Temporary buildings are constructed only for the period of construction. The cost of the temporary building, along with the temporary roads, is one of the main cost items for the temporary construction economy and their reduction is one of the important tasks in the design of the construction genplan. On large objects, permanent type buildings are being erected used by construction workers, or which are part of a permanent construction base. Buildings to be subsequently demolished are also used. However, the need cannot be fully satisfied in this way, due to which temporary buildings have to be erected. The exact calculation of the need, the right choice of building types and their rational placement on the site predetermines the level of costs for temporary construction.

Temporary buildings, unlike permanent ones, have their own characteristics related to the purpose, constructive solution, methods of construction, operation and financing.
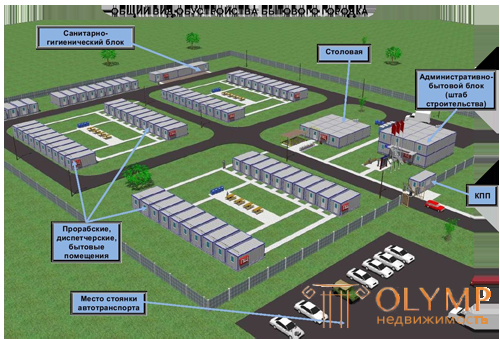
By appointment, temporary buildings are divided into industrial, warehouse, administrative, sanitary, residential, and public buildings. The production includes various workshops (repair. Mechanical, reinforcing, formwork, plumbing) mechanized installations (concrete mortar, asphralted) energy facilities (TP, boiler), transportation facilities (garages, depot, dispensaries).
To warehouse buildings - warehouses are warm, cold, storerooms, sheds. To the administrative - construction management offices, SMU, site manager, foreman, control rooms and walk-throughs.
There are dressing rooms, facilities for drying clothes, showers, canteens and buffets, health centers, red corners, etc.
To residential and public buildings - residential, dormitories, shops, canteens, bathhouses, clubs and other objects of temporary settlements of builders.
According to design solutions, methods of construction and operation, temporary buildings may be non-inventory, constructed for a single use, and inventory, i.e. designed for multiple rebasing and use at various sites. Construction of non-inventory buildings is generally not economically viable and may be allowed as an exception. Adaptation for the construction of existing buildings to be demolished may be appropriate at low cost. During construction, inventory buildings should be used for temporary purposes. All temporary buildings and structures, depending on the sources of funding, are divided into title (offices of construction, SMU, residential and cultural facilities) and non-title (offices of foreman, showers, rooms for heating workers, cloakrooms, walk-throughs and other small objects) - for overhead account.
Calculation of the volume of construction of temporary buildings.
The design of the construction of temporary buildings is made in the composition of the POS and the outage in the following order: determine the required amount of temporary construction by year based on the purpose of the buildings; identify the possibility and feasibility of using for the needs of the construction of existing and advanced construction of the projected auxiliary buildings; determine the volume and set of temporary buildings to be constructed by construction year; in the design of the SPS in the composition of the POS determine the layout of temporary buildings and methods of providing electricity, water, sewage, heat; in the design of the CST in the composition of the PPR specify the set and location of buildings; make their binding, specify ways to connect to communications.
The volume of temporary construction is calculated separately to determine the need for administrative and sanitary buildings constructed directly on the construction site, and the residential area of the village.
The number and nomenclature of temporary buildings and structures is determined depending on the volume and nature of construction and installation work to be performed on this site.
The basis of the calculation is the list number of workers and employees engaged in construction. The list number of workers and employees includes: workers of the main production, employed in construction and installation and non-main production, engineering and technical workers and employees, MOP, workers and employees who are on leave, not working due to illness, and also performing public duties. The number of workers of the main “O” and non-mainstream “H” production is determined in the PIC or in the CPD. If such projects are not drawn up, the number of workers in the main production is determined by the planned annual output in money terms for 1 person. day taken in the development stroyfinplan. The number of workers of non-core production "H" is taken in the amount of 20% of the number of workers of the main production.
The number of engineers and employees "And" is 6-8% of the total number of workers of the main and non-core production, and the MOP (guard, cleaners, couriers (M)) - 3.5%. The number of workers and employees on leave who are not working due to illness is taken at a rate of 5% of the total number of workers and employees. It is assumed that in the first shift of workers 70% work, the other categories - 80%.
The general number of workers and employees N to calculate the volume of temporary construction is determined by the formula N = 1/05 (O + H + And + M).
Under construction conditions, the number of workers fluctuates throughout the year. Therefore, to calculate the need for temporary buildings, determine the number of workers for individual periods of construction (quarter, month), and the area of temporary buildings is calculated by the largest number of workers in each period. The resulting difference in the size of areas in certain periods of construction can be adjusted by increasing or decreasing the number of mobile buildings.
The required area F vm2 temporary buildings is determined by the formula F = N1n: where N1 is the number of workers per shift or per day; n is the area norm per worker in m2.
To calculate the area of the main temporary buildings, you can use the following standards:
Offices - 5-6 m2 for 1 employee
Office foreman - 25 m2
Passage - 5-6 m2
Wardrobe with washbasin - 0.5 m2 for 1 worker (70% of payroll)
Meals for eating - 1 m2 per 1 worker (calculated on 30% working simultaneously)
Premises for heating - 0.5 m2 for 1 working (50% of the payroll)
Summer showers - 2.5 / 4 m2 per 1 horn (capacity of one horn 3 people / hour, based on 30-40% of payroll)
Toilet M - 0.007 m2
W - 0.14 m2
Health center up to 70 m2 for 200/1200 people
up to 100 m2 1201-2000 people
up to 150 m2 of 2001-3000 people.
The calculation of the areas of temporary buildings for cultural, everyday, medical and sanitary purposes in the workers' settlements is carried out in accordance with SNiPII “public buildings and facilities” and SNiPII “auxiliary buildings and premises of industrial enterprises”.
In the general case, the composition of the population of the village is composed of the production contingent of the main and non-main production, service personnel, covering workers in the cultural, social, medical and sanitary, educational and commercial institutions, members of their families. The size of the service group of the population largely depends on the location of the village and the possibility of using existing institutions of this type in the region. The quantitative composition of this group is approximately equal to 20 - 30% of the total number of the production group. The number of family members is defined as the product of the total composition of the total working population by the family coefficient, which fluctuates within 1.8 during the preparatory period to 2.2 (during the main construction period). The size of the living area of the current sanitary standards.
Types of temporary buildings and devices.
Buildings according to the degree of mobility and constructive solution can be classified into the following types:
There are several hundred projects of inventory buildings for various purposes. In order to prepare mass industrial production of such buildings, so-called unified typical sections (TCB) of temporary buildings have been developed. All-Union TCBs are designed on the basis of the possibility of placing objects of any purpose in them.
Consider the general characteristics and examples of design solutions for each of the main types of inventory buildings.
Building collapsible type constructively can be solved as a frame-panel or panel. The advantage of collapsible buildings is the relatively low initial cost and the possibility of installing a building of any size and configuration. The disadvantages include significant in comparison with container and mobile buildings, labor and time costs for assembly and disassembly, as well as the additional consumption of labor and materials for the construction of foundations.
Frame-panel buildings are used mainly for the placement of industrial and less household objects.
In terms of space planning, they are similar to single-storey industrial buildings and have one or several spans from 4.5 to 18 meters, a height of 3 to 8 meters, and are equipped with cranes up to 10 tons. Bearing frame - in metal, at least in wood, reinforced concrete. Fencing structures - mounted or self-supporting, wall panels and roofing slabs.
Buildings can be warm and cold. Panel collapsible buildings have smaller spans compared to frame. In such buildings mainly residential, administrative premises or small warehouses are located. Buildings are usually made of wooden shields. The main element of the CFB collapsible type is a link consisting of wall, two roofing and two floor panels, connected with kerchiefs and bolts. In assembled form, such a link is a 1.5 m wide frame with a tightening and upper bolt, with hinges at the base and upper knot.
Buildings from fabric-cloth materials. Conventionally, it can be attributed to collapsible buildings. There are buildings tent and film construction. Awning constructions have a tent cylindrical shape. Lightweight metal profile frames. Awnings
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (0)