The wide distribution in nature of natural stone materials and the abundance of raw materials for the manufacture of artificial materials, as well as such important properties as strength and durability, fire resistance, contribute to the wide distribution of stone materials in construction.
The purpose of the stone works - the construction of foundations, bearing and enclosing structures of buildings, decorative finish.
Stone structures consist of individual stones, connected in one piece with a solution, which solidifies to form a solid mass.
The disadvantages of masonry - a large relative mass of structures, low-productivity, high material costs, the inability to mechanize the process of laying.
Depending on the type of materials used, masonry is subdivided into masonry of artificial and natural stones. In turn, solid and hollow bricks, solid and hollow coal stones (blocks) are widely used for laying of artificial stones.
Types of masonry, depending on the stones used:
· Brick - made of clay and silicate solid and hollow bricks;
· Brick with facing - from artificial and natural stones and blocks;
· Small - block - from natural (shell rock, porous tuffs) and artificial, concrete and ceramic stones, laid by hand;
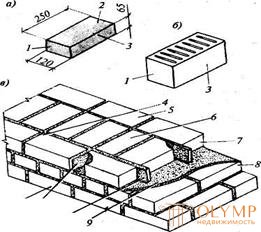
1 211 10 Fig. 11.1. Elements of brickwork: a-brick; b - stone; in - brickwork; 1 - poke; 2 - bed; 3 - spoons; 4 - outdoor mile; 5 - internal mile; 6 - zabotka; 7 - spoon row; 8 - tychkovy number; 9 - horizontal suture (mortar bed); 10 - vertical longitudinal seam; II - vertical transverse seam; 12 - outdoor mile masonry | · Tesovaya - from natural processed stones of the correct form, laid by hand or by crane; · Elements of masonry. Bricks and stones of the correct form are limited to six sides. The lower and upper ones are called beds, the two side ones are larger with spoons, the two side ones are smaller - butting (Fig. 11. 1) Beds - the surface of stones, perceiving and transmitting efforts to the underlying layers of the masonry. |
A spoon is a stone laid with a long side along the wall.
Tap is a stone laid with a short side along the wall.
Stitches - the space between the stones in the longitudinal and transverse directions, filled with mortar.
Miles - the outer rows of brick when laying. There is an outer and inner mile, the filling between the miles is zabotka.
Spoon row is a way of laying when the outer mile is made of spoons.
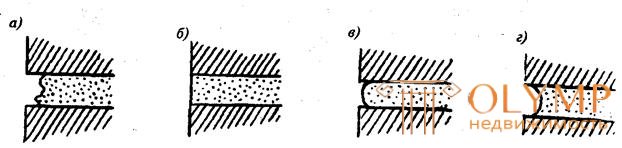
Fig. 11.2. Types of masonry joints:
and - in vostoshkovka; b - with a seam filling (undercutting); in - a convex seam; g - concave seam
Tychkovy row - the outer mile is stacked from the buttings.
There are a whole stone, a half, a three-quarter and a quarter.
A brickwork is called a void if the outer seams at a depth of 1 ... 1.5 cm are not filled with mortar, which leads to a better connection of the masonry and mortar during subsequent plastering.
Masonry is called a jointing if the outer wall is named, the natural appearance and the seams of the masonry are completely filled, giving them a different shape - convex, concave, triangular, rectangular, etc. (Fig. 11. 2).
An undercut is called masonry if the mortar fills the seams flush with the outer surface of the wall.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)