a rule, they are made in the form of a real video camera with a plastic case. Sometimes they are complemented by blinking LEDs, motion sensors and motorized controls.
Infrared lights (IR infra-red) are now the most popular elements for providing light for recording, they are more comfortable for observing eyes, they do not emit bright light.
Infrared illuminators with infrared illumination are used with might and main in modern security systems and really provide quality and round-the-clock surveillance.
Note that the video equipment market includes both cameras with built-in IR illumination, as well as individual IR-illuminators and IR-illumination. So autonomous infrared lights for cameras can be installed anywhere in the room and not necessarily near the surveillance camera itself.
The main task of the IR illuminators is to provide a full viewing angle for the cameras and the maximum range of illumination. The only thing that should not be with the IR illumination is the infrared rays that hit the lens of the camera itself, as this will simply cause the image from the camera to light up.
When choosing infrared lights for video cameras, users should pay attention to three main parameters of such highlights: wavelength, detection range and radiation angle.
If we consider the application of IR illuminators and IR illuminators, we can distinguish the most common cases of their use:
 - the use of a video-eye for apartments with infrared lighting, when, in the absence of illumination on the landing near the door, residents can still see what is happening outside the door;
- the use of a video-eye for apartments with infrared lighting, when, in the absence of illumination on the landing near the door, residents can still see what is happening outside the door;
- IR lights for covert surveillance of a warehouse or production premises at night, when there is an increased risk of theft from both employees and unauthorized intruders;
- IR lights for security cameras in nightclubs, cinemas and theaters, where you need to monitor visitors and what is happening, but there is no possibility to use the usual lighting of these rooms due to their specificity;
- IR lights and IR illuminators for video surveillance on the roads, when it is necessary to fix car numbers, but it is impossible to use conventional illuminators, since such lighting will simply dazzle drivers, which is unacceptable while driving.
Other technical terms:
| The DIS function (digital image stabilization) technology allows the surveillance camera to operate in vibration conditions. A surveillance camera, for example, in production, is very often subject to vibrations, with the result that the image is blurry. This feature prevents, or as far as possible, reduces this problem. | ||
| OSD - menu (On Screen Display). The fact is that at the factory, the parameters of the video cameras are adjusted to the average (optimal) position. But since, on many sites, the average parameters are not ideal, then when using cameras with the OSD menu, you can configure the camera to suit your conditions. In addition to the basic parameters (brightness, contrast, clarity, day / night, color, setting shutter mode, AGC, BLC, etc.) in the menu there are additional settings (motion detection, “name” of the camera, setting the hidden zones, etc.). Attention: if you set up using the menu camera so that the image has become unacceptable, use the setting Reset (reset manual settings and go to factory settings.) |
NUMBER OF DIAPHRAGM (APERTURE)
The number of aperture has the designation F and shows how fast the lens is. The lower this number, the more open the aperture, which means that the lens is adapted for shooting in low light conditions. Here you can draw an analogy with the human eye: the brighter the light in the room we are in, the smaller the pupil becomes, and, conversely, in poor light or at night our pupil expands to capture the most light.
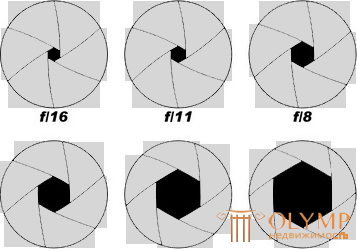
If you see the aperture value F = 1.2 in the lens parameters, we can safely say that this lens is fast, and it is great for video shooting in low light conditions, unlike, for example, the lens with aperture value F = 1.4, which is less suitable for shooting at dusk or at night.
In order to control the security of a large number of objects at the same time, digital surveillance cameras were created. In addition, the main positive quality of these surveillance cameras is the high quality of shooting. We know about the huge number of ways to handle video recordings that are made with digital video cameras. Through the use of a digital camera while monitoring a protected object, recording can be viewed in real time.
Cameras that use computer networks as the video transmission channel, and IP protocol. There are both standard features (signal resolution of 720 * 576) and improved (1600 * 1200 and higher). They have built-in WEB server and access restriction system. Viewing and archiving a video stream can be done both on a PC and using network servers (DVRs). There are models with WiFi network modules (radio network) and with GPRS (cellular) modules. The main output is RG45. It is also possible to transmit one or two way audio streams and camera control signals over the network.
Thus, IP cameras not only form the video signal, but also digitize it. Although it would be more accurate to say, it does not digitize it, i.e. The image in electronic form received from the matrix remains digital, only processed and compressed (in MPEG-4, M-JPEG, H.264, etc.) and transmitted over the LAN / WAN via the Ethernet port. Since IP surveillance cameras, as a rule, have a built-in web server, the image from them can be viewed in a standard web browser window (Internet Explorer). The video quality that the first digital cameras gave left much to be desired, and the assortment included only stationary color cameras, so many installers preferred to use analog cameras connected via video servers. Currently, for almost any analog camera, you can find a full replacement from the group of IP-cameras.
A network of video surveillance based on IP cameras can be easily deployed on the basis of an existing computer network, without requiring investments in additional infrastructure.

In video surveillance systems, video recorders, almost universally, replaced video recorders and quadrants that were previously used for this purpose. Now the main competitor of video recorders in video surveillance systems are video servers based on computers.
DVRs are mass-produced by many enterprises. Common types of DVRs are PC-based, that is, PC-based systems (for example, AceCop, AverMedia, Cyfron, Domination, DSSL, Goal, ISS, ITV | AxxonSoft, UnitECO, Videonet
Video surveillance recorders or as they are also called DVR, are recording devices for video cameras. DVRs have the function of a multiplier, or the so-called quad, in addition, they can act as a VCR, motion detection and similar components of the shooting. Surveillance cameras that have been produced recently have a network interface. With this component of video surveillance, the captured information is transmitted over IP to a personal computer for the necessary further processing. In the form of a recording device in a video surveillance camera, special software or a video capture card can be used. But at the same time the image recording can have limited volumes that correspond to the size of the hard disk.
Network Video Recorders (NVR) are used to record video in a digital format to a hard disk drive (HDD). They typically receive video from IP surveillance cameras over an Ethernet network using Cat5 or Cat6 cables. They are mainly used for physical security. A set of IP video surveillance cameras and NVR NVR will be expensive, however, it will provide much higher resolution and excellent video clarity compared to using analog DVR DVRs and analog video surveillance cameras. Some IP surveillance cameras have resolutions up to 5 megapixels. The range of equipment is not a problem - IP surveillance cameras can be located anywhere, the main thing is that they have access to the network.
Analog Video Recorders (DVRs) are also used to provide hard disk (HDD) recordings of video in digital format. They typically receive video from analog surveillance cameras via coaxial cables. They are usually also used to ensure the security of a facility or territory. This combination is more cost effective and easier to customize, but the resolution of video is usually limited to the D1 format (720 × 480). In this case, the distance is a limitation, since analog cameras cannot be installed any further 700-1000 meters from the analog DVR DVR without visible deterioration in video quality.
Hybrid professional video recorders (HVR) are also used to record video frames in digital format on the hard disk (HDD). It can connect both IP video surveillance cameras and analog video cameras, and receive video over Ethernet via Cat5 / Cat6 cables from network video cameras, as well as through the use of coaxial cables connected to analog video cameras. Hybrid DVRs are mainly used in large-scale security systems. This option will be a good choice when planning the future conversion of an analog video surveillance system to an IP video surveillance system, while existing analog video surveillance cameras can also be used and incorporated into the system.
The main characteristic of DVRs is its consolidated functionality (simplex, triplex, pentaplex)
The simplex recorder will ONLY execute any one function. For example, recording, or playback of recorded.
Duplex - simultaneously performing two functions. For example, during recording, you can view previously recorded information.
Triplex DVR (from the Latin. Triplex - triple) is a DVR that can simultaneously perform three functions.
For example, he may at the same time record a new video, show archived material and perform another additional action. Often the third function of such a DVR is the ability to transfer the stored video over the network or record it to media. Triplex video recorder is convenient to use in video surveillance, if several operators are watching the object at once. Then one of them reads the video directly from the security cameras, and the others get it over the network.
Pentaplex - (Pentaplex or Pentapleks) is one of the characteristics of a digital recorder, indicating that the recorder can perform five independent functions at the same time: monitoring, recording, viewing the archive, archiving, and networking at the same time.
Autostart recording
The function automatically start recording DVR. almost all DVRs have this function, it is used in case of resumption of power supply after its termination.
Weight
The weight of the DVR. important when choosing an installation location and mounting option.
Event recording time
It is possible to record alarm events in a separate file that can be easily found.
Operating time from the built-in or external battery.
The battery life of the recorder (from the built-in battery, if any) in the video recording mode.
Most often, an external battery pack is installed for the DVR
HDMI output
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) - an interface for transmitting high-definition video and multi-channel audio in digital format. HDMI connector is on most modern digital TVs.
Using HDMI, you can connect the DVR to a TV or monitor and watch a video on it.
Audio output
There is a separate connector for audio output from the DVR to an external device. Usually used when connected to a TV or monitor, when you need to play the sound recording on external speakers or headphones.
Video composite output
Using the composite video output, you can connect the DVR to almost any TV. However, please note that it is not possible to transmit high definition video using a composite cable. For these purposes, you should use HDMI.
Motion detector in the frame
Motion detection allows the DVR to detect the presence of any movement in the frame on a particular channel. In the absence of movement, the DVR will not record from this channel, but will start recording as soon as it records movement in the frame. This feature makes it more economical to fill the hard drive and save only important events.
The duration of the gap recording (from 2 to 4 s)
DVR recording video in cyclic mode saves video clips with a duration of 1-45 minutes each. It takes time for the registrar to save the file and start recording the next one. Such pauses (recording gap) are usually 1-4 seconds. If at this moment an abnormal situation occurs, the DVR will not record this event.
Obviously, the shorter the recording gap, the better. It is worth noting that manufacturers of DVRs rarely indicate the value of this parameter.
Roller duration
DVR recording video in cyclic mode saves video clips with a duration of 1-45 minutes each. When the hard disk is full, the recorder deletes the oldest movie and writes a new one instead. Most DVRs allow you to choose the duration of the video.
Battery capacity
From the capacity of the built-in battery depends on the operation time of the DVR in offline mode without power from the external network.
Record time and date
Most DVRs record not only the events, but also the current time and date, the name of the channel. This information is overlaid in the form of subtitles on the video.
Event recording in a separate file or transfer to other devices
With this function, the DVR will save the video before, at the time and after the alarm event in a separate file, protected from deletion, there is also the possibility of transferring to a special connector for connecting to other devices.
Write file after power off
A DVR equipped with this function may continue recording if the mains supply suddenly disappears. In the event of an emergency when the mains power is turned off, some models of DVRs can continue to record the event, using the built-in battery as the power source.
Number of audio inputs (from 1 to 4 and more) and sound recording channels (from 1 to 4 and more)
Audio input is used to connect to the recorder external microphones.
Usually you can connect multiple cameras and multiple microphones to DVRs at the same time. Such a device allows you to record not only from different points of shooting, but also to record separately the sound from each microphone.
Number of video outputs from analog (or hybrid) video cameras (from 4 to 8 and more)
Some models of recorders are equipped with additional connectors for connecting external cameras. Each external camera records its event on a separate channel. The “number of recording channels” just tells us exactly how many channels are provided in the recorder
Number of alarm inputs / sensors (from 1 to 7 and more)
Alarm inputs are used to connect various sensors that tell the recorder about a sudden change in the situation. On a signal from one or several sensors, the recorder starts recording the event. A handy thing, but you need to pay attention to the delay from the moment the signal arrives before the video starts, if it is more than a second, then all significant events can be skipped.
Number of monitors connected
for managing and watching videos from online mode in OnLine mode and in recording.
Video compression
Flash (also supports moving JPEG images)
H.261
H.263
H.264
MNG (supports moving JPEG images)
Motion jpeg
MPEG-1 Part 2
MPEG-2 Part 2
MPEG-4 Part 2
Ogg Theora (distinguished by a lack of patent restrictions)
Sorenson video codec (English)
VC-1 - an attempt by Microsoft to release an open specification for WMV format
One of the most common are Motion JPEG, MPEG-4 and H.264. Each of these video encoding formats has its own characteristics.
The main advantage of video compression Motion JPEG is the ease of implementation, which makes MJPEG suitable for use in devices with limited computing resources. This compression method allows for extremely fast non-linear video editing. If any frame is taken entirely from one MJPEG source, it can be written to the output MJPEG stream as it is, without decoding-compression, which significantly affects the amount of disk space. For example, on a recorder with such a recording format on a 250 Gb hard drive on 4-color cameras with maximum quality, 8-10 hours will suffice.
MJPEG gives high-quality still-frames, which allows using it, for example, in video surveillance systems to determine the number of a passing car. The disadvantages of MJPEG are a lower compression ratio than streaming compression methods, such as MPEG-4.
MPEG-4 is an international standard used primarily to compress digital audio and video. It appeared in 1998, and includes a group of compression standards for audio, video and related technologies approved by ISO - International Organization for Standardization (IEC Moving Picture Experts Group). The MPEG-4 standard is mainly used for broadcasting (streaming video), recording movies on CDs, video telephony (videophone) and broadcasting, which actively use digital video and audio compression.
This format is very complex, and the quality of its compression can be different, based on the system of codecs that it uses to record video streams. In video surveillance systems, it is the most common recording format. Its main advantage is the ability to record an even greater amount of information, unlike MJPEG. For example, on a 250 gb of disk space when recording 4 color cameras you can record approximately 100-140 hours.
The H.264 / AVC / MPEG-4 Part 10 standard contains a number of new features that allow you to significantly improve the efficiency of video compression compared to previous (such as ASP) standards, while also providing greater flexibility in application in a variety of network environments. The H-264 format is a modern compression standard, and is now being universally introduced in security television systems. It has a higher image quality compared to MPEG-4: the image has no blurred and so-called blurry “squares” (artifacts), the image is sharper and more contrast. With all these advantages, disk space is also saved.
Sound compression
MP3 - Defined by MPEG-1 specification
Ogg Vorbis (distinguished by a lack of patent restrictions and higher quality)
AAC, AAC + - exists in several variants defined by MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 specifications, used, for example, in Apple Computer
eAAC + - a format offered by Sony as an alternative to AAC and AAC +
Musepack
WMA - Microsoft Property
ADPCM
ATRAC (Eng.)
Dolby AC-3
DTS
MP2 (English)
VQF
Design
On sale come across several options for the design of the DVR. Fortunately, they are standardized and there are no surprises to expect even from the Chinese.
Maximum video resolution
The maximum resolution with which the recorder is recording.
Resolution refers to the number of points in the frame horizontally and vertically. Together with the frame refresh rate, the resolution determines the quality of the resulting image. The higher the resolution at the maximum possible number of frames per second for a given DVR, the better the shooting, the more details in the frame can be clearly distinguished. Therefore, we recommend choosing a recorder to pay attention to the frame refresh rate at maximum resolution. The formula for high quality shooting is simple: 1280 resolution at 720 or 1920 at 1080 at 30 fps - the picture quality with these parameters will be excellent.
Maximum frame rate (from 15 to 120 fps)
The maximum number of frames that the recorder can record in one second.
Immediately to the point: a good video is obtained at a frame rate of 24-30 fps. Anything below will give you only a general idea of what is happening, a theater of colored shadows and no more. Be sure to take this into account when choosing a registrar.
Maximum size of supported hard disk (from 2 TB) and connector option
Different DVRs are able to support hard drives with different maximum capacity.
Supply voltage
Typically, a standard European power supply 220 V (160-280 V), 50 Hz, 12 V is used to connect a possible external battery.
Timer shutdown
Among the DVRs there are DVRs with a useful timer-off function. You choose what time after switching on the power from the built-in battery to stop recording. This feature is designed to save power on the built-in battery of the DVR or external battery.
Battery powered
The possibility of power from the built-in battery.
A number of manufacturers complete their recorders with built-in batteries. This layout allows you to record after turning off the external fist.
Ethernet LAN connection, DHCP server
the local IP address is named for the device on which it will be available in the local network
Connect to the global WAN
The device can connect to the Internet without a router, t. has a router function
Remote control
Remote control. Significantly facilitates the setup of the recorder. With the remote you can not only configure all the necessary functions of the recorder, but also control the viewing of recorded clips.
Working temperature
The temperature range in which the recorder will be guaranteed to work.
The DVR is a complex electronic device that has its own temperature limits for storage. It can not be refrozen and can not be overheated. Keep this in mind if you want to install it in the sun or in the cold.
Recording mode
The mode that the recorder uses when recording a video file. There are two modes: cyclical and continuous.
Continuous recording is conducted without pauses and stops, in one file, as long as free space remains on the hard disk. When the entire hard disk is full, recording stops.
Loop recording splits video into chunks. In this mode, video is recorded in small sections of 3-45 minutes each. When the entire memory is full, the earliest file created is deleted, and recording continues. The main drawback of loop recording is the presence of a pause of several seconds between the end of one video and the beginning of another. When choosing a recorder, pay attention to the length of the recording gap. It is highly desirable that it does not exceed 3 seconds.
Installing a hard disk or flash memory
Ability to install an internal hard drive. On this coin, almost all DVRs allow you to connect inside the hard drive.
Not to be confused with connecting an external drive.
The hard drive is used to store recorded videos. . However, the sensitivity of hard drives to mechanical stress casts doubt on the appropriateness of their use in mobile objects, for example, on vehicles or aircraft.
For moving objects, it is preferable to use SSD drives or flash memory.
Battery format
Sizes.
Recording format
The file format that the DVR uses when recording a video.
The most popular formats are: AVI, MOV and MP4.MPEG Some DVRs use their own format to store video.
Hard drive formatting
The ability to format the hard disk directly in the DVR.
Formatting allows you to delete all files in seconds.
FTP copy or remote access function
The ability to copy the selected video from the memory of the DVR to a remote server.
Editing function
The ability to cut a short segment of the roller, using the program inside the recorder or CMS. The resulting segment is saved as a separate file.
Frame rate at max. resolution (from 5 to 60 fps)
Maximum frame refresh rate at maximum video resolution. Good video is obtained at a frame rate of 24-30 fps. By reducing the frequency to 10-15 fps, the movement on the screen becomes jerky and sharp.
Most IP cameras or DVRs work correctly only with Internet Explorer (IE), which Microsoft itself has already refused. And even when used in IE, there and then there are problems with incorrect operation of a particular camera function, which forces the use of alternative proprietary software of the DVR. Which is called a content management system (CMS, Content Management System).
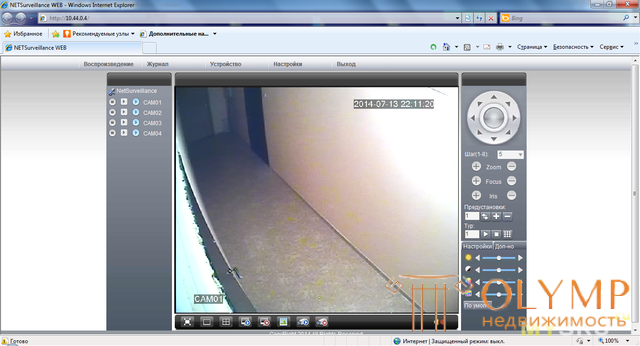
an example of a web interface for access control dvua DVR
CMS software is usually completely free of charge delivered with a DVR, HVR or NVR recorder. And allows using a PC to do things that the registrar himself is “too tough”. Thanks to the CMS, the user can work with the registrar from anywhere in the world, if only the Internet is at hand. CMS allows you to combine dozens and even hundreds of recorders into one system, forming a large-scale network of video surveillance. Moreover, the CMS makes it possible to integrate video recorders of completely different manufacturers into a single surveillance system. To ease the load on the network, CMS offers the ability to view an additional video stream at a much lower bitrate, and also to play back video streams only from cameras of interest, not all in a row. At the same time, video and screenshots can be recorded on the hard disk of a computer that works with the CMS, plus it is possible to work with the archive of the DVR itself - you can view the records stored there and transfer them to a PC hard disk, for example, for backup. CMS also keeps an event log.

Additionally, the CMS allows you to adjust the brightness, contrast and color rendition of the image, regulate the parameters of the cameras and recorders, control the PTZ cameras using a computer mouse. Naturally, access to the CMS program is password protected. Therefore, only authorized users can use it. Moreover, the CMS password is completely independent of the password of a particular registrar.
With the help of third-party commercial software, for example, such as Hunter 3, additional functionality is available for the video surveillance system: vehicle license plate recognition, vehicle registration in the parking lot or parking, counting items on the production conveyor, face recognition, bills, etc.
Video surveillance can be easily integrated into the alarm system and access control. For example, if the organization is not poor, it is possible to combine the video with the access control system: during the passage through the checkpoint with an electronic key, a video or photo fixation of the person takes place and the record is entered into the access database, making sure that the access card has been used right, not a stranger.
If you are going to browse through the Internet (including from wireless devices), you must first connect the Internet in this room. Internet should be wired. The speed of the Internet channel is only important to reverse (Upload): do not forget that in advertising brochures, providers often indicate only direct (Download) channel speed - it does not matter to us. The greater the upload speed, the greater the number of frames per second you will receive when viewing. The minimum required is from 0.5 to 2 Mbps for each video camera. It is also necessary to connect the service “Direct (white, external and static) IP-address + open ports to your provider.
The choice of location for the cameras must be made so that the cameras are located as high as possible. This is necessary so that the cameras are directed ("looked") down, not sideways, or, especially, upwards - as this will lead to strong glare from light sources.
However, if it is important for you to recognize faces or to see them clearly, then it is better to position the camera at a level of 1.5–2 m from the floor and direction to the side, that is, at the level of people's faces.
For the same reason, cameras are usually mounted near windows - so that the camera “looks” from the window; the worst case is the location of the camera on the wall or in the corner opposite to the window when the camera “looks” at the window. By the way, notice how the camcorders are mounted in various other places. Provide illumination of the scene, especially when using HD cameras: without it, the advantages of HD pictures will not be so obvious, even to the absence of a noticeable difference. Regular office artificial (electric) lighting is enough for ordinary (non-HD) devices to work. For showrooms, exhibitions and aesthetically significant installations using HD cameras, be sure to apply additional lighting. We can say that the lighting is already enough, if the additional lighting does not lead to an increase in the detail of the picture. Daylight (solar) lighting is usually sufficient for the operation of any type of camera.
Any video camera, like a camera, is strictly forbidden to be directed to the Sun: the camera will be damaged, and such a case is not guaranteed.
Also in special cases, an anti-vandal grille is installed on the outdoor video camera.
Video server or DVR should be located in a place that excludes its use as a normal office computer or as another device. If there are several options for its location, select the most equidistant from all intended video cameras. It is forbidden to place equipment in a cabinet (except for special ventilated racks for IT equipment). The equipment should be located in a heated room on a stand with a height of 0.2 to 0.8 m from the floor. The power supply must provide for grounding in accordance with the EMP (Electrical Installation Regulations). In the CIS countries, there are slightly different rules, so study them before connecting the server power supply yourself.
Cables are laid and connected according to the enclosed instruction. If necessary, cables are extended and terminated (“crimped”) as well as regular cables (twisted pair) for a local network. When laying kaoksialnyh cables, you must not exceed the maximum radius of curvature, and for kaoksialnyh cables and for twisted pair does not exceed the maximum length. Cables should have a secure mounting, very preferably crossing cables with power lines, or other high-frequency devices, for example, this can adversely affect the quality of the audio or video signal.
As a rule, after the design and installation of the video surveillance system, the settings are added to it.
a) setting the focal length of the video camera - if the camera allows it and this setting is manual (mechanical)
b) setting the sensitivity of the camera - if there is such an opportunity
c) tuning and checking the microphone - if it is used
d) setting the IP address of the video camera or DVR, or setting up an Internet connection directly on the video camera or DVR if the router does not use a local network. if remote surveillance is planned, then a stable transfer rate of at least necessary with a static white IP address with open ports must be provided. If a static order is not possible then you will have to use the DynDNS service or nalogically.
e) setting up using the web interface or CMS additional functions, time and video recording parameters, the ability to transfer data to a remote FTP server, setting up a zone and time of motion recognition, with the possibility of generating a signal for a signaling system, setting access rights to the system, etc.
As a video server, a regular computer with special capture video cards and special software can be used, which provides maximum flexibility in the functionality of all video surveillance systems, recognition of persons, autonumbers, etc.
There are various options for solving the client's problem. The search for the most optimal solution leads to the use of non-standard and non-typical solutions of typical problems. The system presented in this typical solution should be used in the following cases:
An example of implementation of the video surveillance system for 8 IP cameras with a connection of 8 analog cameras (hybrid server)
The system consists of a hybrid video server VIDEOMAX-IntLt (IP8) -8-25-4000-19 "-4CIF-ID3 with Intellect Light software installed.
As the active equipment, the switch is used by one of the leading companies in the field of network technologies Allied Telesis (Japan).
LTV analog and IP cameras are used as image sources, which have gained popularity due to good quality indicators and low prices.
The video server, switch, backup power sources and switching devices are installed in a 19 "communication rack. The rack must be located in a protected room (server room) with limited access. Also in the server room it is necessary to ensure the temperature conditions necessary for the correct functioning of the equipment.
The video stream from analog video cameras goes to the switching panel with the protection of the video signal VIDEOMAX-UZV-01. The panel is intended for switching video signals from security surveillance television cameras from BNC inputs to DB25M outputs and protecting transmitting and receiving equipment from
From the panel, the video stream enters the video server, where it is digitized with the parameters specified in the settings and then stored.
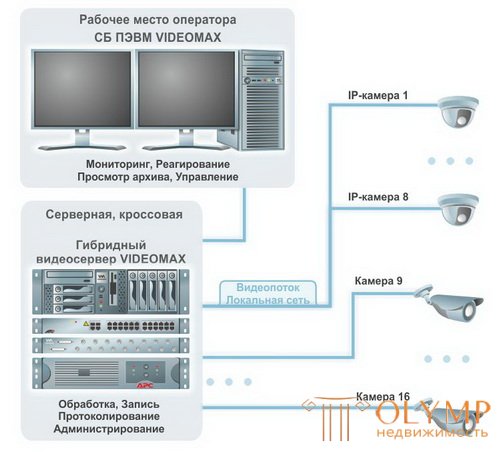
Data from the IP camera enters the switch and then to the video server, where it processes, transfers to the Remote workstation and stores.
Viewing cameras in real time and working with the archive is carried out from a remote operator’s workplace, which is made on the basis of a personal computer SB PC VIDEOMAX-URM with the connection of two monitors.
The system can be equipped at any time with any number of remote workplaces. For example, it is possible to organize an additional workplace for system administration by a security chief or an IT specialist responsible for operating the system.

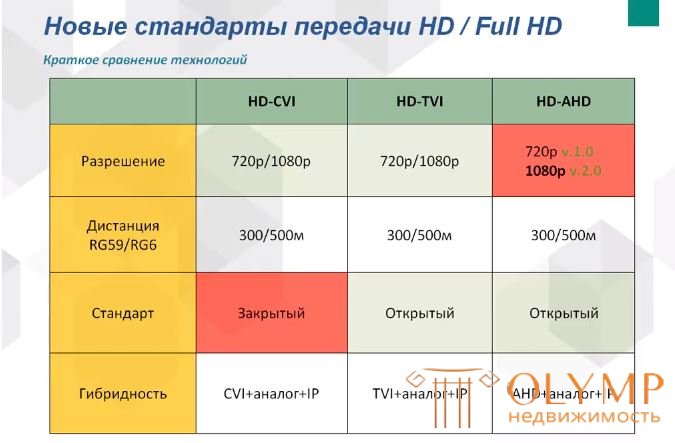
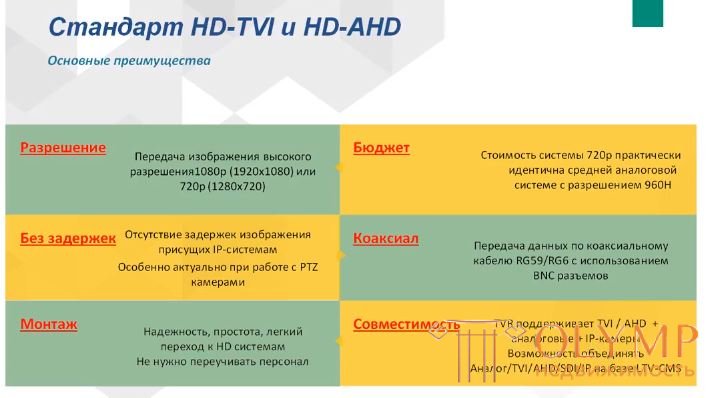
There are three leading companies in the world that produce approximately, in terms of signal quality, the same solution. This is Dahua with its HD-CVI format, Techpoint in collaboration with HIKVISION with the HD-TVI standard and nextchip with the HD-AHD standard. These new formats allow us to transmit over cable lines, over a coaxial cable in particular, signals of the HD format 1 megapixel, or Full HD up to 2 megapixels. There are already developments with the transfer already up to 5 megapixels, but so far they have not yet arrived at our market. We transmit the analog signal in each of these formats (well, it cannot be called analog, that is, there, as it were ...). That is, each of the manufacturers does not quite reveal what its signals are encoded / decoded in and in what format, in its own way, it is a commercial secret, but these signals differ in frequency, these standards are not compatible with each other. That is, a TVI format camera will never work with a recorder that supports only HD-CVI, and also HD-AHD will never work with HD-TVI and HD-CVI formats only if these recorders do not support each other formats. if there is no possibility to switch. With each other, they are not fully compatible. At the same time, the transmission range increased with everything: if in the good old PAL we could throw 100 meters of a good cable, under ideal conditions, I don’t know, there are 120, in some cases, a good cable, now with RG59 we can Throw a signal to a distance of 300 meters, and when using the RG6 - 500 meters. What advantages does this give us? We can use old cable lines to replace the objects for image optimization, which previously did not exceed 100 meters, and even if they are laid by some very cheap Chinese cable that does not pull up to 300 meters or up to 500 meters, it will be 100 meters not critical, and it will be an easy way to go from the good old PAL.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)