This type of insulation is usually used to insulate pipes with hot and cold surfaces. To obtain high-quality insulation, it is necessary that during the production of insulation works, the insulated surfaces have their own working temperature, since the possible temperature difference on the surface may affect the quality of the insulation.
Asbosurite is a powdered material consisting of diatomite and asbestos of soft grades. Used in the form of mastic when mixing with water. Apply as greasing and for plastering of small difficult surfaces. As an exception, asbosurite is prescribed as the main layer in mastic and backfill insulation. Refers to non-combustible materials, the limiting temperature for the use of asbosurite is 900 ° C.
Foam plastics are made on the basis of phenol-formaldehyde resin. Applied in building structures as thermal insulation and as the main layer of mastic thermal insulation of pipelines of thermal networks of underground gaskets. The limiting temperature of use of the material is from-60 to +150 ° C. The production of pipes with factory-installed phenol foam insulation for channelless laying of heat networks has been mastered.
Mastic insulation is made of mastic based on asbestos fibers, polymeric materials, liquid glass, etc. Mastic is applied on horizontal surfaces in strips without additional fastenings, on vertical surfaces - only on a metal grid; fixing the mesh to the insulated surface is similar to that used for backfill insulation.
Thermal insulation of pipelines is made of powdered, granular and fibrous materials - asbestos, asbotrepla, sovelita, etc., which are mixed with water in a ratio of 1: 3.5 with the obligatory addition of asbestos until the mastic is homogeneous, porous and plastic; Mastic is applied to the surface on a metal grid, usually galvanized. Depending on the material of the insulated surface, the mesh, which fixes the thickness of the insulation, is attached in the design position with studs welded to the insulated surface of the pipe, as well as to tightening rings, clamps and bandages, which are fixed and fixed to the insulated surface for rigidity and serve to fix the overall thickness of the applied protective insulation layers.
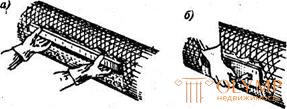
The first layer, the most liquid, called the spray, is applied with a layer of not more than 5 mm. After it dries, the main insulating layer is applied (in one or several techniques), which is compacted and smoothed to a thickness that is approximately 10 mm less than the required one. The last layer, 5 ... 20 mm thick, of the thickest consistency, is applied on the previous layer which has not yet fully grasped; this layer is used to align the entire insulation (fig. 20.1).
Fig.20.1. Application of mastic insulation to the surface: a - leveling under the rail; 6 — smoothing down with a scraper | Mastic can be applied both manually and with the use of pneumosuperchargers. After complete drying, the insulation is covered with fabric and dyed. The advantages of isolation - the simplicity of the device, solidity, the ability to work on surfaces of any configuration. Disadvantages - large labor intensity, the duration of the process of the device of all layers of insulation, the instability of the properties used |
materials. For these reasons, at present, they strive to carry out most of the insulation in factory conditions in order to isolate at the construction site only the junctions of communications and curvilinear sections of pipelines. In addition, pipelines that are under the open air in areas exposed to vibration in areas with a high probability of mechanical damage and violations of the integrity of the insulation above are covered with a protective metal casing.
Fig. 20.2. Insulation hladoprovoda rigid insulation products: 1- bituminous mastic; 2- heat insulation segments; 3-wire rings; 4 - plastic film; 5 protective coating | The technology of installation of thermal insulation of surfaces with negative temperatures provides for the performance of work with special care to prevent the moisture layer from freezing and freezing during the operation. For insulation, materials are allowed only with a closed, fine-pore structure. Insulated surfaces and metal parts |
Insulation fasteners must be protected from corrosion. When using rigid insulating materials, they are glued with bitumen adhesives, which perform the function of anti-corrosion protection (Fig. 20.2).
To resist the applied thermal insulation of pipelines to external influences, an additional coating of insulation with sheaths of synthetic films or fiberglass plastics is used. Folgoisol has found wide use (Fig. 20.3).







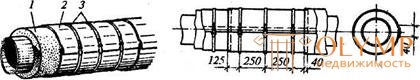
Fig. 20.3. Coating pipelines with folgoisol:
1- insulating layer; 2 - folgoizol; 3- bandages
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)