Educational architectural design as an activity has much in common with practical architectural design, however, in the educational process, design methods acquire their own specifics. During training, the relationship between the project and the project activity itself is different than in practice: in real design, “the process is extinguished in the product,” whereas in a higher architectural school, the product has no self-sufficient significance, and the process is also important.
The system of educational architectural and design activity is represented by the unity of its two main sides - the process and the product. The process of design modeling is a dynamic, temporal characteristic of this unity, the product - the project is its spatial side.
The method of architectural design transforms learning activities into a targeted and programmable process with its goals, means and results.
The purpose of the architectural and design activities - mastering the student's profession of an architect and his education as a person. Knowledge of scientific and technical disciplines and professional and creative skills acquired in the course of training, methods and operational engineering techniques are used as a means of architectural and design activity.
The socially significant result of the activity is the training of a professional architect. The product of the activity - a series of projects - is aimed at transforming the consciousness of the student, at forming a creative worldview, developing compositional abilities, and establishing his spiritual appearance (Figure 1). Among the tasks of architectural and design activities include the development of artistic and aesthetic taste and graphic skills, the development of student intelligence, spatial thinking and figurative structural imagination.

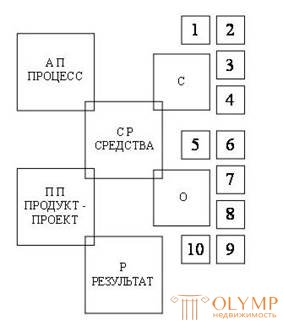
Scheme 1. The structure of the architectural and design activities
P - the result - the preparation of the professional and the individual; C - subjective means; 1 - individual project experience, 2 - knowledge update, 3 - creative skills, 4 - intuition and heuristic rules; O - objective means: 5 - initial information, program requirements, public experience, theoretical, scientific and technical knowledge, 7 - logical thinking, skills of scientific research, 8 - means of displaying information, sign means and schemes, 9 - professional methods, 10 - operating technique
Что бы оставить комментарий войдите
Комментарии (1)