
Hydraulic concrete is intended for structures in water or periodically in contact with water. The concrete of the outer zone repeatedly freezes and thaws, being always in a wet state, therefore the main requirement for it is frost resistance. The concrete of the inner zone of massive structures is protected by the outer concrete from the direct influence of the environment. The main requirement for this concrete is the minimum amount of heat release during hardening, since uneven heating of the massif can cause the formation of temperature cracks. Therefore, for such concretes, slag and pozzolanic Portland cements are used, which have low heat release and resistance to leaching.
Road concrete is intended for foundations and coatings of highways and airfields. The coating works in bending like a slab on an elastic base, therefore the main strength characteristic of concrete is the design grade in bending tensile.
Large aggregate (crushed stone, gravel, crushed stone from slag) must be checked for wear resistance in a shelf drum: it is standardized in accordance with the purpose of the concrete. Pavement concrete is exposed to the combined action of water and frost, together with the effects of salts, which are used to prevent icing and facilitate ice removal from roads. Therefore, concrete must have frost resistance not lower than F100 ... F200 (depending on
climate). To do this, use Portland cement M500 with a tricalcium aluminate content of not more than 10%, hydrophobic and plasticized Portland cements, and the W / C concrete is limited to 0.5 ... 0.55.
Colored concretes Colored concretes are used for decorative purposes in the construction of pedestrian crossings, dividing strips
on road surfaces, park paths, as well as in the manufacture of urban amenities, obtained by introducing alkali- and light-resistant pigments into the concrete mixture in an amount of 8 ... 10% of the mass cement (ocher, mummy, red lead, etc.)
or the use of colored cements. In some cases, aggregates with the required color are used, for example, tuffs, red quartzites, marble and other colored rocks.

Heat-resistant concreteintended for industrial units (boiler lining, furnace lining, etc.) and building structures subject to heating (for example, for chimneys). Under the action of high temperature on the cement stone, crystalline hydrates are dehydrated and calcium hydroxide decomposes with the formation of CaO. When exposed to moisture, calcium oxide hydrates with an increase in volume and causes cracking of concrete. Therefore, finely ground materials (pumice, ash, granulated blast furnace slag, chamotte) containing active silica SiO2, which reacts with CaO at a temperature of 700 ... 900 ° C and binds calcium oxide, are introduced into refractory concrete on Portland cement. Heat-resistant concrete is made on Portland cement, Portland slag cement, liquid glass (under conditions of acid corrosion), alumina and high-alumina cement
(with an alumina content of 65 ... 80%), phosphate and aluminophosphate binders. The aggregate for heat-resistant concrete must not only be resistant at high temperatures, but also have a uniform thermal expansion. Prefabricated elements and monolithic structures made of heat-resistant concrete are widely used in various industries: energy, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, in chemical and oil refining, in the
production of building materials; they are used instead of semi-acidic and chamotte products intended for temperatures of 800 ... 1400 ° C, and also instead of highly refractory products at temperatures above 1400 ° C.

The binder for acid-resistant concrete is water glass with a polymer additive. To increase the density of concrete, fillers are introduced: acid-resistant mineral powders obtained by grinding pure quartz sand, andesite, basalt, diabase, etc. Sodium fluorosilicon (Na2SiF6) is used as a hardener, quartz sand, crushed stone from granite, quartzite, andesite and other resistant rocks are used as filler. Acid-resistant concrete withstands the action of concentrated acids well; water destroys it in 5 ... 10 years, alkaline solutions destroy it faster. Acid-resistant concrete is used as protective layers (linings) for reinforced concrete and metal.

The materials used for radioactive shielding concrete must provide the highest possible concrete density and a certain hydrogen content - usually in the form of water associated with a binder - Portland cement or Portland slag cement. Heavy aggregates are used as aggregates: iron ores (magnetite, hematite, brown iron ore), barite ores, metal coarse aggregate, cast iron and lead shot. The density of concrete on a metal aggregate reaches 6000 kg / m3. The mechanical properties of especially heavy magnetite, hematite, limonite and barite concretes are similar. Particularly heavy concrete has strength grades M100, M200 and M300, while axial tensile grades are 10, 20.
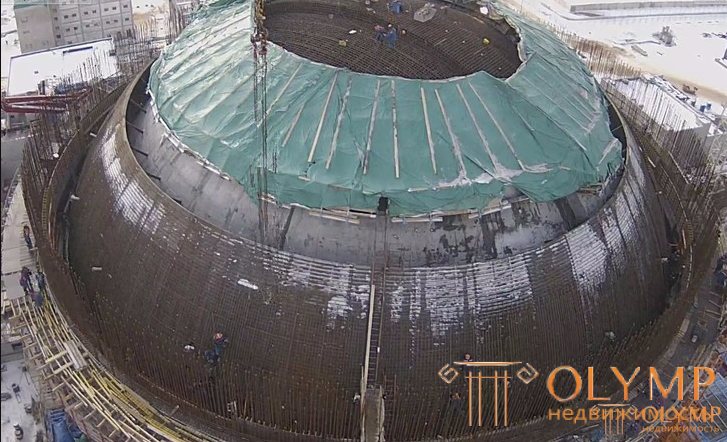

Materials used in the construction of a nuclear power plant,
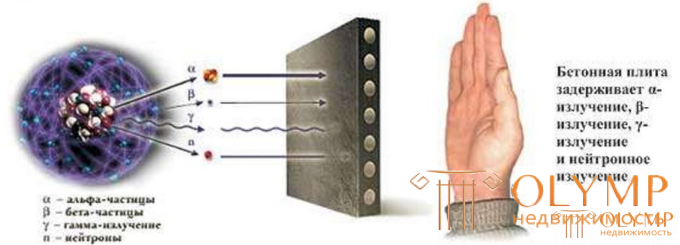
Fine-grained concreten does not contain coarse aggregate, it is used in the manufacture of thin-walled, including reinforced-cement structures. The properties of fine-grained concrete are characterized by the same factors as ordinary concrete. However, due to the absence of a coarse aggregate, the water demand of the concrete mixture increases and in order to obtain an equal strength concrete and an equally mobile concrete mixture, the consumption of cement increases by 20 ... 40% in comparison with ordinary concrete. Reducing cement consumption is possible due to the use of high-strength sand, superplasticizer, reinforced compaction. Fine-grained concrete has increased bending strength, good water resistance and frost resistance. Improving the efficiency of fine-grained concrete is possible due to the use of waste ash from thermal power plants and the main slags of the foundry.Fine-grained concrete is widely used in the manufacture of autoclaved silicate products.

Sulfur concrete is a mixture of dry aggregates - crushed stone, sand, mineral flour heated to 140 ... 150 ° C, and molten sulfur binder at a mixing temperature of 145 ... 155 ° C. The process of producing sulfur concrete is based on the property of sulfur to change its viscosity at different temperatures - at 119 ... 122 ° C, sulfur completely passes from the crystalline state into the melt. Acid-resistant cement, andesite or quartz flour, quartz sand and other acid-resistant mineral fillers are used as fillers. In many countries, sulfur concrete is used for the manufacture of piles,
foundations, containers, road surfaces and chemically resistant floors. One of the factors restraining the widespread introduction of sulfur concrete in our country is its cost, which is approximately 2 times higher than concrete on Portland cement. However, there are many chemical plants that have sulfur-containing wastes that contain 25 to 80% technical sulfur. Also, a large amount of sulfur-containing waste is generated during the extraction of sulfur.

Dispersed-reinforced concrete (fiber-reinforced concrete) is a fiber-reinforced composite material. It combines low tensile strength and plasticity of the matrix (concrete) with a high-modulus fiber with high tensile strength. The efficiency of reinforcement with short fibers depends on the orientation of the fibers to the action of tensile forces and in the case of perpendicular orientation is 40 ... 50%,
and with a volumetric arbitrary only about 20% with respect to the parallel orientation. Fibers prevent the development of shrinkage cracks, their presence increases the adhesion strength of reinforcement to concrete by about 40%. The fibers must be resistant to the alkaline environment of cement mortar or concrete. Depending on the design, fibers are used: mineral (glass - from alkali-free glass, basalt, quartz, etc.), metal (mainly from ordinary or stainless steel), synthetic (propylene, nylon, etc.).

Fiber concrete is a special type of concrete that is obtained by mixing concrete with additional fibers. Steel fibers, fiberglass, plant fibers, polypropylene, nylon, etc. used in concrete.

Self-healing concrete is defined as special types of concrete capable of self-healing and returning to its original position or back to its old position, due to the contact of water or air with unhydrated cement, further hydration occurs.
Self-healing concrete is introduced into the concrete, which helps to eliminate cracks due to the formation of calcium carbonate crystals, which block microcracks and pores in the concrete.
In B. Pasteurii, Bacillus Subtilis and B. Spharicus, etc. bacteria can be used as an independent regenerating agent.
Self-compacting concrete is a special type of concrete that flows under its own weight and fills the formwork space without mechanical vibration. It is also known as flowable concrete.
Self-compacting concrete is used where concrete is difficult to compact by various mechanical vibration devices.
The mechanism of action of the new superplasticizer is that polycarboxylate particles are adsorbed on the surface of cement grains and impart a negative charge to them. As a result, the cement grains are mutually repelled and set in motion the cement slurry (Fig. 2). Only a small part of the cement grain is covered with polymer, and the free surface of the cement floccule is sufficient for water to enter and the hydration reaction proceeds. Note that polymer structures differ in the length of the main chain, the length of the side chains, the number of side chains, and ionic charge. Therefore, the properties of these polymers can be controlled by changing the molecular structure and directly affecting the properties of concrete.
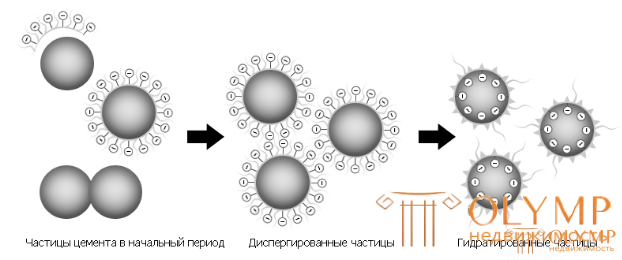
Figure: 2. The mechanism of action of the polycarboxylate additive
Translucent concrete is a special kind of concrete that lets light through it. Translucent concrete is also known as light-transmitting concrete or translucent concrete.
Light transmission through concrete Due to some coarse aggregate, concrete is replaced by light transmission material or optical fibers .
This concrete uses a large amount of fine aggregate or fine material.
Transparent concrete is similar to regular concrete because the strength of both concrete is the same. But the main disadvantage is that transparent concrete is more expensive than regular concrete.
Transparent concrete is a unique building material invented by Mr. Losonczi, one of the leading Hungarian architects. He was looking for the possibility of providing his structures with additional lighting, while the technical characteristics of the cement composition did not deteriorate in any way. As a result, the architect decided to change the internal components of the building material.
After 15 years of incessant searches and experiments, he managed to develop and introduce into the construction industry a fundamentally new decorative and finishing material - transparent concrete. He was named Litracon. The composition of the material incorporates composite fine-grained joints based on fiberglass.
The main disadvantage of transparent concretes is that production is impossible on a large scale and volume, so they are produced mainly in the form of building blocks.
Despite the obvious advantages of transparent concrete, one should not ignore their key disadvantage - the high price of the materials used. In total, the price tag is approaching several thousand dollars.

Litracon is used to form unique design elements:

Lightweight concrete is a special type of concrete that is lighter in weight and less dense than other concrete.
The density of ordinary concrete is 2400 kg / m3 . But lightweight concrete has a density of 400 to 2000 kg / m3 .
Lightweight concrete can be prepared in three main ways:
Lightweight concrete properties:
The properties of lightweight concrete are shown below.
Construction density:
The density of lightweight concrete is from 400 to 2000 kg / m3 . Low density lightweight concrete is used as thermal insulation material in construction, while high density lightweight concrete is used as a structural block in construction.
Compressive strength:
The compressive strength of lightweight concrete is relatively high in density. As the density increases, the compressive strength increases from 0.5 N / mm2 to 35 N / mm2.
Strength limit:
Its tensile strength is 15 to 20% of the compressive strength.
Thermal insulation:
The thermal insulation of lightweight concrete is three to six times greater than that of bricks and ten times that of concrete.
Fire resistance:
Lightweight concrete has very good fire resistance, and due to its low thermal conductivity, the building can be protected from fire.
Maintainability:
Lightweight concrete easily breaks, cuts, loosens. Thus, the structure is easily repaired.
Durability:
Due to the porosity and low alkalinity of lightweight concrete, it does not protect the iron from corrosion. Therefore, a special treatment is required to protect the iron from corrosion.
As shown below, there are three types of lightweight concrete.
There is no literal translation of this term into Russian. Some experts suggest the term "high functionality concretes", which are distinguished not only by high performance characteristics, but mainly by the fact that they are more consistent with the requirements of this particular stage of the material's life. So, when laying the HPC, it exhibits workability properties (the mobility of the mixture is 8 ... 16 cm OK), upon aging it gains high (55 ... 80 MPa) and ultra-high (80 ... 120 MPa) compressive strength, and in operation it has low permeability (W16 ... W20 ), high corrosion resistance,
frost resistance, durability. Such concretes are obtained using a complex additive of
superplasticizers (1.5 ... 2.0% of the mass of cement) and microsilica (from 15 to 20%) at
consumption of Portland cement in the range of 500 ... 550 kg / m3
, water-cement ratio 0.24 ... 0.28 and the
use of crushed granite. With the additional introduction of a gas-forming component
- polyhydrosiloxane of the "136-41" grade, simultaneously with high strength R = 90 ... 100 MPa
, high frost resistance F1000 is provided.
The emergence of such concretes opened a new era in construction. Their unique properties
made it possible to implement such construction projects, which until relatively recently
it was difficult even to dream of: a bridge over the Akashi Strait in Japan with a central span of 1990
m, a tunnel under the English Channel, a 125-storey skyscraper with a height of 610 m in Chicago, etc. P.
And this is not the limit. Experimentally obtained concrete with very high characteristics, called powdered concrete - Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC). The main principle
of RPC production is to ensure uniformity of the structure by eliminating coarse aggregate, compacting the mixture by optimizing the particle size distribution, using pressure and elevated temperature during hardening. Distinguish between RPC200 and RPC800. This is a new generation of concrete with compressive strength from 200 to 800 MPa and tensile strength 25 ... 150 MPa, fracture energy 3000 J / m3
and average density 2500 ... 3000 kg / m3
.
The components of such concrete are Portland cement, microsilica (25 ... 30% of the mass of cement), fine-grained sand with a maximum grain size of 0.3-0.4 mm (40 ... 50% of the mass
cement), steel microfiber and superplasticizer (2.0 ... 3.0% of the mass of cement) with a water-solid ratio in the range of 0.12 ... 0.15. Concrete is called reactive powder due to the high dispersion of the components and the increased amount of hydraulically active
materials. The RPC concept is to obtain a material with a minimum of structural defects - microcracks and pores. The strength of such concretes depends on the hardening conditions.
Strength of
800 MPa in compression and 150 MPa in tension was achieved by reinforcement with fiber reinforcement of powder concrete . High-carbon wire with a strength of up to 2000 MPa has recently been used for the manufacture of fibers.
This material has minimal porosity, is practically impermeable to liquids and gases, has high frost resistance and therefore
surpasses steel in some cases in terms of functional properties , but is much cheaper than steel. Of course, it is 5 ... 10 times more expensive than LDCs, so it should be used where weight reduction or complete impermeability plays an important role (nuclear waste storage). Disadvantages - increased deformability, lack of study of behavior in long periods of operation.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)