Calculation of electrical wiring involves the determination of the required cross-section and brands used wires and cables. Ultimately, electrical wiring made from selected materials must comply with fire and electrical safety standards.
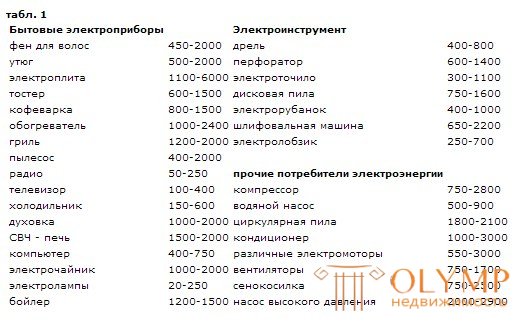
To determine the cross-section of the input power cable, it is necessary to calculate the total power of all energy consumers planned for use (household electrical appliances, heaters, electric boilers, stoves and ovens, lighting fixtures), and multiply it by a factor of 1.5. Even better - by 2, to create a margin of safety.
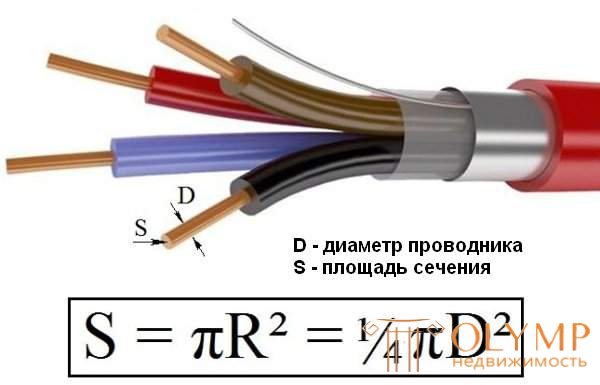
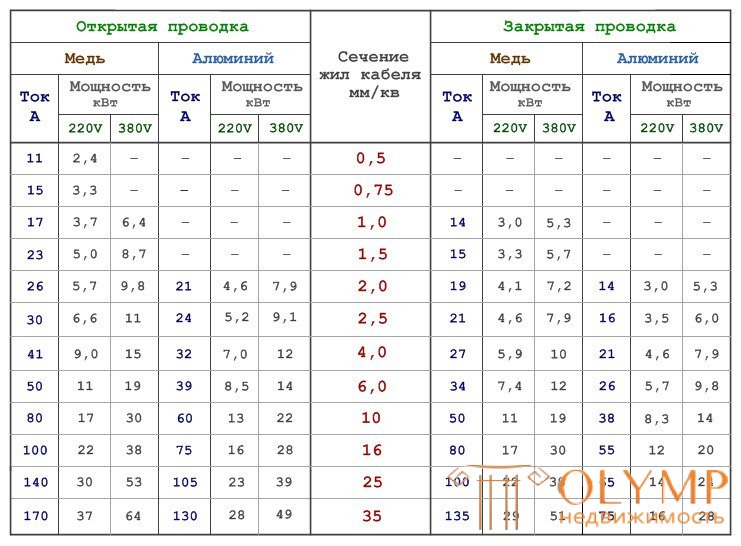
The electric current passing through the conductor (the larger it is, the greater the power of the powered appliance) causes the conductor to heat up. Allowed for the most common insulated wires and cables heating is 55-75 ° C. Based on this, the cross section of the conductors of the input cable is chosen. If the calculated total capacity of the future load does not exceed 10–15 kW, it is sufficient to use a copper cable with a cross section of 6 mm2 and aluminum - 10 mm2. With an increase in the power of the load, the double section is tripled. These figures are valid for single-phase open laying of the power cable. If it is laid hidden, the section is increased by one and a half times. With three-phase wiring, the power of consumers can be doubled if the gasket is open, and 1.5 times with hidden gasket.
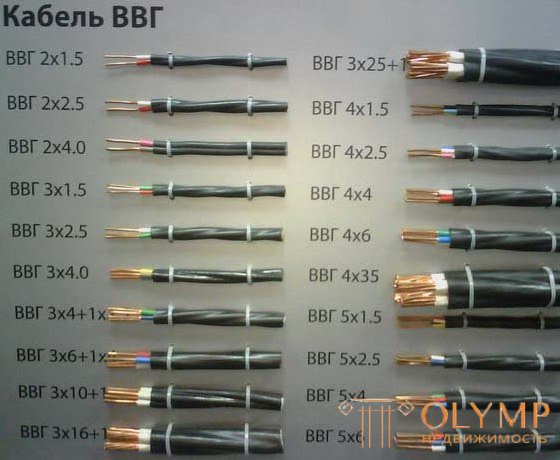
For electrical wiring rosette and lighting groups traditionally use wires with a cross section of 2.5 mm² (sockets) and 1.5 mm² (lighting). Since many kitchen appliances, power tools and heating appliances are very powerful consumers of electricity, they are supposed to be powered with separate lines. The following figures are guided here: a wire with a cross section of 1.5 mm² can “pull” a load of 3 kW, a cross section of 2.5 mm² - 4.5 kW, for 4 mm² the allowable load power is already 6 kW, and for 6 mm² - 8 kW .


The choice of cable and wire cross-sections is a mandatory and very important point when installing and designing the layout of any electrical installation.
For the correct choice of the power wire cross-section, it is necessary to take into account the value of the maximum current consumed by the load.
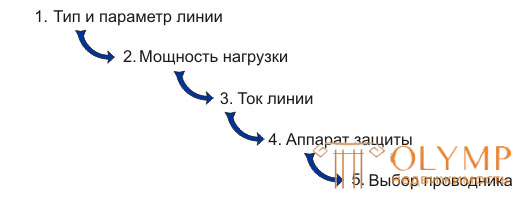
In general, the order of selection of the power supply line can be determined as follows:
When installing capital structures for the installation of internal power networks, it is allowed to use only cables with copper conductors (ПУЭ item 7.1.34).
Power supply of power consumers from the 380/220 V network must be performed with the TN-S or TN-CS earthing system (PUE 7.1.13), therefore all cables supplying single-phase consumers must contain three conductors:
- phase conductor
- zero working conductor
- protective (grounding conductor)
The cables supplying three-phase consumers must contain five conductors:
- phase conductors (three pieces)
- zero working conductor
- protective (grounding conductor)

The exception is the cables that supply three-phase consumers without output for the neutral operating conductor (for example, an asynchronous motor with a k. S. Rotor). In such cables, the neutral conductor may be missing.
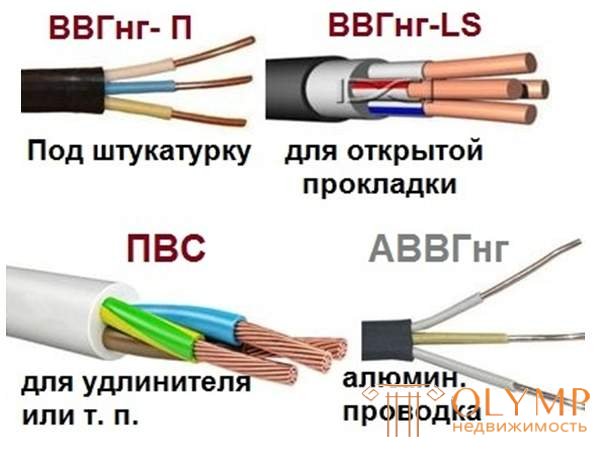
Of all the variety of cable products on the market today, only two types of cables meet strict electric and fire safety requirements: VVG and NYM.
Internal power grids must be made with a flame-retardant cable, that is, with the “NG” index (SP – 110–2003 p. 14.5). In addition, the electrical wiring in the cavities above the suspended ceilings and in the voids of the partitions should be with reduced smoke emission, as indicated by the “LS” index.
The total load capacity of a group line is defined as the sum of the capacities of all consumers in this group. That is, to calculate the power of a group lighting line or a group socket line, it is necessary to simply add up all the powers of the consumers in this group.
The values of currents are easy to determine, knowing the consumers' passport capacity by the formula: I = P / 220.
1. To determine the cross-section of the input power cable, it is necessary to calculate the total power of all energy consumers planned for use and multiply it by a factor of 1.5. Even better - by 2, to create a margin of safety.
2. As is well known, the electric current passing through a conductor (and it is the greater, the greater the power of the powered electrical device) causes the heating of this conductor. Allowed for the most common insulated wires and cables heating is 55-75 ° C. Based on this, the cross section of the conductors of the input cable is chosen. If the calculated total capacity of the future load does not exceed 10–15 kW, it is sufficient to use a copper cable with a cross section of 6 mm2 and aluminum - 10 mm2. With an increase in the power of the load, the double section is tripled.
3. These figures are valid for single-phase open laying of the power cable. If it is laid hidden, the section is increased by one and a half times. With three-phase wiring, the power of consumers can be doubled if the gasket is open, and 1.5 times with hidden gasket.
4. For electrical wiring rosette and lighting groups traditionally use wires having a cross section of 2.5 mm2 (sockets) and 1.5 mm2 (lighting). Since many kitchen appliances, power tools and heating appliances are very powerful consumers of electricity, they are supposed to be powered with separate lines. Here they are guided by the following figures: a wire having a cross section of 1.5 mm2 can “pull” a load of 3 kW, a cross section of 2.5 mm2 is 4.5 kW, for 4 mm2 the allowable load power is already 6 kW, and for 6 mm2 it is 8 kw.
Knowing the total current of all consumers and taking into account the ratio of the permissible current load wire (open wiring) to the wire cross section:
- for copper wire 10 amps per millimeter square,
- for aluminum 8 amps per millimeter square, you can determine whether the wire you have is suitable or if you need to use another.
When performing hidden power wiring (in a tube or in a wall), the reduced values are reduced by multiplying by a correction factor of 0.8.
It should be noted that open power wiring is usually performed with a wire with a cross section of at least 4 mm2 on the basis of sufficient mechanical strength.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)