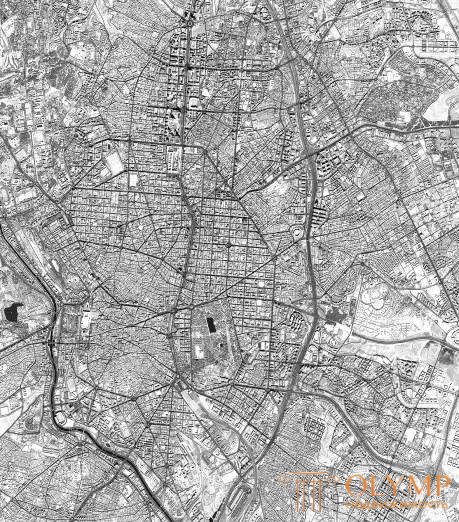
Road network
Definition: the street-road network of the city is formed as a complete system, in conjunction with the network of highways in the area of settlement. The structure of the network is determined by the overall planning structure and size of the city, the interposition of its parts (Fig. 183).

The city decided to allocate various categories of roads and streets (Fig. 187).
Classification of roads and streets of the city (JV urban planning)
Category of roads and streets | The main purpose of roads and streets |
Main roads: speeding 3.75 / 4-8 / 120 * | High-speed transport links between remote industrial and planning areas in major and large cities: access to external highways. Intersections with main streets and roads in different levels (Fig. 185). |
adjustable motion 3,5 / 2-6 / 80 * | Transport links between the city’s districts, exits to external highways, intersections with streets and roads, like |
Category of roads and streets | The main purpose of roads and streets |
usually at the same level. | |
Main streets: citywide: continuous movement 3.75 / 4-8 / 100 * | Transport links between residential, industrial areas and public centers in major, large and large cities, as well as with other main streets, urban and external highways. Ensuring the movement of transport in major areas in different levels. |
adjustable movement 3.5 / 4-8 / 80 * | Transportation links between residential, industrial areas and the city center, centers of planning areas; exits to main streets. Intersections with the main streets and roads, usually in the same level. |
district value: transport and pedestrian 3.5 / 2-4 / 70 * | Transport and pedestrian communications between residential areas, as well as between residential and industrial areas, public centers, exits to other main streets. |
pedestrian 4/2/50 * | Pedestrian and transport links (mainly public passenger transport) within the planning area. |
Streets and local roads: streets in residential buildings 3 / 2-3 / 40 * | Transport (without passing cargo and public transport) and pedestrian communication in the residential areas (housing estates), exits to the main streets. |
streets and roads in scientific production areas 3.5 / 2-4 / 50 * | Transport communication mainly of passenger and freight transport within the zones (districts), access to the main urban roads. Intersections with streets and roads are arranged in the same level. |
pedestrian streets and roads | Pedestrian communication with places of employment, institutions and service enterprises, including within public centers, recreation areas. |
park roads | Transport communication within the territory of parks and forest parks mainly for the movement of passenger cars. |
Passages the main 2.75 / 2/20 * minor 3.5 / 1/20 * | The access of vehicles to residential and public buildings, institutions, enterprises and other objects of urban development within districts, neighborhoods, neighborhoods. |
bike lanes | Travel by bike, communication within planning areas. |
* width of a lane (m) / number of lanes (units) / speed (km / h) (fig. 186).
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)