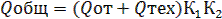
Heat supply at the construction site is carried out to perform construction and installation works (concrete heating, soil thawing, and heating of greenhouses), including:
- heating and drying of construction objects;
- heating and hot water supply of temporary sonar, residential and administrative buildings;
- ensuring production. installations (heating of water and aggregates for switchgear, steaming chambers, etc.).
The design of temporary heating is performed in the following order:
The PIC outlines only general decisions on heat supply based on calculations for aggregate indicators for 1 million rubles.
Refinement and specification in the project is made when developing an outage.
Calculation of the need for heat.
The calculation of the need for heat for technological needs and for the performance of work in winter conditions is carried out according to the current standards, taking into account the adopted technology of work. Total heat demand Qor. (kJ) is determined by summing the calculated consumption for individual consumers with the introduction of increasing coefficients K1 - for unaccounted heat consumption and K2 - for losses in the network approximately equal to 1.15.
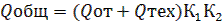
Qot - the amount of heat for the heating of buildings and hot houses;
Qtech - the same for technological needs;
The scope of work is selected by the calculated part. The provision of production, enterprises is calculated taking into account their operational characteristics and intensity of work.
Heat consumption for heating buildings Qot according to aggregates (in the PIC) or according to the formula (in the CPD)
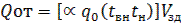
design temperatures of the harnessed air: (at tн≥10 °; 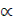 = 1.2; at tн≥-20 °;
= 1.2; at tн≥-20 °; 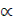 = 1.1; at
= 1.1; at 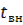 ≥30 °;
≥30 °; 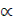 = 1; at tн≥-40 °
= 1; at tн≥-40 ° 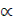 = 0.9);
= 0.9);
q - specific relative characteristic of buildings kJ / m3 · h · hail;
V - the volume of buildings on the external dimension m3.
Heat consumption for technological purposes is established every time by special calculations on the basis of specified volumes and terms of work, adopted regimes and other conditions determining the amount of heat and the intensity of its consumption.
The source of temporary heat supply is, as a rule, the existing or projected heating systems of boiler houses of an enterprise under construction or CHP. Temporary boilers are used in the absence and inability to use the existing permanent source of heat supply or in case of its insufficiency (especially for drying buildings).
Determine the total surface F (m2) heating boilers temporary boiler can be by the formula:
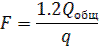
1.2 - safety factor;
Q total - the total need for heat kJ / h;
q is the specific heat removal of the boiler, kJ / m2h (according to reference books).
Temporary mobile boiler rooms:
- heaters
- heat generators
- gas installations.
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)