General characteristics of the Gothic architecture

Amiens Cathedral
A peculiar Gothic style in architecture took shape in the north of modern France, in the province of le de France, as well as in the territory of modern Belgium and Switzerland. Somewhat later - in Germany. There is evidence that already at the beginning of the XII century. The masters of Saint-Denis Abbey near Paris, under the leadership of Abbot Souzher, began the development of a new design of a typically Gothic pointed arch. The church of the monastery of Saint-Denis, designed by the abbot Sugieria, is considered the first Gothic architectural structure. When it was built, many of the pillars and internal walls were removed, and the church acquired a more graceful appearance compared to the Romanesque “fortresses of God”. In most cases, the chapel of Saint-Chapelle in Paris was taken as a sample.
From the Romanesque style Gothic inherited the primacy of architecture in the arts and the traditional types of religious buildings. A special place in the art of Gothic took the cathedral - the highest example of the synthesis of architecture, sculpture and painting . Unlike the Romanesque style with its round arches, massive walls and small windows, Gothic features arches with a pointed top, narrow and tall towers and columns, an ornate facade with carved details (vimpergi, timpans, archivolts) and multicolored stained-glass windows with lancers. All elements of style emphasize the vertical.

Chapel of Sainte Chapelle
The cathedral as a central phenomenon of the Gothic style was the focus of all types of artistic activity in their aggregate manifestation: architecture, painting (stained glass and painting), music and literature (liturgy and preaching). Also, the cathedral was the most important center of life of a European city, besides the church service, university lectures, theatrical performances were held there, sometimes the city council and the royal parliament met. The cathedral, in contrast to the Romanesque church, is a city building: contrasting with the small surrounding buildings, it dominated the city. The first Gothic cathedrals appeared in Northern France, then the style became widespread. After the crusades, she was assimilated in Syria, on the islands of Cyprus and Rhodes. Christian princes of England, Spain, Germany adopted the Gothic as a sign-symbol of divine providence and monarchical power. Approved Gothic architecture and monastic orders.
The space of the cathedral, incommensurable with man, the verticalism of its towers and vaults, the subordination of sculpture to the rhythms of the dynamism of architecture, the multicolor shine of stained glass windows had a strong emotional impact on believers. Along with the divine service, theological disputes were arranged in it, the mysteries were played out, the meetings of the townspeople took place. The cathedral was thought of as a kind of knowledge (mainly theological), a symbol of the Universe, and its artistic structure expressed not only the ideas of the medieval social hierarchy and the power of divine forces over man, but also the growing self-consciousness of citizens. The grandiose Gothic cathedrals differed sharply from the monastic churches of the Romanesque style. They were roomy, tall, elegant, spectacularly decorated. The dynamism, ease and beauty of the cathedrals determine the character of the urban landscape.
The main difference of the Gothic cathedral is a stable frame system in which the cross-rib pointed arches, lance-shaped arches, which largely determine the inner and outer appearance of the cathedral, play a constructive role. The structure of the building consists of rectangular cells (grass), bounded by 4 pillars and 4 arches, which together with the arch-ribs form the core of the cross vault. The lateral spreading of the roof of the main nave is transmitted by means of supporting arches (arkbutans) to the outer pillars — buttresses. Freed from the walls in the gaps between the pillars are cut through arched windows.
Romanesque churches were clearly isolated from the surrounding space. In the Gothic cathedrals, on the contrary, a sample of the complex interaction, the interpenetration of the inner space and the external natural environment is given. This is facilitated by huge window openings, through-carving of tower tents, a forest crowned with pinnacles of buttresses. Carved stone ornaments were also of great importance: crucifers-fleurons; stone thorns, growing like flowers and leaves, on the branches of the stone forest of buttresses, archbutans and spiers of towers.
Following the cathedral rushed up and urban buildings. On the main square of the city built the town hall with a rich decor, often with a tower (Town Hall in Saint-Quentin, 1351-1509). The castles were transformed into stately palaces with rich interiors (the papal palace complex in Avignon), mansions ("hotels") of wealthy citizens were built.
The construction of the Gothic cathedral. The system of ribs, arcbutans and buttresses.
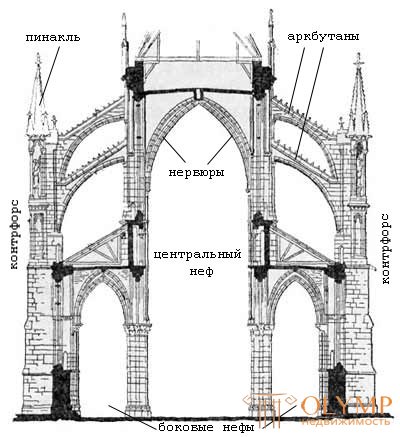
The construction of the Gothic cathedral
In the Gothic era, the organization of the construction business changed - urban lay artisans, organized in workshops, were built. Here technical skills were usually passed down from father to son. However, there were important differences between the bricklayers and all other artisans. Every craftsman - gunsmith, shoemaker, weaver, etc. - worked in his workshop, in a particular city. The artels of bricklayers worked where large buildings were erected, where they were invited and where they were needed. They moved from city to city and even from country to country; between the construction associations of different cities there was a community, there was an intensive exchange of skills and knowledge. Therefore, in Gothic there is no longer the abundance of sharply different local schools, which is characteristic of the Romanesque style. The art of Gothic, especially architecture, is distinguished by a great stylistic unity. However, the essential features and differences in the historical development of each of the European countries caused a significant uniqueness in the artistic culture of individual nations. It is enough to compare the French and English cathedrals in order to feel the big difference between the external forms and the general spirit of French and English Gothic architecture.
The surviving plans and working drawings of the grandiose cathedrals of the Middle Ages (Cologne, Vienna, Strasbourg) are such that not only compose them, but also to use them could only be well-trained masters. In the XII-XIV centuries. cadres of professional architects were created, whose training was at a very high theoretical and practical level.

Notre Dame de Paris Cathedral of Notre Dame ..
The transition from the Romanesque to the Gothic style is marked by a number of technological innovations, which in turn were stylistically understood in the history of the Gothic. The opinion is justified that the introduction of a pointed arch was the source of changes in architectural thinking: it had less spread - pressure on the wall, the load was directed downwards, onto the support. The basic principle of operation of the structure is as follows: the arch no longer rests on the walls (as in Roman buildings), now the pressure of the cross vault is transmitted by arches and ribs to the columns (pillars), and the lateral thrust is perceived by archbutans and counterforts. The cross rib arch was the main architectural discovery of the Gothic, it was used in conjunction with a system of internal abutments (columns or pillars) and external supports - buttresses. The Gothic buttress is a technical development and further improvement of the buttress of the Romanesque. As established Gothic architects, he worked the more successful than he was wider below. Therefore, the builders began to give the buttresses a stepped form, relatively narrow at the top and wider at the bottom.
It was not difficult to neutralize the lateral spread of the vault in the lateral naves, since their height and width were relatively small, and the buttress could be placed directly at the outer abutment pillar. Quite differently, it was necessary to solve the problem of lateral thrusting of the arches in the middle nave. Gothic architects used in such cases, a special arch of wedge stones, the so-called arcbutan; one end of this arch, thrown over the side aisles, rested in the sinuses of the arch, and the other - on the buttress. The place of its support on the buttress was strengthened by a turret, the so-called Pinnacle. Pinnacles are pinnacle-shaped pinnacles that are often of constructive importance. They could be simply decorative elements and already in the period of the mature Gothic were actively involved in creating the image of the cathedral. Initially, the arcbutan adjoined the arch of the arch at a right angle and perceived, therefore, only the lateral thrust of the arch. Later, the arkbutan began to be set at an acute angle to the sinuses of the vault, and he thus assumed a partial and vertical pressure of the vault.
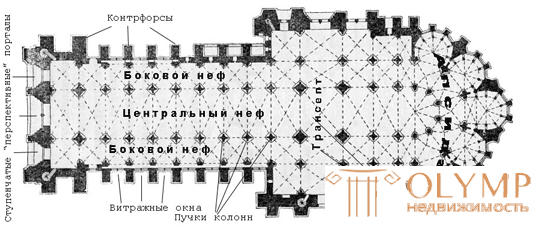
Plan of the Reims Cathedral.
Almost always built two tiers of arcbutans. The first, upper tier was intended to support roofs that became steeper over time, and therefore heavier. The second tier of the arkbutans also opposed the wind pushing the roof.
This innovation made it possible to greatly simplify the structure due to the redistribution of loads, and the walls turned into a simple light "shell", their thickness no longer affected the overall load-bearing capacity of the building, which allowed making many windows and wall paintings, for lack of walls, gave way to stained glass and sculpture . Lancet arches, which as the development of Gothic architecture is becoming more and more elongated, pointed, expressed the main idea of Gothic architecture - the idea of the aspiration of the temple up.

Interior of Reims Cathedral
In Romanesque cathedrals and churches, a cylindrical vault was usually used, which rested on massive thick walls, which inevitably led to a reduction in the building's volume and created additional difficulties during construction, not to mention the fact that this predetermined a small number of windows and their modest size. With the advent of the cross vault, the system of columns, arch-butters and buttresses, the cathedrals took on the form of huge openwork fantastic structures. The possible span of the vault determined the width of the central nave and, accordingly, the capacity of the cathedral, which was important for the time when the cathedral was one of the main centers of city life, along with the town halls.
The improvement of the technical side and the gradual expansion of the internal space led to the fact that the walls in the Gothic temple almost disappeared, replaced by huge windows that were filled with luminous panels of stained glass.
In conclusion, it is impossible not to note the quantity and quality of manual labor expended on the construction of Gothic cathedrals. Both the most important parts of the temple and the smallest details were performed with equal care. Cathedrals were not built for people, but for God, who sees everything. A common impulse united masons and sculptors, carpenters and glassblowers, masters of bronze casting and roofers - artisans with a capital letter, in their own spirit - real artists who have invested in their works and soul, and talent, and skill. Having emerged in the monastic environment, the Gothic style became the style of city cathedrals, which were erected by the inhabitants of the city at their own expense, thus demonstrating their independence. Therefore, the construction of Gothic cathedrals often stretched for several centuries, however, the original idea was not distorted. The most striking examples of such a "protracted construction" are the Cologne and Milan cathedrals, the first of which was built for 312 years, and the second - 470. By the time of their completion, in many European countries, in particular, in England and Austria, the current called neo-Gothic and developed on the basis of national romanticism. Delight, admiration for the ability of Gothic masters to "revive" the inert mass of stone, to make it live by the laws of organic matter, inspired such masters of architecture of the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries as Antonio Gaudi, even in the construction of his famous Sagrada Familius Cathedral in Barcelona pore not completed), repeating the experience of Gothic masters.
The most famous Gothic cathedrals:
- In France:
- - The church of the abbey of Saint-Denis (XII century);
- The existing frame system of the Gothic cathedral appeared in the church of Saint-Denis Abbey (12th century). The abbot of this monastery, regent and royal adviser, can rightly be called the "godfather" of the Gothic style. It was he who began the construction of the abbey of the patron and apostle of France abbot of Saint Dionysius (Saint-Denis). The temple was supposed to give importance and grandeur to the monastery as an ancient tomb of the French kings. Unfortunately, a detailed description of all stages of the construction of the temple, what now defines the essence of the Gothic style, has been lost. The temple built by Sugerim turned out to be "an amazing and continuous light that saturated the whole interior with beauty". Caring for the strengthening of royal prestige, Louis IX ordered that at least sixteen tombstones of French monarchs be renewed and rebuilt in Saint-Denis. These were complex structures either in the form of a canopy, resembling a Gothic cathedral, or sarcophagi with figures of saints around the perimeter. Often here used the motive of the funeral procession. The figures of the dead in the XIII century. stereotyped in their idealized elegant youthfulness; in the XIV century. they become more individualized, portrait features appear in the guise.
- - Cathedral in Chartres (XII - XIV centuries);
- The original building of the cathedral in Chartres was built in the XII century. The western facade of the cathedral was completed in 1170 and happily avoided complete destruction during the fire of 1194 (the rest of the building was destroyed). The transitional nature of architecture is clearly visible in the western facade. The early north tower (1134–50) has a foundation completely romance in spirit (the open-air tent crowning the tower was completed at the beginning of the 16th century). The central part of the facade has retained a heavy Romanesque wall, into which three portals are embedded, the rose window appeared later. The south tower, the so-called “old bell tower” (1145-65), is closer to the main ideas of the Gothic style: the verticals of the buttresses are picked up by the powerful take-off of the octahedral tent. After a fire in 1194, the building was rebuilt. The architects of Chartres thought of the building as a whole, subdivided into subordinate parts, between which there is a close connection. The interior reveals itself to the viewer as a consistent chain of contrasts and increasingly complex architectural rhythms that are given a clear and precise order. The wall has a three-part division of the arcade supports, triforii and windows. Service columns, rising from the base of the abutment, are collected in bundles in the second tier and ascend to the arches with an almost continuous movement. The architects were able to give the vertical weights a feeling of free and inspired lifting. Notre Dame in Chartres is considered to be one of the most beautiful cathedrals in Europe. Chartres - one of the few Gothic cathedrals of France, which has kept its glazing almost unchanged. This is the largest surviving ensemble of stained glass windows of the 12th — 13th centuries. Stained-glass windows, blind and almost colorless on the outside, revealed all their magic in the interior, when the sun's rays, penetrating through the colored glass, gave each paint the greatest sonority. The intangible light falling from the windows of the temple, in combination with the color painting of the vaults, vaults and capitals, gave rise to a special feeling of the environment in which each object magically transformed, introduced a special shade of jubilant radiance into the solemn and rapidly tense inner space of the cathedral. In the high windows of Chartres, stained glass windows of the XII century, with bright rich tones, side by side with a darker range of colors of the windows of the XIII century. The general lilac-pink tonality of the temple lighting is pierced on a sunny day by the flashes of red glass, in cloudy weather the immaterial blue shimmer dominates. The theme of the images in the windows of Chartres was extremely diverse. Along with scenes from the Old and New Testaments, the prophets and saints - about a hundred subjects from the lives of artisans who donated stained glass windows to the cathedral are presented in the lower part; one of the stained-glass roses is dedicated to the peasants. Mastery of performance, memorable power of the image stand out in Chartres windows with the image of the Mother of God (the Virgin of the “beautiful window”), the cycle “Life of St. Eustachey ", as well as the cycle" Charlemagne ". The sculptural decoration of the “Royal Portal” on the western facade of the cathedral was relatively well preserved. In the work of Chartres masters, universal human ideas came to the fore - a picture of the universe as a whole, the essence of the divine cosmos and the place of man in it. The consistent humanization of the sacred image, which touched primarily the spiritual world of the characters, began with the Chartres portal. Inner enlightenment characterizes the “ancestors of Christ” on the slopes of the “Royal Gates”.Thinly worked spiritualized faces, now tremulous and mentally open, sometimes closed and arrogant, sometimes severely focused, open up a long way for the gothic masters of the spiritual beauty of man to comprehend. The column statues in the hollows of the Chartres portals are included in the overall structure of the architectural image. On the one hand, they serve as a physical support, “pillars”, also in the figurative sense - in the allegorical and plot plan for the timpans and the New Testament scenes located in them. On the other hand, the elongated, internally tense figures of the “ancestors of Christ” are included in the rhythm of the vertical divisions of the facade. Due to this, the lines of force of architecture are filled with vital energy, and the spiritual power of man is compared with the universal scale outlined by architecture.From simple decoration and edifying commentary, the statue turns into a link of an inseparable, holistic imaginative system.
- - the Cathedral of Reims (1211-1330), the place of coronation of the French kings;
- A masterpiece of mature Gothic and “Academy of Arts” for medieval masters was the Cathedral of Notre Dame in Reims. The city in the heart of Champagne has long been the site of the coronation of French kings, and since 1179 this rite has been performed there constantly. Existed in the XII century. The basilica died in the fire of 1210. Construction of the new cathedral began immediately, as early as 1211, and lasted until 1481. The history of the cathedral in Reims is the story of several generations of architects. On the basis of the inscriptions of the "labyrinth", a complex mosaic floor ornament, the names of the architects and the stages of the construction of the grand building are known. The Cathedral in Reims, despite the long construction time, retained the unity of design: the variety of talents of architects and sculptors who worked here merged into a common, full of inspiration "stone symphony". The complexity of the development of the architectural theme is inherent in the western facade of the temple; individual motifs are intertwined, contrasted, complement each other. The mass of the building, heavy and inert at the ground, is becoming increasingly light and mobile as it rises. Deep portals with pointed arches and triangles of vimperg covering them begin. In the second tier, the stream is divided, decays in the center and acquires rapid dynamics on the sides: a round “rose” with a gentle arch over it is opposed by side windows that anticipate the victorious take-off of the towers, underlined by a short burst of vimperga between them. But the facade of the Reims Cathedral is permeated not only by vertical movement - it is in a complex and dynamic interaction with the environment. The portals are separated from the wall and “attack” on the space of the square in front of them, their funnel-shaped niches seem to involve him in themselves. In the second tier, pinnacles with light columns are permeated with air, the walls recede, the window openings make them incorporeal, the towers are divided into many partitions and openings. The agitated overture of the facade is replaced by the strict grandeur of measured but intense rhythms of the interior. The inner space of the temple in Reims is distinguished by a clear structure, nobility and harmony of proportions of both the whole and individual parts, the naturalness and plasticity of their transitions, the high perfection of stone processing, the thoroughness of finishing every detail, the freedom and thoughtfulness of the architectural design. The sculptural decoration of the cathedral in Reims is considered to be the pinnacle of French Gothic plastics. The influence of antiquity in Reims manifested itself most strongly in the works of 1211–25. Sculpture of St. Peter from the so-called Portal of the Last Judgment on the north transept is a vivid example of the ancient influence in the plastic of Reims.
- - the cathedral in Amiens (1218-1260);
- Almost simultaneously with Reims, construction began on the cathedral in Amiens. The first stone was laid in 1220, immediately after the fire that destroyed the Romanesque building. The construction of the building began with the longitudinal part, the choir was built later. The western facade was completed mainly in the XIII century. Its upper part was completed in the XIV and updated in the XV century. The arrangement of parts of the facade is picturesque - it was not by chance that during the construction process towers of various heights and designs appeared. The Labyrinth, dismantled at the beginning of the 19th century, carried the names of the builders. From 1220, Robert de Luzarsh worked here, then Tom de Cormont and his son. The works were mainly completed in 1288. Just as in Reims, the Cathedral in Chartres served as an example for the architects, but the sample was noticeably modified. In Amiens two axial directions interact: the grass of the aphids echo the transept; The middle of the seven chapels of the choir, significantly advanced, emphasizes the longitudinal axis of the plan. Gentle pointed arches majestically complete the interior, giving rise to a feeling of free movement of space, which was also achieved by an absolute increase in the size of the building. Amiens Cathedral is the largest among the Gothic temples of France and one of the largest in Europe. The width of its avenues is 33 m, the transept is stretched to 59 m, the arches of the central nave are raised to a height of 42.3 m.
- - Cathedral in Bourges (1194)
- - Cathedral of Notre Dame (1163 - XIV century.)
- The building of the cathedral was erected on the site of the temple of Jupiter, which stood here under the Romans. Since ancient times this place was considered sacred, and later the churches of the new Christian God were built on it. In the XII century, Maurice de Sully planned a huge Notre-Dame de Paris, and in 1163 King Louis VII and Father Alexander III, who had specially arrived in Paris for the ceremony, laid the first foundation stone in the eastern part of the city. Construction proceeded gradually from east to west and lasted more than a hundred years. The cathedral was supposed to contain all residents of the city - 10,000 people. But while it was being built, more than 150 years passed, and the population of Paris grew many times over. The cathedral in the medieval city was the center of social life. He is covered with some shops and stalls in which they sold all sorts of things. At the entrance, visiting merchants laid out their goods and made deals. Here urban women of fashion came to brag about their clothes, and gossip girls - to listen to the news. Here dances and processions of mummers took place, sometimes they even played ball. During the danger in the cathedral, the inhabitants of the surrounding villages took shelter not only with their belongings, but even with their cattle. Professors lectured to students, interrupted during worship services. The inner space of the cathedral is the realm of vertical lines, slender stone pillars of the frame, connected by pointed arches. Here everything is subject to a rapid rise up to the sky. In the frame of stained glass windows with complex lines of lead binding colored glass is inserted. Diffused light penetrating through stained glass windows pours onto statues of men, women, children, kings, bishops, warriors standing upright, kneeling, horseback, marble, silver and even wax ... There are no walls at all, they are replaced by a frame made of United arches pillars. This frame is filled with huge pointed windows, not even windows - but multicolored paintings with dozens of figures. Sunlight makes the glass play with all the colors of the rainbow and makes the stained glass look like huge gems. The shimmering mystical light is intoxicating to a person, bringing him to a pious religious state. Notre Dame Cathedral is divided into five naves, the middle one is higher and wider than the rest. Its height is 35 meters. Under such arches could fit a house of 12 floors. In the middle, the main nave is crossed by another nave of the same height, two naves (longitudinal and transverse) form a cross. This was done specifically to make the cathedral look like a cross on which Jesus Christ was crucified. Buildings like the Coliseum or the Thermal Baths of Caracalla needed to be built quickly and the entire building erected at once, in its entirety. A long suspension of work or the slow construction of separate parts of such structures threatened that different rooms would have different strengths. For the construction needed huge funds, required an army of slaves. The Parisians had none of this. The Gothic cathedral was built, as a rule, for decades, or even centuries. The citizens slowly raised money and the building of the cathedral grew slowly.
By the middle of the XIX century, Notre Dame de Paris was significantly different from what it was seen by the Parisians in the XIII century. All eleven steps of the stairs disappeared, absorbed by the soil of Cite. There was no bottom row of statues in the niches of the three portals. Not even the top row of statues that once adorned the gallery. Inside the cathedral also suffered greatly. Gorgeous statues and stained glass windows disappeared, replaced by a Gothic altar. Crowds of cupids, bronze clouds, marble and metal medallions appeared instead. The cathedral was ruined. Moreover, he was threatened with complete destruction.
In 1841, in order to save Notre-Dame de Paris, a special government decision was made, and in 1845 the capital restoration of the cathedral began under the guidance of the famous architect E.E. Viollet-le-Duc. In its original form to this day, only partially stained glass windows of the western, southern and northern facades, sculptures on the facades and in the choir have been preserved.
- In Germany:
- - Cologne Cathedral (1248 - XIX century);
- The grandiose five-oil Cologne Cathedral (1248— 1880) was built in the style of Amiens. Light towers with gabled roofs on the western facade, an unusually high middle nave and elegant architectural decoration of all details of the structure characterize its appearance. Replacing the rose with a pointed window increases the swiftness of the movement. Cologne Cathedral is distinguished by dry forms. The western part of it was completed only in the 19th century. In the era of Gothic art, the importance of secular architecture, private, palace and public, increased. Developed political life and a growing self-consciousness of citizens were reflected in the construction of monumental town halls.
- - Cathedral in Worms (XII century);
- - Cathedral of Notre Dame in Ulm;
- - Naumburg Cathedral
- In England:
- - The Cathedral of Canterbury (XII-XIV centuries), the main temple of the English kingdom;
- - The Cathedral of Westminster Abbey (XII-XIV centuries) in London;
- - The Cathedral of Salisbury (1220–1266);
- - Cathedral of Exeter (1050);
- - Cathedral in Lincoln (end of XI century);
- - Cathedral in Gloucester (XI-XIV centuries.)
- In the Czech Republic:
- - Gothic architecture of Prague;
- - St. Vitus Cathedral (1344-1929)
- In Italy:
- - Palazzo Doge;
- This is a vivid example of Venetian Gothic, which took not the constructive principles, but the decorativeness of this style. Its facade is unusual in composition: the lower tier of the palace is surrounded by a white marble colonnade with interlocking pointed arches. The huge monumental building accurately presses squat columns into the ground. A solid open loggia with keeled arches, with thin, often located columns, forms the second floor, which is distinguished by its elegance and lightness. Above the marble carvings of lace, a pink third-floor wall shimmering and vibrating in the sun rises with rarely placed windows. The whole plane of this part of the wall is covered with geometric white ornament. Pink-pearl from afar, the palace near admires with the sound of a decorative solution that facilitates the shape. The architecture of Venice combines the strict splendor of Byzantium with oriental and gothic decorativeness, with secular cheerfulness.
- - Milan Cathedral (1386 - XIX century);
- - Palazzo d "Oro (Golden Palace) in Venice







Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)